Abstract
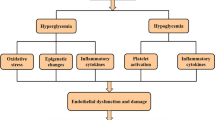
Microvascular complications in diabetes are associated with poor long-term diabetes control as measured by HbA1c levels. Glucose fluctuations are related to oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and inflammation, factors traditionally associated with the pathogenesis of vascular damage. Glucose variability has been associated with macrovascular disease in some studies but any association with microvascular disease remains controversial. This overview summarizes recent findings in the field of glucose variability and its possible relationship with retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy. It is concluded that randomized prospective follow-up trials could possibly help estimate whether short-term glucose variability should be considered as an independent risk factor for microvascular complications in diabetes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nathan DM, McGee P, Steffes MW, Lachin JM. Relationship of glycated albumin to blood glucose and HbA(1c) values and to retinopathy, nephropathy and cardiovascular outcomes in the DCCT/EDIC study. Diabetes. 2014;63:282–90.
Saisho Y. Glycemic variability and oxidative stress: a link between diabetes and cardiovascular disease? Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:18381–406.
Brownlee M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications – a unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 2005;54:1615–25.
El-Osta A, Brasacchio D, Yao DC, Pocai A, Jones PL, Roeder RG, et al. Transient high glucose causes persistent epigenetic changes and altered gene expression during subsequent normoglycemia. J Exp Med. 2008;205:2409–17.
Salisbury D, Bronas U. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Impact on endothelial dysfunction. Nurs Res. 2015;64:53–66.
Wang L, Wang J, Fang J, Zhou HY, Liu XL, Su SB. High glucose induces and activates Toll-like receptor 4 in endothelial cells of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015;7:89. doi:10.1186/s13098-015-0086-4.
De Nigris V, Pujadas G, La Sala L, Testa R, Genovese S, Ceriello A. Short-term high glucose exposure impairs insulin signaling in endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015;14:114. doi:10.1186/s12933-015-0278-0.
Monnier L, Mas E, Ginet C, Michel F, Villon L, Cristol JP, et al. Activation of oxidative stress by acute glucose fluctuations compared with sustained chronic hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. JAMA. 2006;295:1681–7.
Zhang XG, Zhang YQ, Zhao DK, Wu JX, Zhao J, Jiao XM, et al. Relationship between blood glucose fluctuation and macrovascular endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary heart disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18:3593–600.
Ceriello A, Esposito K, Piconi L, Ihnat MA, Thorpe JE, Testa R, et al. Oscillating glucose is more deleterious to endothelial function and oxidative stress than mean glucose in normal and type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes. 2008;57:1349–54.
Schisano B, Tripathi G, McGee K, McTernan PG, Ceriello A. Glucose oscillations, more than constant high glucose, induce p53 activation and a metabolic memory in human endothelial cells. Diabetologia. 2011;54:1219–26.
Pena AS, Couper JJ, Harrington J, Gent R, Fairchild J, Tham E, et al. Hypoglycemia, but not glucose variability, relates to vascular function in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012;14:457–62.
Ceriello A, Novials A, Ortega E, Pujadas G, La Sala L, Testa R, et al. Hyperglycemia following recovery from hypoglycemia worsens endothelial damage and thrombosis activation in type 1 diabetes and in healthy controls. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2014;24:116–23.
Kumar B, Kowluru A, Kowluru RA. Lipotoxicity augments glucotoxicity-induced mitochondrial damage in the development of diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56:2985–92.
Yang HK, Kang B, Lee SH, Yoon KH, Hwang BH, Chang K, et al. Association between hemoglobin A1c variability and subclinical coronary atherosclerosis in subjects with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complicat. 2015;29:776–82.
Chang CH, Chuang LM. Glycated hemoglobin variability and retinopathy progression in type 1 diabetes: is month-to-month instability a better predictor? J Diabetes Investig. 2014;5:149–51.
Cheng DS, Fei Y, Liu Y, Li JH, Xue Q, Wang XX, et al. HbA1c variability and the risk of renal status progression in diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9, e115509. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115509.
Kohnert KD, Heinke P, Vogt L, Salzsieder E. Utility of different glycemic control metrics for optimizing management of diabetes. World J Diabetes. 2015;6:17–29.
Service FJ. Glucose variability. Diabetes. 2013;62:1398–404.
Saisho Y, Tanaka C, Tanaka K, Roberts R, Abe T, Tanaka M, et al. Relationships among different glycemic variability indices obtained by continuous glucose monitoring. Primary Care Diabetes. 2015;9:290–6.
Fabris C, Facchinetti A, Sparacino G, Zanon M, Guerra S, Maran A, et al. Glucose variability indices in Type 1 diabetes: parsimonious set of indices revealed by Sparse Principal Component Analysis. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014;16:644–52.
Selvin E, Rawlings AM, Grams M, Klein R, Steffes M, Coresh J. Association of 1,5-anhydroglucitol with diabetes and microvascular conditions. Clin Chem. 2014;60:1409–18.
Ceriello A, Novials A, Ortega E, Canivell S, La Sala L, Pujadas G, et al. Vitamin C further improves the protective effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 on acute hypoglycemia-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:4104–8.
Yousetzade G, Nakhaee A. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia and stress oxidative state in healthy people. Acta Diabetol. 2012;49:S81–5.
Wang JL, Alexanian A, Ying R, Kizhakekuttu TJ, Dharmashankar K, Vasquez-Vivar J, et al. Acute exposure to low glucose rapidly induces endothelial dysfunction and mitochontrial oxidative stress role for AMP kinase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32:712–20.
Jaiswal M, McKeon K, Comment N, Henderson J, Swanson S, Plunkett C, et al. Association between impaired cardiovascular autonomic function and hypoglycemia in patients with Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:2616–21.
Hirsch IB. Glycemic variability and diabetes complications: does it matter? Of course it does! Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1610–4.
Rodbard D. Evaluating quality of glycemic control: graphical displays of hypo- and hyper-glycemia, time in target range, and mean glucose. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2015;9:56–62.
Ceriello A, Kilpatrick ES. Glycemic variability: both sides of the story. Diabetes Care. 2013;36 Suppl 2:S272–5.
Bergenstal RM. Glycemic variability and diabetes complications: does it matter? Simply put, there are better glycemic markers! Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1615–21.
Cryer PE. Severe hypoglycemia predicts mortality in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:1814–6.
Niskanen L, Virkamäki A, Hansen JB, Saukkonen T. Fasting plasma glucose variability as a marker of nocturnal hypoglycemia in diabetes: evidence from the PREDICTIVE study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009;86:e15–8.
Cryer PE. Hypoglycemia: still the limiting factor in the glycemic management of diabetes. Endocr Pract. 2008;14:750–6.
Smith-Palmer J, Brändle M, Trevisan R, Orsini Federici M, Liabat S, Valentine W. Assessment of the association between glycemic variability and diabetes-related complications in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;105:273–84.
Šoupal J, Škrha Jr J, Fajmon M, Horová E, Mráz M, Škrha J, et al. Glycemic variability is higher in type 1 diabetes patients with microvascular complications irrespective of glycemic control. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014;16:198–203.
Lachin JM, Genuth S, Nathan DM, Zinman B, Rutledge BN. Effect of glycemic exposure on the risk of microvascular complications in the diabetes control and complications trialrevisited. Diabetes. 2008;57:995–1001.
Gorst C, Kwak CS, Aslam S, Buchan I, Kontopantelis E, Myint PK, et al. Long-term glycemic variability and risk of adverse outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:2354–69.
Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Atkin SL. The effect of glucose variability on the risk of microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1486–90.
Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Atkin SL. A1C variability and the risk of microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes: data from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:2198–202.
Hermann JM, Hammes HP, Rami-Mehar B, Rosenbauer J, Schütt M, Siegel E, et al. HbA1c variability as an independent risk factor for diabetic retinopathy in Type 1 diabetes: A German/Austrian multicenter analysis on 35,891 patients. PLoS One. 2014;9, e91137.
Hietala K, Waden J, Forsblom C, Harjutsalo V, Kytö J, Summanen P, et al. HbA1c variability is associated with an increased risk of retinopathy requiring laser treatment in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2013;56:737–45.
Gimeno-Orna JA, Castro-Alonso FJ, Boned-Juliani B, Lou-Arnal LM. Fasting plasma glucose variability as a risk factor of retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. J Diabetes Complicat. 2003;17:78–81.
Zoppini G, Verlato G, Targher G, Casati S, Gusson E, Biasi V, et al. Is fasting glucose variability a risk factor for retinopathy in people with type 2 diabetes? Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009;19:334–9.
Hirakawa Y, Arima H, Zoungas S, Ninomyia T, Cooper M, Hamet P, et al. Impact of visit-to-visit glycemic variability on the risks of macrovascular and microvascular events and all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetes: the ADVANCE trial. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:2359–65.
Takao T, Ide T, Yanagisawa H, Kikuchi M, Kawazu S, Matsuyama Y. The effect of fasting plasma glucose variability on the risk of retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients: retrospective long-term follow-up. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;89:296–302.
Takao T, Ide T, Yanagisawa H, Kikuchi M, Kawazu S, Matsuyama Y. The effects of fasting plasma glucose variability and time-dependent glycemic control on the long-term risk of retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;91:e40–2.
Nazim J, Fendler W, Starzyk J. Metabolic control and its variability are major risk factors for microalbuminuria in children with type 1 diabetes. Endokrynol Pol. 2014;65:83–9.
Jin SM, Kim TH, Baek SOJ, Joung JY, Park SM, Cho YY, et al. Association between the extent of urinary albumin excretion and glycaemic variability indices measured by continuous glucose monitoring. Diabet Med. 2015;32:274–9.
Hou X, Wang C, Wang S, Yang WF, Ma ZQ, Wang YL et al. Fluctuation between fasting and 2-H postload glucose state is associated with glomerular hyperfiltration in newly diagnosed diabetes patients with HbA1c, 7%. PLoS One 2014;9: doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111173.
Hsu CC, Chang HY, Huang MC, Hwang SJ, Yang YC, Lee YS, et al. HbA1c variability is associated with microalbuminuria development in type 2 diabetes: a 7-year prospective cohort study. Diabetologia. 2012;55:3163–72.
Penno G, Solini A, Bonora E, Fondelli C, Orsi E, Zerbini G, et al. HbA1c variability as an independent correlate of nephropathy, but not retinopathy, in patients with type 2 diabetes. The Renal Insufficiency And Cardiovascular Events (RIACE) Italian multicenter study. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:2301–10.
Bragd J, Adamson U, Bäcklund LB, Lins PE, Moberg E, Oskarsson P. Can glycaemic variability, as calculated from blood glucose self-monitoring, predict the development of complications in type 1 diabetes over a decade? Diabetes Metab. 2008;34:612–6.
Sharma D, Morrison G, Joseph F, Purewal TS, Weston PJ. The role of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy in patients with diabetic gastroparesis. Diabetologia. 2011;54:2768–70.
Samsom M, Akkermans LM, Jebbink RJ, van Isselt H, van BergeHenegouwen GP, Smout AJ. Gastrointestinal motor mechanisms in hyperglycaemia induced delayed gastric emptying in type I diabetes mellitus. Gut. 1997;40:641–6.
Bellastella G, Maiorino MI, Olita L, Della Volpe E, Giugliano D, Esposito K. Premature ejaculation is associated with glycemic control in Type 1 diabetes. J Sex Med. 2015;12(1):93–9.
Iwasaki S, Kozawa J, Fukui K, Iwahashi H, Imagawa A, Shimomura I. Coefficient of variation of R-R interval closely correlates with glycemic variability assessed by continuous glucose monitoring in insulin-depleted patients with type 1 diabetes. Diab Res Clin Pract. 2015;109:397–403.
Xu F, Zhao L, Su J, Chen T, Wang X, Chen J, et al. The relationship between glycemic variability and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes with well-controlled HbA1c. Diabet Metab Syndr. 2014;6:139–45.
Jun JE, Jin SM, Baek J, Oh S, Hur KY, Lee MS, et al. The association between glycemic variability and diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015;14:70–8.
Martín-Cora FJ, Fornal CA, Metzler CW, Jacobs BL. Insulin induced hypoglycemia decreases single-unit activity of serotonergic medullary raphe neurons in freely moving cats: relationship to sympathetic and motor output. Eur J Neurosci. 2002;16:722–34.
Hsu CR, Chen YT, Sheu WHH. Glycemic variability and diabetes retinopathy: a missing link. J Diabetes Complicat. 2015;29:302–6.
The FLAT-SUGAR Trial investigators. Design of FLAT-SUGAR: Randomized trial of prandial insulin versus prandial GLP-1 receptor agonist together with basal insulin and metformin for high-risk Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1558–66.
Acknowledgments
This review was supported the Czech Health Research Council and the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic with grant Nr. 15-26705A and by research project P25/LF1/2 of Charles University, Prague.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Škrha, J., Šoupal, J., Škrha, J. et al. Glucose variability, HbA1c and microvascular complications. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 17, 103–110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-016-9347-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-016-9347-2