Abstract
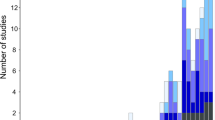
Baited Remote Underwater Video Stations (BRUVS) is a popular technique to assess mobile nektonic and demersal assemblages, particularly for fish communities. The benefits of using BRUVS have been well documented, with their non-destructive and non-extractive nature, ease to replicate, relatively-cheap personnel costs, and low risk to personnel often cited. However, there is a wide variability in the set-up, experimental design, and implementation of this method. We performed a literature review of 161 peer-reviewed studies from all continents published from 1950 to 2016 to describe how BRUVS has been used by quantitatively assessing 24 variables, including camera set-up and orientation, soak time, bait quantity, type and preparation method, habitat and depth deployed in, and number of replicates used. Such information is critical to gauge the comparability of the results obtained across BRUVS studies. Generally, there was a wide variety in the location, deployment method, bait used, and for the purpose that BRUVS was deployed. In some studies, the methods were adequately described so that they included information on the 24 variables analysed, but there were 34 % of studies which failed to report three or more variables. We present a protocol for what minimal information to include in methods sections and urge authors to include all relevant information to ensure replicability and allow adequate comparisons to be made across studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguzzi J, Jamieson A, Fujii T, Sbragaglia V, Costa C, Menesatti P, Fujiwara Y (2012) Shifting feeding behaviour of deep-sea buccinid gastropods at natural and simulated food falls. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 458:247–253
Anderson GS, Bell LS (2014) Deep coastal marine taphonomy: investigation into carcass decomposition in the Saanich Inlet, British Columbia using a baited camera. PLoS One 9:e110710
Anderson MJ, Santana-Garcon J (2015) Measures of precision for dissimilarity-based multivariate analysis of ecological communities. Ecol Lett 18:66–73
Bailey DM, Wagner H-J, Jamieson AJ, Ross MF, Priede IG (2007) A taste of the deep-sea: the roles of gustatory and tactile searching behaviour in the grenadier fish Coryphaenoides armatus. Deep Sea Res Part I 54:99–108
Barord GJ, Dooley F, Dunstan A, Ilano A, Keister KN, Neumeister H, Preuss T, Schoepfer S, Ward PD (2014) Comparative population assessments of Nautilus sp. in the Philippines, Australia, Fiji, and American Samoa using baited remote underwater video systems. PLoS One 9:e100799
Bassett DK, Montgomery JC (2011) Investigating nocturnal fish populations in situ using baited underwater video: with special reference to their olfactory capabilities. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 409:194–199
Bernard ATF, Götz A (2012) Bait increases the precision in count data from remote underwater video for most subtidal reef fish in the warm-temperate Agulhas bioregion. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 471:235–252
Birt MJ, Harvey ES, Langlois TJ (2012) Within and between day variability in temperate reef fish assemblages: learned response to baited video. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 416–417:92–100
Bond ME, Babcock EA, Pikitch EK, Abercrombie DL, Lamb NF, Chapman DD (2012) Reef sharks exhibit site-fidelity and higher relative abundance in marine reserves on the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef. PLoS One 7:e32983
Bornt K, McLean D, Langlois T, Harvey E, Bellchambers L, Evans S, Newman S (2015) Targeted demersal fish species exhibit variable responses to long-term protection from fishing at the Houtman Abrolhos Islands. Coral Reefs 34:1297–1312
Bouchet PJ, Meeuwig JJ (2015) Drifting baited stereo-videography: a novel sampling tool for surveying pelagic wildlife in offshore marine reserves. Ecosphere 6:art137
Brooks EJ, Sloman KA, Sims DW, Danylchuk AJ (2011) Validating the use of baited remote underwater video surveys for assessing the diversity, distribution and abundance of sharks in the Bahamas. Endanger Species Res 13:231–243
Campbell MD, Pollack AG, Gledhill CT, Switzer TS, DeVries DA (2015) Comparison of relative abundance indices calculated from two methods of generating video count data. Fish Res 170:125–133
Cappo M, Speare P, Wassenberg TJ, Harvey E, Rees M, Heyward A, Pitcher R (2001) Use of Baited Remote Underwater Video Stations (BRUVS) to survey demersal fish—how deep and meaningful? In: Harvey ES, Cappo M (eds) Direct sensing of the size frequency and abundance of target and non-target fauna in Australian Fisheries, 4–7 September 2000, Rottnest Island, Western Australia. Fisheries Research and Development Corporation, pp 63–71, ISBN 1 74052 057 2
Cappo M, Speare P, De’ath G (2004) Comparison of baited remote underwater video stations (BRUVS) and prawn (shrimp) trawls for assessments of fish biodiversity in inter-reefal areas of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 302:123–152
Cappo M, Harvey E, Shortis M (2007) Counting and measuring fish with baited video techniques—an overview. In: Lyle JM, Furlani DM, Buxton CD (eds) Proceedings of the 2006 Australian society of fish biology conference and workshop cutting edge technologies in fish and fisheries science. ASFB, Hobart, Hobart, August 2006, pp 101–114
Colefax AP, Haywood MDE, Tibbetts IR (2016) Effect of angling intensity on feeding behaviour and community structure of subtropical reef-associated fishes. Mar Biol 163:1–14
Coleman MA, Bates AE, Stuart-Smith RD, Malcolm HA, Harasti D, Jordan A, Knott NA, Edgar GJ, Kelaher BP (2015) Functional traits reveal early responses in marine reserves following protection from fishing. Divers Distrib 21:876–887
Collins MA, Yau C, Guilfoyle F, Bagley P, Everson I, Priede IG, Agnew D (2002) Assessment of stone crab (Lithodidae) density on the South Georgia slope using baited video cameras. ICES J Mar Sci 59:370–379
Colton M, Swearer S (2010) A comparison of two survey methods: differences between underwater visual census and baited remote underwater video. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 400:19–36
Costanza R, d’Arge R, de Groot R, Faber S, Grasso M, Hannon B, Limburg K, Naeem S, O’Neill R, Paruelo J, Raskin R, Sutton P, Van den Belt M (1997) The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 387:253–260
Craig J, Jamieson AJ, Bagley PM, Priede IG (2011) Naturally occurring bioluminescence on the deep-sea floor. J Mar Syst 88:563–567
Denny CM, Willis TJ, Babcock RC (2004) Rapid recolonisation of snapper Pagrus auratus: Sparidae within an offshore island marine reserve after implementation of no-take status. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 272:183–190
D’Onghia G, Capezzuto F, Cardone F, Carlucci R, Carluccio A, Chimienti G, Corriero G, Longo C, Maiorano P, Mastrototaro F, Panetta P, Rosso A, Sanfilippo R, Sion L, Tursi A (2015a) Macro- and megafauna recorded in the submarine Bari Canyon (southern Adriatic, Mediterranean Sea) using different tools. Mediterr Mar Sci 16:180–196
D’Onghia G, Capezzuto F, Carluccio A, Carlucci R, Giove A, Mastrototaro F, Panza M, Sion L, Tursi A, Maiorano P (2015b) Exploring composition and behaviour of fish fauna by in situ observations in the Bari Canyon (Southern Adriatic Sea, Central Mediterranean). Mar Ecol 36:541–556
Dorman SR, Harvey ES, Newman SJ (2012) Bait effects in sampling coral reef fish assemblages with stereo-BRUVs. PLoS One 7:e41538
Dunstan AJ, Ward PD, Marshall NJ (2011) Nautilus pompilius life history and demographics at the Osprey Reef Seamount, Coral Sea, Australia. PLoS One 6:e16312
Ebner BC, Morgan DL (2013) Using remote underwater video to estimate freshwater fish species richness. J Fish Biol 82:1592–1612
Ebner BC, Fulton CJ, Cousins S, Donaldson JA, Kennard MJ, Meynecke J-O, Schaffer J (2015) Filming and snorkelling as visual techniques to survey fauna in difficult to access tropical rainforest streams. Mar Freshw Res 66:120–126
Ellis D, DeMartini E (1995) Evaluation of a video camera technique for indexing abundances of juvenile pink snapper, Pristipomoides filamentosus, and other Hawaiian insular shelf fishes. Oceanogr Lit Rev 9:786
Fitzpatrick BM, Harvey ES, Heyward AJ, Twiggs EJ, Colquhoun J (2012) Habitat specialization in tropical continental shelf demersal fish assemblages. PLoS One 7:e39634
Fitzpatrick C, McLean D, Harvey ES (2013) Using artificial illumination to survey nocturnal reef fish. Fish Res 146:41–50
Gage JD, Tyler PA (1991) Deep sea biology: a natural history of organisms at the deep-sea floor. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gardner JPA, Struthers CD (2013) Comparisons among survey methodologies to test for abundance and size of a highly targeted fish species. J Fish Biol 82:242–262
Gladstone W, Lindfield S, Coleman M, Kelaher B (2012) Optimisation of baited remote underwater video sampling designs for estuarine fish assemblages. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 429:28–35
Gomelyuk VE (2009) Fish assemblages composition and structure in three shallow habitats in north Australian tropical bay, Garig Gunak Barlu National Park, Northern Territory, Australia. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 89:449–460
Gutteridge AN, Bennett MB, Huveneers C, Tibbetts IR (2011) Assessing the overlap between the diet of a coastal shark and the surrounding prey communities in a sub-tropical embayment. J Fish Biol 78:1405–1422
Hannah RW, Blume MTO (2014) The influence of bait and stereo video on the performance of a video lander as a survey tool for marine demersal reef fishes in Oregon waters. Mar Coast Fishe 6:181–189
Harasti D, Gallen C, Malcolm H, Tegart P, Hughes B (2014) Where are the little ones: distribution and abundance of the threatened serranid Epinephelus daemelii (Günther, 1876) in intertidal habitats in New South Wales, Australia. J Appl Ichthyol 30:1007–1015
Harasti D, Malcolm H, Gallen C, Coleman MA, Jordan A, Knott NA (2015) Appropriate set times to represent patterns of rocky reef fishes using baited video. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 463:173–180
Hardinge J, Harvey ES, Saunders BJ, Newman SJ (2013) A little bait goes a long way: the influence of bait quantity on a temperate fish assemblage sampled using stereo-BRUVs. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 449:250–260
Harvey E, Fletcher D, Shortis M (2002a) Estimation of reef fish length by divers and by stereo-video: a first comparison of the accuracy and precision in the field on living fish under operational conditions. Fish Res 57:255–265
Harvey E, Shortis M, Stadler M, Cappo M (2002b) A comparison of the accuracy and precision of measurements from single and stereo-video systems. Mar Technol Soc J 36:38–49
Harvey ES, Cappo M, Butler JJ, Hall N, Kendrick GA (2007) Bait attraction affects the performance of remote underwater video stations in assessment of demersal fish community structure. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 350:245–254
Harvey ES, Butler JJ, McLean DL, Shand J (2012a) Contrasting habitat use of diurnal and nocturnal fish assemblages in temperate Western Australia. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 426–427:78–86
Harvey ES, Newman SJ, McLean DL, Cappo M, Meeuwig JJ, Skepper CL (2012b) Comparison of the relative efficiencies of stereo-BRUVs and traps for sampling tropical continental shelf demersal fishes. Fish Res 125–126:108–120
Heagney E, Lynch T, Babcock R, Suthers I (2007) Pelagic fish assemblages assessed using mid-water baited video: standardising fish counts using bait plume size. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 350:255–266
Holmlund CM, Hammer M (1999) Ecosystem services generated by fish populations. Ecol Econ 29:253–268
Howarth LM, Pickup SE, Evans LE, Cross TJ, Hawkins JP, Roberts CM, Stewart BD (2015) Sessile and mobile components of a benthic ecosystem display mixed trends within a temperate marine reserve. Mar Environ Res 107:8–23
Jamieson A, Bailey D, Wagner H-J, Bagley P, Priede I (2006) Behavioural responses to structures on the seafloor by the deep-sea fish Coryphaenoides armatus: implications for the use of baited landers. Deep Sea Res Part I 53:1157–1166
Jamieson A, Fujii T, Solan M, Matsumoto A, Bagley P, Priede I (2009) First findings of decapod crustacea in the hadal zone. Deep Sea Res Part I 56:641–647
Langlois T, Chabanet P, Pelletier D, Harvey E (2006) Baited underwater video for assessing reef fish populations in marine reserves. Fish Newslett S Pac Comm 118:53
Langlois TJ, Harvey ES, Fitzpatrick B, Meeuwig JJ, Shedrawi G, Watson DL (2010) Cost-efficient sampling of fish assemblages: comparison of baited video stations and diver video transects. Aquat Biol 9:155
Langlois TJ, Fitzpatrick BR, Fairclough DV, Wakefield CB, Hesp SA, McLean DL, Harvey ES, Meeuwig JJ (2012a) Similarities between line fishing and baited stereo-video estimations of length-frequency: novel application of kernel density estimates. PLoS One 7:e45973
Langlois TJ, Radford BT, Van Niel KP, Meeuwig JJ, Pearce AF, Rousseaux CSG, Kendrick GA, Harvey ES (2012b) Consistent abundance distributions of marine fishes in an old, climatically buffered, infertile seascape. Global Ecol Biogeogr 21:886–897
Langlois TJ, Newman SJ, Cappo M, Harvey ES, Rome BM, Skepper CL, Wakefield CB (2015) Length selectivity of commercial fish traps assessed from in situ comparisons with stereo-video: is there evidence of sampling bias? Fish Res 161:145–155
Letessier TB, Meeuwig JJ, Gollock M, Groves L, Bouchet PJ, Chapuis L, Vianna GMS, Kemp K, Koldewey HJ (2013) Assessing pelagic fish populations: the application of demersal video techniques to the mid-water environment. Methods Oceanogr 8:41–55
Letessier TB, Juhel J-B, Vigliola L, Meeuwig JJ (2015) Low-cost small action cameras in stereo generates accurate underwater measurements of fish. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 466:120–126
Løkkeborg S, Siikavuopio S, Humborstad O-B, Utne-Palm A, Ferter K (2014) Towards more efficient longline fisheries: fish feeding behaviour, bait characteristics and development of alternative baits. Rev Fish Biol Fish 24:985–1003
Lowry M, Folpp H, Gregson M, Suthers I (2012) Comparison of baited remote underwater video (BRUV) and underwater visual census (UVC) for assessment of artificial reefs in estuaries. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 416–417:243–253
Malcolm HA, Gladstone W, Lindfield S, Wraith J, Lynch TP (2007) Spatial and temporal variation in reef fish assemblages of marine parks in New South Wales, Australia—baited video observations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 350:277–290
Mallet D, Pelletier D (2014) Underwater video techniques for observing coastal marine biodiversity: a review of sixty years of publications (1952–2012). Fish Res 154:44–62
Marouchos A, Sherlock M, Barker B, Williams A (2011). Development of a stereo deepwater baited remote underwater video system (DeepBRUVS), OCEANS, 2011 IEEE, Spain, pp 1–5
McIlwain JL, Harvey ES, Grove S, Shiell G, Al Oufi H, Al Jardani N (2011) Seasonal changes in a deep-water fish assemblage in response to monsoon-generated upwelling events. Fish Oceanogr 20:497–516
McLean DL, Green M, Harvey ES, Williams A, Daley R, Graham KJ (2015) Comparison of baited longlines and baited underwater cameras for assessing the composition of continental slope deepwater fish assemblages off southeast Australia. Deep Sea Res Part I 98:10–20
Merritt D, Donovan MK, Kelley C, Waterhouse L, Parke M, Wong K, Drazen JC (2011) BotCam: a baited camera system for nonextractive monitoring of bottomfish species. Fish Bull 109:56–67
Misa WFXE, Richards BL, DiNardo GT, Kelley CD, Moriwake VN, Drazen JC (2016) Evaluating the effect of soak time on bottomfish abundance and length data from stereo-video surveys. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 479:20–34
Moore C, Harvey E, Van Niel K (2010) The application of predicted habitat models to investigate the spatial ecology of demersal fish assemblages. Mar Biol 157:2717–2729
Murphy HM, Jenkins GP (2010) Observational methods used in marine spatial monitoring of fishes and associated habitats: a review. Mar Freshwr Res 61:236–252
Rees M, Knott N, Fenech G, Davis A (2015) Rules of attraction: enticing pelagic fish to mid-water remote underwater video systems (RUVS). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 529:213–218
Richardson JR, Shears NT, Taylor RB (2015) Using relative eye size to estimate the length of fish from a single camera image. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 538:213–219
Ricker WE (1975) Computation and interpretation of biological statistics of fish populations. J Fish Res Board Can 191:1–367
Rizzari JR, Frisch AJ, Connolly SR (2014) How robust are estimates of coral reef shark depletion? Biol Conserv 176:39–47
Robbins WD, Peddemors VM, Kennelly SJ (2011) Assessment of permanent magnets and electropositive metals to reduce the line-based capture of Galapagos sharks, Carcharhinus galapagensis. Fish Res 109:100–106
Ryan L, Meeuwig J, Hemmi J, Collin S, Hart N (2015) It is not just size that matters: shark cruising speeds are species-specific. Mar Biol 162:1307–1318
Santana-Garcon J, Braccini M, Langlois TJ, Newman SJ, McAuley RB, Harvey ES (2014a) Calibration of pelagic stereo-BRUVs and scientific longline surveys for sampling sharks. Methods Ecol Evol 5:824–833
Santana-Garcon J, Leis J, Newman S, Harvey E (2014b) Presettlement schooling behaviour of a priacanthid, the purplespotted bigeye Priacanthus tayenus (Priacanthidae: Teleostei). Environ Biol Fishes 97:277–283
Santana-Garcon J, Newman SJ, Harvey ES (2014c) Development and validation of a mid-water baited stereo-video technique for investigating pelagic fish assemblages. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 452:82–90
Santana-Garcon J, Newman SJ, Langlois TJ, Harvey ES (2014d) Effects of a spatial closure on highly mobile fish species: an assessment using pelagic stereo-BRUVs. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 460:153–161
Schobernd ZH, Bacheler NM, Conn PB (2014) Examining the utility of alternative video monitoring metrics for indexing reef fish abundance. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 71:464–471
Scott ME, Smith JA, Lowry MB, Taylor MD, Suthers IM (2015) The influence of an offshore artificial reef on the abundance of fish in the surrounding pelagic environment. Mar Freshw Res 66:429–437
Seiler J (2013). Testing and evaluating non-extractive sampling platforms to assess deep-water rocky reef ecosystems on the continental shelf. PhD Thesis, University of Tasmania, Hobart
Sih A, Bell A, Johnson JC (2004) Behavioral syndromes: an ecological and evolutionary overview. Trends Ecol Evol 19:372–378
Smale DA, Barnes DKA, Fraser KPP, Mann PJ, Brown MP (2007) Scavenging in Antarctica: intense variation between sites and seasons in shallow benthic necrophagy. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 349:405–417
Stobart B, García-Charton JA, Espejo C, Rochel E, Goñi R, Reñones O, Herrero A, Crec’hriou R, Polti S, Marcos C, Planes S, Pérez-Ruzafa A (2007) A baited underwater video technique to assess shallow-water Mediterranean fish assemblages: methodological evaluation. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 345:158–174
Stobart B, Díaz D, Álvarez F, Alonso C, Mallol S, Goñi R (2015) Performance of baited underwater video: does it underestimate abundance at high population densities? PLoS One 10:e0127559
Svane I, Barnett J (2008) The occurrence of benthic scavengers and their consumption at tuna farms off Port Lincoln, South Australia. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 363:110–117
Svane I, Roberts S, Saunders T (2008) Fate and consumption of discarded by-catch in the Spencer Gulf prawn fishery, South Australia. Fish Res 90:158–169
Taylor MD, Baker J, Suthers IM (2013) Tidal currents, sampling effort and baited remote underwater video (BRUV) surveys: are we drawing the right conclusions? Fish Res 140:96–104
Trobbiani GA, Venerus LA (2015) A novel method to obtain accurate length estimates of carnivorous reef fishes from a single video camera. Neotrop Ichthyol 13:93–102
Udyawer V, Cappo M, Simpfendorfer CA, Heupel MR, Lukoschek V (2014) Distribution of sea snakes in the great barrier reef marine park: observations from 10 yrs of baited remote underwater video station (BRUVS) sampling. Coral Reefs 33:777–791
Unsworth RKF, Peters JR, McCloskey RM, Hinder SL (2014) Optimising stereo baited underwater video for sampling fish and invertebrates in temperate coastal habitats. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci Part B 150:281–287
Wakefield CB, Lewis PD, Coutts TB, Fairclough DV, Langlois TJ (2013) Fish assemblages associated with natural and anthropogenically-modified habitats in a marine embayment: comparison of baited videos and opera-house traps. PLoS One 8:e59959
Walsh AT, Barrett N, Hill N (2016) Efficacy of baited remote underwater video systems and bait type in the cool-temperature zone for monitoring ‘no-take’ marine reserves. Mar Freshw Res. doi:10.1071/MF15165
Watson D, Harvey E, Anderson M, Kendrick G (2005) A comparison of temperate reef fish assemblages recorded by three underwater stereo-video techniques. Mar Biol 148:415–425
Watson DL, Anderson MJ, Kendrick GA, Nardi K, Harvey ES (2009) Effects of protection from fishing on the lengths of targeted and non-targeted fish species at the Houtman Abrolhos Islands, Western Australia. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 384:241–249
Watson D, Harvey E, Fitzpatrick B, Langlois T, Shedrawi G (2010) Assessing reef fish assemblage structure: how do different stereo-video techniques compare? Mar Biol 157:1237–1250
White J, Simpfendorfer CA, Tobin AJ, Heupel MR (2013) Application of baited remote underwater video surveys to quantify spatial distribution of elasmobranchs at an ecosystem scale. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 448:281–288
Whitmarsh S (2012) Methods of monitoring shallow seagrass communities of Kangaroo Island, South Australia, Honours Thesis, School of Biological Sciences. Flinders University, Adelaide
Whitmarsh S, Fairweather P, Brock D, Miller D (2014) Nektonic assemblages determined from baited underwater video in protected versus unprotected shallow seagrass meadows on Kangaroo Island, South Australia. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 503:205–218
Willis TJ, Babcock RC (2000) A baited underwater video system for the determination of relative density of carnivorous reef fish. Mar Freshw Res 51:755–763
Willis TJ, Millar RB, Babcock RC (2000) Detection of spatial variability in relative density of fishes: comparison of visual census, angling, and baited underwater video. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 198:249–260
Worm B, Barbier EB, Beaumont N, Duffy JE, Folke C, Halpern BS, Jackson JB, Lotze HK, Micheli F, Palumbi SR (2006) Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services. Science 314:787–790
Wraith J, Lynch T, Minchinton T, Broad A, Davis A (2013) Bait type affects fish assemblages and feeding guilds observed at baited remote underwater video stations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 477:189–199
Yau C, Collins MA, Bagley PM, Everson I, Priede IG (2002) Scavenging by megabenthos and demersal fish on the South Georgia slope. Antarct Sci 14:16–24
Acknowledgments
We thank two anonymous reviewers for their comments which improved our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whitmarsh, S.K., Fairweather, P.G. & Huveneers, C. What is Big BRUVver up to? Methods and uses of baited underwater video. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries 27, 53–73 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-016-9450-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-016-9450-1