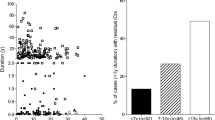
Abstract
In the last 10 years, several studies have shown that the pancreas of patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), and even of subjects at risk for T1D, was smaller than the pancreas from healthy subjects. This arose the question of the relationships between the endocrine and exocrine parts of the pancreas in T1D pathogenesis. Our review underlines that histological anomalies of the exocrine pancreas are common in patients with T1D: intralobular and interacinar fibrosis, acinar atrophy, fatty infiltration, leucocytic infiltration, and pancreatic arteriosclerosis are all frequent observations. Moreover, 25% to 75% of adult patients with T1D present with pancreatic exocrine dysfunction. Our review summarizes the putative causal factors for these structural and functional anomalies, including: 1/ alterations of insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide secretion, 2/ global pancreatic inflammation 3/ autoimmunity targeting the exocrine pancreas, 4/ vascular and neural abnormalities, and 5/ the putative involvement of pancreatic stellate cells. These observations have also given rise to new theories on T1D: the primary event of T1D pathogenesis could be non-specific, e.g bacterial or viral or chemical, resulting in global pancreatic inflammation, which in turn could cause beta-cell predominant destruction by the immune system. Finally, this review emphasizes that it is advisable to evaluate pancreatic exocrine function in patients with T1D presenting with gastro-intestinal complaints, as a clinical trial has shown that pancreatic enzymes replacement therapy can reduce the frequency of hypoglycemia and thus might improve quality of life in subjects with T1D and exocrine failure.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoppe-Seyler. Deutsches archiv fuer klinische medizin [Internet]. 1904 [cited 2018 May 31]. Available from: http://archive.org/details/deutschesarchiv68unkngoog. Accessed 31 May 2018.
Cecil RL. A study of the pathological anatomy of the pancreas in ninety cases of diabetes mellitus. J Exp Med. 1909;11:266–90.
Opie EL. Pathological changes affecting the islands of Langerhans of the pancreas. J Boston Soc Med Sci. 1900;4:251–60.
Katsarou A, Gudbjörnsdottir S, Rawshani A, Dabelea D, Bonifacio E, Anderson BJ, et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17016.
Fonseca V, Berger LA, Beckett AG, Dandona P. Size of pancreas in diabetes mellitus: a study based on ultrasound. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1985;291:1240–1.
Chiarelli F, Verrotti A, Altobelli E, Blasetti A, Morgese G. Size of the pancreas in type I diabetic children and adolescents. Diabetes Care. 1995;18:1505–6.
Hardt PD, Krauss A, Bretz L, Porsch-Ozcürümez M, Schnell-Kretschmer H, Mäser E, et al. Pancreatic exocrine function in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 2000;37:105–10.
Icks A, Haastert B, Giani G, Rathmann W. Low fecal elastase-1 in type I diabetes mellitus. Z Gastroenterol. 2001;39:823–30.
Korsgren S, Molin Y, Salmela K, Lundgren T, Melhus A, Korsgren O. On the etiology of type 1 diabetes: a new animal model signifying a decisive role for bacteria eliciting an adverse innate immunity response. Am J Pathol. 2012;181:1735–48.
Skog O, Korsgren S, Melhus A, Korsgren O. Revisiting the notion of type 1 diabetes being a T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2013;20:118–23.
Campbell-Thompson M, Wasserfall C, Montgomery EL, Atkinson MA, Kaddis JS. Pancreas organ weight in individuals with disease-associated autoantibodies at risk for type 1 diabetes. JAMA. 2012;308:2337–9.
Rodriguez-Calvo T, Ekwall O, Amirian N, Zapardiel-Gonzalo J, von Herrath MG. Increased immune cell infiltration of the exocrine pancreas: a possible contribution to the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2014;63:3880–90.
Longnecker DS. Anatomy and Histology of the Pancreas. Pancreapedia: The Exocrine Pancreas Knowledge Base [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2018 Aug 21]; Available from: /reviews/anatomy-and-histology-of-pancreas.
Maclean N, Ogilvie RF. Observations on the pancreatic islet tissue of young diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1959;8:83–91.
Löhr M, Klöppel G. Residual insulin positivity and pancreatic atrophy in relation to duration of chronic type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and microangiopathy. Diabetologia. 1987;30:757–62.
Alzaid A, Aideyan O, Nawaz S. The size of the pancreas in diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 1993;10:759–63.
Silva ME, Vezozzo DP, Ursich MJ, Rocha DM, Cerri GG, Wajchenberg BL. Ultrasonographic abnormalities of the pancreas in IDDM and NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:1296–7.
Gilbeau JP, Poncelet V, Libon E, Derue G, Heller FR. The density, contour, and thickness of the pancreas in diabetics: CT findings in 57 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992;159:527–31.
Goda K, Sasaki E, Nagata K, Fukai M, Ohsawa N, Hahafusa T. Pancreatic volume in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 2001;38:145–9.
Philippe M-F, Benabadji S, Barbot-Trystram L, Vadrot D, Boitard C, Larger E. Pancreatic volume and endocrine and exocrine functions in patients with diabetes. Pancreas. 2011;40:359–63.
Virostko J, Hilmes M, Eitel K, Moore DJ, Powers AC. Use of the electronic medical record to assess pancreas size in type 1 diabetes. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0158825.
Lu J, Hou X, Pang C, Zhang L, Hu C, Zhao J, et al. Pancreatic volume is reduced in patients with latent autoimmune diabetes in adults. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32:858–66.
Sasamori H, Fukui T, Hayashi T, Yamamoto T, Ohara M, Yamamoto S, et al. Analysis of pancreatic volume in acute-onset, slowly-progressive and fulminant type 1 diabetes in a Japanese population. J Diabetes Investig. 2018.
Bilgin M, Balci NC, Momtahen AJ, Bilgin Y, Klör H-U, Rau WS. MRI and MRCP findings of the pancreas in patients with diabetes mellitus: compared analysis with pancreatic exocrine function determined by fecal elastase 1. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;43:165–70.
Gaglia JL, Guimaraes AR, Harisinghani M, Turvey SE, Jackson R, Benoist C, et al. Noninvasive imaging of pancreatic islet inflammation in type 1A diabetes patients. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:442–5.
Williams AJK, Thrower SL, Sequeiros IM, Ward A, Bickerton AS, Triay JM, et al. Pancreatic volume is reduced in adult patients with recently diagnosed type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:E2109–13.
d’Annunzio G, Chiara A, Lorini R. Pancreatic gland size reduction and exocrine impairment in type 1 diabetic children. Diabetes Care. 1996;19:777–8.
Regnell SE, Peterson P, Trinh L, Broberg P, Leander P, Lernmark Å, et al. Pancreas volume and fat fraction in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2016;33:1374–9.
Saisho Y, Butler AE, Meier JJ, Monchamp T, Allen-Auerbach M, Rizza RA, et al. Pancreas volumes in humans from birth to age one hundred taking into account sex, obesity, and presence of type-2 diabetes. Clin Anat. 2007;20:933–42.
Kou K, Saisho Y, Jinzaki M, Itoh H. Relationship between body mass index and pancreas volume in Japanese people. JOP. 2014;15:626–7.
Bonnet-Serrano F, Diedisheim M, Mallone R, Larger E. Decreased α-cell mass and early structural alterations of the exocrine pancreas in patients with type 1 diabetes: an analysis based on the nPOD repository. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0191528.
DeSouza SV, Singh RG, Yoon HD, Murphy R, Plank LD, Petrov MS. Pancreas volume in health and disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;12:757–66.
Gepts W. Pathologic anatomy of the pancreas in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1965;14:619–33.
Geraghty EM, Boone JM, McGahan JP, Jain K. Normal organ volume assessment from abdominal CT. Abdom Imaging. 2004;29:482–90.
Raeder H, Haldorsen IS, Ersland L, Grüner R, Taxt T, Søvik O, et al. Pancreatic lipomatosis is a structural marker in nondiabetic children with mutations in carboxyl-ester lipase. Diabetes. 2007;56:444–9.
Van Dalem A, Demeester S, Balti EV, Keymeulen B, Gillard P, Lapauw B, et al. Prediction of impending type 1 diabetes through automated dual-label measurement of proinsulin:C-peptide ratio. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0166702.
Saisho Y. Pancreas volume and fat deposition in diabetes and Normal physiology: consideration of the interplay between endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Rev Diabet Stud. 2016;13:132–47.
Hardt PD, Killinger A, Nalop J, Schnell-Kretschmer H, Zekorn T, Klör HU. Chronic pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus. A retrospective analysis of 156 ERCP investigations in patients with insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Pancreatology. 2002;2:30–3.
Olsen TS. The incidence and clinical relevance of chronic inflammation in the pancreas in autopsy material. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1978;86A:361–5.
Waguri M, Hanafusa T, Itoh N, Miyagawa J, Imagawa A, Kuwajima M, et al. Histopathologic study of the pancreas shows a characteristic lymphocytic infiltration in Japanese patients with IDDM. Endocr J. 1997;44:23–33.
Foulis AK, Stewart JA. The pancreas in recent-onset type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: insulin content of islets, insulitis and associated changes in the exocrine acinar tissue. Diabetologia. 1984;26:456–61.
Diedisheim M, Mallone R, Boitard C, Larger E. β-Cell mass in nondiabetic autoantibody-positive subjects: an analysis based on the network for pancreatic organ donors database. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:1390–7.
Kopito LE, Shwachman H. The pancreas in cystic fibrosis: chemical composition and comparative morphology. Pediatr Res. 1976;10:742–9.
Mohapatra S, Majumder S, Smyrk TC, Zhang L, Matveyenko A, Kudva YC, et al. Diabetes mellitus is associated with an exocrine Pancreatopathy: conclusions from a review of literature. Pancreas. 2016;45:1104–10.
Majumder S, Zhang L, Philip N, Sah R, Mohapatra S, Zamboni G, et al. 959 exocrine Pancreatopathy (EP) associated with diabetes mellitus (DM) is histologically distinct from chronic pancreatitis (CP): an international multi-reader blinded study. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:S191.
Bytzer P, Talley NJ, Leemon M, Young LJ, Jones MP, Horowitz M. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: a population-based survey of 15,000 adults. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:1989–96.
Jones CM, Castle WB, Mulholland HB, Bailey F. Pancreatic and hepatic activity in diabetes mellitus: the alterations with some observations on the etiology of the disease. Arch Intern Med (Chic). 1925;35:315–36.
Löser C, Möllgaard A, Fölsch UR. Faecal elastase 1: a novel, highly sensitive, and specific tubeless pancreatic function test. Gut. 1996;39:580–6.
Vanga RR, Tansel A, Sidiq S, El-Serag HB, Othman MO. Diagnostic performance of measurement of fecal Elastase-1 in detection of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16:1220–1228.e4.
Lankisch PG, Schmidt I, König H, Lehnick D, Knollmann R, Löhr M, et al. Faecal elastase 1: not helpful in diagnosing chronic pancreatitis associated with mild to moderate exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Gut. 1998;42:551–4.
Domínguez-Muñoz JE, Hieronymus C, Sauerbruch T, Malfertheiner P. Fecal elastase test: evaluation of a new noninvasive pancreatic function test. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90:1834–7.
Leeds JS, Oppong K, Sanders DS. The role of fecal elastase-1 in detecting exocrine pancreatic disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8:405–15.
Conwell DL, Lee LS, Yadav D, Longnecker DS, Miller FH, Mortele KJ, et al. American pancreatic association practice guidelines in chronic pancreatitis: evidence-based report on diagnostic guidelines. Pancreas. 2014;43:1143–62.
Lindkvist B. Diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:7258–66.
Agren G, Lagerlög H, Berglund H. The Secretin Test of Pancreatic Function in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Disease1 - ÅGREN - 1936 - Acta Medica Scandinavica - Wiley Online Library [Internet]. 1936 [cited 2018 Jun 8]. Available from: https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com.gate2.inist.fr/doi/abs/10.1111/j.0954-6820.1936.tb14607.x. Accessed 8 June 2018.
Diamond JS, Siegel SA, Kantor JL. The secretin test in the diagnosis of pancreatic diseases with a report of one hundred thirty tests. Am J Dig Dis. 1940;7:435–42.
Pollard HM, Miller L, Brewer WA. The external secretion of the pancreas and diabetes mellitus. Am J Dig Dis. 1943;10:20–3.
Lankisch PG, Manthey G, Otto J, Koop H, Talaulicar M, Willms B, et al. Exocrine pancreatic function in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Digestion. 1982;25:211–6.
Frier BM, Adrian TE, Saunders JH, Bloom SR. Serum trypsin concentration and pancreatic trypsin secretion in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta. 1980;105:297–300.
Frier BM, Saunders JH, Wormsley KG, Bouchier IA. Exocrine pancreatic function in juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus. Gut. 1976;17:685–91.
Creutzfeldt W, Gleichmann D, Otto J, Stöckmann F, Maisonneuve P, Lankisch PG. Follow-up of exocrine pancreatic function in type-1 diabetes mellitus. Digestion. 2005;72:71–5.
Frier BM, Faber OK, Binder C, Elliot HL. The effect of residual insulin secretion on exocrine pancreatic function in juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1978;14:301–4.
Chey WY, Shay H, Shuman CR. External pancreatic secretion in diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1963;59:812–21.
Dandona P, Freedman DB, Foo Y, Perkins J, Katrak A, Mikhailidis DP, et al. Exocrine pancreatic function in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Pathol. 1984;37:302–6.
Skrha J, Stĕpán J, Pacovský V. Serum lipase, isoamylase and pancreatic function test (PFT) in juvenile-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1983;20:357–61.
Li X, Campbell-Thompson M, Wasserfall CH, McGrail K, Posgai A, Schultz AR, et al. Serum Trypsinogen Levels in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:577–82.
Mohan V, Snehalatha C, Ahmed MR, Madanagopalan N, Chari S, Jayanthi V, et al. Exocrine pancreatic function in tropical fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1989;12:145–7.
Adrian TE, Barnes AJ, Bloom SR. Hypotrypsinaemia in diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta. 1979;97:213–6.
Kamarýt J, Stejskal J, Osicková L. Urinary isoamylases in juvenile diabetics. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1978;16:539–41.
Keller J, Layer P, Brückel S, Jahr C, Rosien U. 13C-mixed triglyceride breath test for evaluation of pancreatic exocrine function in diabetes mellitus. Pancreas. 2014;43:842–8.
Hardt PD, Hauenschild A, Nalop J, Marzeion AM, Jaeger C, Teichmann J, et al. High prevalence of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in diabetes mellitus. A multicenter study screening fecal elastase 1 concentrations in 1,021 diabetic patients. Pancreatology. 2003;3:395–402.
Shivaprasad C, Pulikkal AA, Kumar KMP. Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in type 1 and type 2 diabetics of Indian origin. Pancreatology. 2015;15:616–9.
Cavalot F, Bonomo K, Perna P, Bacillo E, Salacone P, Gallo M, et al. Pancreatic elastase-1 in stools, a marker of exocrine pancreas function, correlates with both residual beta-cell secretion and metabolic control in type 1 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2052–4.
Bolado F, Prieto-Martínez C, Ruiz-Clavijo D, Urman J, Casi MA, Vila JJ. 918 low levels of pancreatic Elastase-1 may not reflect exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:S-174.
Larger E, Philippe MF, Barbot-Trystram L, Radu A, Rotariu M, Nobécourt E, et al. Pancreatic exocrine function in patients with diabetes: pancreatic function in patients with diabetes. Diabet Med. 2012;29:1047–54.
Canaway S, Phillips I, Betts P. Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Br J Nurs. 2000;9:2030–2.
Laass MW, Henker J, Thamm K, Neumeister V, Kuhlisch E. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and its consequences on physical development and metabolism in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pediatr. 2004;163:681–2.
Hahn J-U, Kerner W, Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB, Lankisch PG. Low fecal elastase 1 levels do not indicate exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in type-1 diabetes mellitus. Pancreas. 2008;36:274–8.
Rodieux F, Dirlewanger M, Hanquinet S, Tempia-Caliera MG, Schwitzgebel V. P135 - L’insuffisance pancréatique exocrine est rare chez les enfants avec un diabète de type 1. /data/revues/12623636/v37i1sS1/S1262363611707613/ [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2018 Jun 11]; Available from: http://www.em-consulte.com/en/article/291510. Accessed 11 June 2018.
Vujasinovic M, Zaletel J, Tepes B, Popic B, Makuc J, Epsek Lenart M, et al. Low prevalence of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in patients with diabetes mellitus. Pancreatology. 2013;13:343–6.
Landin-Olsson M, Borgström A, Blom L, Sundkvist G, Lernmark A. Immunoreactive trypsin(ogen) in the sera of children with recent-onset insulin-dependent diabetes and matched controls. The Swedish childhood diabetes group. Pancreas. 1990;5:241–7.
Sato M, Yamamoto K, Mayama H, Yamashiro Y. Exocrine pancreatic function in diabetic children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984;3:415–20.
Ewald N, Raspe A, Kaufmann C, Bretzel RG, Kloer HU, Hardt PD. Determinants of exocrine pancreatic function as measured by fecal Elastase-1 concentrations (FEC) in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eur J Med Res. 2009;14:118–22.
Domschke W, Tympner F, Domschke S, Demling L. Exocrine pancreatic function in juvenile diabetics. Am J Dig Dis. 1975;20:309–12.
Vacca JB. The exocrine pancreas in diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1964;61:242.
Kondrashova A, Nurminen N, Lehtonen J, Hyöty M, Toppari J, Ilonen J, et al. Exocrine pancreas function decreases during the progression of the beta-cell damaging process in young prediabetic children. Pediatr Diabetes. 2017.
Fraser PA, Henderson JR. The arrangement of endocrine and exocrine pancreatic microcirculation observed in the living rabbit. Exp Physiol. 1980;65:151–8.
Henderson JR, Moss MC. A morphometric study of the endocrine and exocrine capillaries of the pancreas. Q J Exp Physiol. 1985;70:347–56.
Cohrs CM, Chen C, Jahn SR, Stertmann J, Chmelova H, Weitz J, et al. Vessel network architecture of adult human islets promotes distinct cell-cell interactions in situ and is altered after transplantation. Endocrinology. 2017;158:1373–85.
Unger RH, Aguilar-Parada E, Müller WA, Eisentraut AM. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970;49:837–48.
Walczak M, Mrozikiewicz D, Dmochowski K, Rewers M, Cichy W. Serum pancreatic polypeptide and glucagon immunoreactivity in fasting healthy and diabetic children. Mater Med Pol. 1989;21:38–42.
Ertan A, Arimura A, Akdamar K, Shibata T, Groot K, Luciano M, et al. Pancreatic immunoreactive somatostatin and diabetes mellitus. Dig Dis Sci. 1984;29:625–30.
Hellman B, Wallgren A, Petersson B. Cytological characteristics of the exocrine pancreatic cells with regard to their position in relation to the islets of Langerhans. A study in normal and obese-hyperglycaemic mice. Acta Endocrinol. 1962;39:465–73.
Henderson JR, Daniel PM, Fraser PA. The pancreas as a single organ: the influence of the endocrine upon the exocrine part of the gland. Gut. 1981;22:158–67.
Wallgren A, Hellman B. Influence of the islet a and B cells on the exocrine pancreatic tissue in the duck. Acta Anat (Basel). 1962;48:137–41.
Kramer MF, Tan HT. The peri-insular acini of the pancreas of the rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;86:163–70.
Hegyi P, Takács T, Jármay K, Nagy I, Czakó L, Lonovics J. Spontaneous and cholecystokinin-octapeptide-promoted regeneration of the pancreas following L-arginine-induced pancreatitis in rat. Int J Pancreatol. 1997;22:193–200.
Mössner J, Logsdon CD, Williams JA, Goldfine ID. Insulin, via its own receptor, regulates growth and amylase synthesis in pancreatic acinar AR42J cells. Diabetes. 1985;34:891–7.
Williams JA, Goldfine ID. The insulin-pancreatic acinar axis. Diabetes. 1985;34:980–6.
Korc M, Owerbach D, Quinto C, Rutter WJ. Pancreatic islet-acinar cell interaction: amylase messenger RNA levels ar determined by insulin. Science. 1981;213:351–3.
Söling HD, Unger KO. The role of insulin in the regulation of -amylase synthesis in the rat pancreas. Eur J Clin Investig. 1972;2:199–212.
Lee KY, Zhou L, Ren XS, Chang TM, Chey WY. An important role of endogenous insulin on exocrine pancreatic secretion in rats. Am J Phys. 1990;258:G268–74.
Otsuki M, Williams JA. Effect of diabetes mellitus on the regulation of enzyme secretion by isolated rat pancreatic acini. J Clin Invest. 1982;70:148–56.
Adler G, Kern HF. Regulation of exocrine pancreatic secretory process by insulin in vivo. Horm Metab Res. 1975;7:290–6.
Saito A, Williams JA, Kanno T. Potentiation of cholecystokinin-induced exocrine secretion by both exogenous and endogenous insulin in isolated and perfused rat pancreata. J Clin Invest. 1980;65:777–82.
Benabdeljlil A, Palla JC, Desnuelle P. Effect of insulin on pancreatic amylase and chymotrypsinogen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965;18:71–5.
Lam WF, Gielkens HA, Coenraad M, Souverijn JH, Lamers CB, Masclee AA. Effect of insulin and glucose on basal and cholecystokinin-stimulated exocrine pancreatic secretion in humans. Pancreas. 1999;18:252–8.
Patel R, Singh J, Yago MD, Vilchez JR, Martínez-Victoria E, Mañas M. Effect of insulin on exocrine pancreatic secretion in healthy and diabetic anaesthetised rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004;261:105–10.
Couture Y, Dunnigan J, null M. Stimulation of pancreatic amylase secretion and protein synthesis by insulin. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1972;7:257–63.
Sherr J, Tsalikian E, Fox L, Buckingham B, Weinzimer S, Tamborlane WV, et al. Evolution of abnormal plasma glucagon responses to mixed-meal feedings in youth with type 1 diabetes during the first 2 years after diagnosis. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:1741–4.
Salter JM, Davidson IW, Best CH. The pathologic effects of large amounts of glucagon. Diabetes. 1957;6:248–52; discussion, 252–5.
Cameron JM, Melrose AG. Changes in liver, pancreatic and stomach morphology following chronic glucagon administration in Guinea-pigs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962;43:384–6.
Lazarus SS, Volk BW, Lofaro P. The effect of protracted glucagon administration on blood glucose and on pancreatic morphology. Endocrinology. 1958;63:359–71.
Necheles H. Effects of glucagon on external secretion of the pancreas. Am J Phys. 1957;191:595–7.
Nakajima S, Magee DF. Inhibition of exocrine pancreatic secretion by glucagon and D-glucose given intravenously. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1970;48:299–305.
Dyck WP, Rudick J, Hoexter B, Janowitz HD. Influence of glucagon on pancreatic exocrine secretion. Gastroenterology. 1969;56:531–7.
Shaw HM, Heath TJ. The effect of glucagon on the formation of pancreatic juice and bile in the rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1973;51:1–5.
Liddle RC and RA. Regulation of Pancreatic Secretion. Pancreapedia: The Exocrine Pancreas Knowledge Base [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2018 Aug 22]; Available from: /reviews/regulation-of-pancreatic-secretion.
Gyr K, Beglinger C, Köhler E, Trautzl U, Keller U, Bloom SR. Circulating somatostatin. Physiological regulator of pancreatic function? J Clin Invest. 1987;79:1595–600.
Boden G, Sivitz MC, Owen OE, Essa-Koumar N, Landor JH. Somatostatin suppresses secretin and pancreatic exocrine secretion. Science. 1975;190:163–5.
Heintges T, Lüthen R, Niederau C. Inhibition of exocrine pancreatic secretion by somatostatin and its analogues. Digestion. 1994;55:1–9.
Adrian TE. Pancreatic polypeptide. J Clin Pathol. 1978;43–50:s1–8.
Greenberg GR, Mitznegg P, Bloom SR. Effect of pancreatic polypeptide on DNA-synthesis in the pancreas. Experientia. 1977;33:1332–3.
Rahier J, Wallon J, Loozen S, Lefevre A, Gepts W, Haot J. The pancreatic polypeptide cells in the human pancreas: the effects of age and diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983;56:441–4.
Luce S, Briet C, Bécourt C, Lemonnier F, Boitard C. The targeting of β-cells by T lymphocytes in human type 1 diabetes: clinical perspectives. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(Suppl 3):89–97.
Martin S, Kardorf J, Schulte B, Lampeter EF, Gries FA, Melchers I, et al. Autoantibodies to the islet antigen ICA69 occur in IDDM and in rheumatoid arthritis. Diabetologia. 1995;38:351–5.
Mally MI, Cirulli V, Hayek A, Otonkoski T. ICA69 is expressed equally in the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Diabetologia. 1996;39:474–80.
Wiberg A, Granstam A, Ingvast S, Härkönen T, Knip M, Korsgren O, et al. Characterization of human organ donors testing positive for type 1 diabetes-associated autoantibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015;182:278–88.
Endo T, Takizawa S, Tanaka S, Takahashi M, Fujii H, Kamisawa T, et al. Amylase alpha-2A autoantibodies: novel marker of autoimmune pancreatitis and fulminant type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2009;58:732–7.
Taniguchi T, Okazaki K, Okamoto M, Seko S, Tanaka J, Uchida K, et al. High prevalence of autoantibodies against carbonic anhydrase II and lactoferrin in type 1 diabetes: concept of autoimmune exocrinopathy and endocrinopathy of the pancreas. Pancreas. 2003;27:26–30.
Hardt PD, Ewald N, Bröckling K, Tanaka S, Endo T, Kloer HU, et al. Distinct autoantibodies against exocrine pancreatic antigens in European patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. JOP. 2008;9:683–9.
di Cesare E, Previti M, Lombardo F, Mazzù N, di Benedetto A, Cucinotta D. Prevalence of autoantibodies to carbonic anhydrase II and lactoferrin in patients with type 1 diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1037:131–2.
Kobayashi T, Nakanishi K, Kajio H, Morinaga S, Sugimoto T, Murase T, et al. Pancreatic cytokeratin: an antigen of pancreatic exocrine cell autoantibodies in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1990;33:363–70.
Panicot L, Mas E, Thivolet C, Lombardo D. Circulating antibodies against an exocrine pancreatic enzyme in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 1999;48:2316–23.
Yamada T, Hiraoka E, Miyazaki T, Sato J, Ban N. Diabetes as first manifestation of autoimmune pancreatitis. Am J Med Sci. 2017;353:498–9.
Ennazk L, Mghari GE, Ansari NE. Association of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes and autoimmune pancreatitis. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2016;2016.
Papaccio G, Chieffi-Baccari G, Mezzogiorno V, Esposito V. Extraislet infiltration in NOD mouse pancreas: observations after immunomodulation. Pancreas. 1993;8:459–64.
Coppieters KT, Dotta F, Amirian N, Campbell PD, Kay TWH, Atkinson MA, et al. Demonstration of islet-autoreactive CD8 T cells in insulitic lesions from recent onset and long-term type 1 diabetes patients. J Exp Med. 2012;209:51–60.
Culina S, Lalanne AI, Afonso G, Cerosaletti K, Pinto S, Sebastiani G, et al. Islet-reactive CD8+ T cell frequencies in the pancreas, but not in blood, distinguish type 1 diabetic patients from healthy donors. Sci Immunol. 2018;3.
Gonzalez-Duque S, Azoury ME, Colli ML, Afonso G, Turatsinze J-V, Nigi L, et al. Conventional and neo-antigenic peptides presented by β cells are targeted by circulating Naïve CD8+ T cells in type 1 diabetic and healthy donors. Cell Metab. 2018.
Radenkovic M, Silver C, Arvastsson J, Lynch K, Lernmark Å, Harris RA, et al. Altered regulatory T cell phenotype in latent autoimmune diabetes of the adults (LADA). Clin Exp Immunol. 2016;186:46–56.
Schenkel JM, Masopust D. Tissue-resident memory T cells. Immunity. 2014;41:886–97.
Valle A, Giamporcaro GM, Scavini M, Stabilini A, Grogan P, Bianconi E, et al. Reduction of circulating neutrophils precedes and accompanies type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2013;62:2072–7.
Semakula C, Vandewalle CL, Van Schravendijk CF, Sodoyez JC, Schuit FC, Foriers A, et al. Abnormal circulating pancreatic enzyme activities in more than twenty-five percent of recent-onset insulin-dependent diabetic patients: association of hyperlipasemia with high-titer islet cell antibodies. Belgian diabetes registry. Pancreas. 1996;12:321–33.
Rowe P, Wasserfall C, Croker B, Campbell-Thompson M, Pugliese A, Atkinson M, et al. Increased complement activation in human type 1 diabetes pancreata. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:3815–7.
Sarkar SA, Lee CE, Victorino F, Nguyen TT, Walters JA, Burrack A, et al. Expression and regulation of chemokines in murine and human type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2012;61:436–46.
Zhang Q, Fillmore TL, Schepmoes AA, Clauss TRW, Gritsenko MA, Mueller PW, et al. Serum proteomics reveals systemic dysregulation of innate immunity in type 1 diabetes. J Exp Med. 2013;210:191–203.
Burch TC, Morris MA, Campbell-Thompson M, Pugliese A, Nadler JL, Nyalwidhe JO. Proteomic analysis of disease stratified human pancreas tissue indicates unique signature of type 1 diabetes. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0135663.
Lewis MP, Reber HA, Ashley SW. Pancreatic blood flow and its role in the pathophysiology of pancreatitis. J Surg Res. 1998;75:81–9.
El-Gohary Y, Tulachan S, Branca M, Sims-Lucas S, Guo P, Prasadan K, et al. Whole-mount imaging demonstrates hypervascularity of the pancreatic ducts and other pancreatic structures. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012;295:465–73.
Saladino CFJ. Age changes in the canine pancreas: histomorphological, electron microscopic, and biochemical study. 1971;246.
Funk HU. Veränderungen an Pankreaskapillaren bei Diabetikern. Diabetologia. 1966;1:228–32.
Levy BI, Schiffrin EL, Mourad J-J, Agostini D, Vicaut E, Safar ME, et al. Impaired tissue perfusion: a pathology common to hypertension, obesity, and diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2008;118:968–76.
Pollak OJ. Human pancreatic atherosclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968;149:928–39.
Blumenthal HT, Probstein JG, Berns AW. Interrelationship of diabetes mellitus and pancreatitis. Arch Surg. 1963;87:844–50.
Berns AW, Owens CT, Blumenthal HT. A histo- and immunopathologic study of the vessels and islets of langerhans of the pancreas in diabetes mellitus. J Gerontol. 1964;19:179–89.
Reiner L, Jimenez FA, Rodriguez FL. Atherosclerosis in the mesenteric circulation. Observations and correlations with aortic and coronary atherosclerosis. Am Heart J. 1963;66:200–9.
Clair JRS, Ramirez D, Passman S, Benninger RKP. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound measurement of pancreatic blood flow dynamics predicts type 1 diabetes progression in preclinical models. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1742.
Kivisaari L. The effect of experimental pancreatitis and diabetes on the microvasculature of the rat pancreas. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1979;14:689–95.
Canzano JS, Nasif LH, Butterworth EA, Fu DA, Atkinson MA, Campbell-Thompson M. Islet Microvasculature Alterations With Loss of Beta-cells in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 2018;22155418778546.
Sasson A, Rachi E, Sakhneny L, Baer D, Lisnyansky M, Epshtein A, et al. Islet Pericytes are required for β-cell maturity. Diabetes. 2016;65:3008–14.
Almaça J, Weitz J, Rodriguez-Diaz R, Pereira E, Caicedo A. The Pericyte of the pancreatic islet regulates capillary diameter and local blood flow. Cell Metab. 2018;27:630–644.e4.
Babic T, Browning KN, Kawaguchi Y, Tang X, Travagli RA. Pancreatic insulin and exocrine secretion are under the modulatory control of distinct subpopulations of vagal motoneurones in the rat. J Physiol Lond. 2012;590:3611–22.
Love JA, Yi E, Smith TG. Autonomic pathways regulating pancreatic exocrine secretion. Auton Neurosci. 2007;133:19–34.
Solomon TE, Grossman MI. Effect of atropine and vagotomy on response of transplanted pancreas. Am J Phys. 1979;236:E186–90.
Valenzuela JE, Weiner K, Saad C. Cholinergic stimulation of human pancreatic secretion. Dig Dis Sci. 1986;31:615–9.
Razavi R, Chan Y, Afifiyan FN, Liu XJ, Wan X, Yantha J, et al. TRPV1+ sensory neurons control beta cell stress and islet inflammation in autoimmune diabetes. Cell. 2006;127:1123–35.
Lundberg M, Lindqvist A, Wierup N, Krogvold L, Dahl-Jørgensen K, Skog O. The density of parasympathetic axons is reduced in the exocrine pancreas of individuals recently diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0179911.
Masamune A, Watanabe T, Kikuta K, Shimosegawa T. Roles of pancreatic stellate cells in pancreatic inflammation and fibrosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:S48–54.
Czakó L, Hegyi P, Rakonczay Z, Wittmann T, Otsuki M. Interactions between the endocrine and exocrine pancreas and their clinical relevance. Pancreatology. 2009;9:351–9.
Nomiyama Y, Tashiro M, Yamaguchi T, Watanabe S, Taguchi M, Asaumi H, et al. High glucose activates rat pancreatic stellate cells through protein kinase C and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Pancreas. 2007;34:364–72.
Watanabe S, Nagashio Y, Asaumi H, Nomiyama Y, Taguchi M, Tashiro M, et al. Pressure activates rat pancreatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;287:G1175–81.
Zang G, Sandberg M, Carlsson P-O, Welsh N, Jansson L, Barbu A. Activated pancreatic stellate cells can impair pancreatic islet function in mice. Ups J Med Sci. 2015;120:169–80.
Foulis AK, Farquharson MA, Hardman R. Aberrant expression of class II major histocompatibility complex molecules by B cells and hyperexpression of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules by insulin containing islets in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1987;30:333–43.
Skog O, Korsgren S, Wiberg A, Danielsson A, Edwin B, Buanes T, et al. Expression of human leukocyte antigen class I in endocrine and exocrine pancreatic tissue at onset of type 1 diabetes. Am J Pathol. 2015;185:129–38.
Battaglia M, Atkinson MA. The streetlight effect in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2015;64:1081–90.
Magalhaes I, Pingris K, Poitou C, Bessoles S, Venteclef N, Kiaf B, et al. Mucosal-associated invariant T cell alterations in obese and type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:1752–62.
Kuric E, Krogvold L, Hanssen KF, Dahl-Jørgensen K, Skog O, Korsgren O. No evidence for presence of mucosal-associated invariant T cells in the Insulitic lesions in patients recently diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Am J Pathol. 2018;188:1744–8.
Stechova K, Kolouskova S, Sumnik Z, Cinek O, Kverka M, Faresjo MK, et al. Anti-GAD65 reactive peripheral blood mononuclear cells in the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis related diabetes mellitus. Autoimmunity. 2005;38:319–23.
Bizzarri C, Giannone G, Benevento D, Montemitro E, Alghisi F, Cappa M, et al. ZnT8 antibodies in patients with cystic fibrosis: an expression of secondary beta-cell damage? J Cyst Fibros. 2013;12:803–5.
Scuro LA, Bovo P, Sandrini T, Angelini G, Cavallini G, Mirakian R. Autoimmunity and diabetes associated with chronic pancreatitis. Lancet. 1983;1:424.
Cummings MH, Chong L, Hunter V, Kar PS, Meeking DR, Cranston IC. Gastrointestinal symptoms and pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Practical Diabetes. 2015;32:54–8.
Gotfried J, Priest S, Schey R. Diabetes and the small intestine. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2017;15:490–507.
Cavalot F, Bonomo K, Fiora E, Bacillo E, Salacone P, Chirio M, et al. Does pancreatic elastase-1 in stools predict steatorrhea in type 1 diabetes? Diabetes Care. 2006;29:719–21.
Hardt PD, Hauenschild A, Jaeger C, Teichmann J, Bretzel RG, Kloer HU, et al. High prevalence of steatorrhea in 101 diabetic patients likely to suffer from exocrine pancreatic insufficiency according to low fecal elastase 1 concentrations: a prospective multicenter study. Dig Dis Sci. 2003;48:1688–92.
Lindkvist B, Domínguez-Muñoz JE, Luaces-Regueira M, Castiñeiras-Alvariño M, Nieto-Garcia L, Iglesias-Garcia J. Serum nutritional markers for prediction of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2012;12:305–10.
Lindkvist B, Nilsson C, Kvarnström M, Oscarsson J. Importance of pancreatic exocrine dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized crossover study. Pancreatology. 2018.
Alexandre-Heymann L, Lemoine AY, Nakib S, Kapel N, Ledoux S, Larger E. Nutritional markers in patients with diabetes and pancreatic exocrine failure. Acta Diabetol. 2019.
Tignor AS, Wu BU, Whitlock TL, Lopez R, Repas K, Banks PA, et al. High prevalence of low-trauma fracture in chronic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:2680–6.
Mohan V, Poongothai S, Pitchumoni CS. Oral pancreatic enzyme therapy in the control of diabetes mellitus in tropical calculous pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol. 1998;24:19–22.
Whitcomb DC, Bodhani A, Beckmann K, Sander-Struckmeier S, Liu S, Fuldeore M, et al. Efficacy and safety of Pancrelipase/Pancreatin in patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and a medical history of diabetes mellitus. Pancreas. 2016;45:679–86.
Knop FK, Vilsbøll T, Larsen S, Højberg PV, Vølund A, Madsbad S, et al. Increased postprandial responses of GLP-1 and GIP in patients with chronic pancreatitis and steatorrhea following pancreatic enzyme substitution. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;292:E324–30.
Ebert R, Creutzfeldt W. Reversal of impaired GIP and insulin secretion in patients with pancreatogenic steatorrhea following enzyme substitution. Diabetologia. 1980;19:198–204.
Suzuki S, Miura J, Shimizu K, Tokushige K, Uchigata Y, Yamamoto M. Clinicophysiological outcomes after total pancreatectomy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016;51:1526–31.
Ewald N, Bretzel RG, Fantus IG, Hollenhorst M, Kloer HU, Hardt PD, et al. Pancreatin therapy in patients with insulin-treated diabetes mellitus and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency according to low fecal elastase 1 concentrations. Results of a prospective multi-Centre trial. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2007;23:386–91.
Keller J, Aghdassi AA, Lerch MM, Mayerle JV, Layer P. Tests of pancreatic exocrine function - clinical significance in pancreatic and non-pancreatic disorders. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;23:425–39.
Zsóri G, Illés D, Terzin V, Ivány E, Czakó L. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: do we need to treat it? A systematic review. Pancreatology. 2018;
Struyvenberg MR, Martin CR, Freedman SD. Practical guide to exocrine pancreatic insufficiency - breaking the myths. BMC Med. 2017;15:29.
Löhr J-M, Oliver MR, Frulloni L. Synopsis of recent guidelines on pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. United European Gastroenterol J. 2013;1:79–83.
Working Party of the Australasian Pancreatic Club, Smith RC, Smith SF, Wilson J, Pearce C, Wray N, et al. Summary and recommendations from the Australasian guidelines for the management of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. Pancreatology. 2016;16:164–80.
Piciucchi M, Capurso G, Archibugi L, Delle Fave MM, Capasso M, Delle Fave G. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in diabetic patients: prevalence, mechanisms, and treatment. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:595649.
O’Keefe SJ, Cariem AK, Levy M. The exacerbation of pancreatic endocrine dysfunction by potent pancreatic exocrine supplements in patients with chronic pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;32:319–23.
Acknowledgements
Images in this manuscript were provided by Network for Pancreatic Organ Donors with Diabetes (nPOD) online pathology site. nPOD is a collaborative type 1 diabetes research project sponsored by JDRF and the Helmsley Charitable Trust. Organ Procurement Organizations partnering with nPOD to provide research resources are listed at http://www.jdrfnpod.org//for-partners/npod-partners/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexandre-Heymann, L., Mallone, R., Boitard, C. et al. Structure and function of the exocrine pancreas in patients with type 1 diabetes. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 20, 129–149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-019-09501-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-019-09501-3