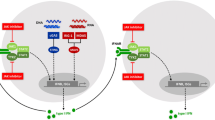
Abstract
Cytokines, particularly those endowed with pro-inflammatory properties, are known to influence the release of anterior pituitary hormones by a direct and indirect action at the level of pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Type I interferons (IFNs) represent a group of cytokines that act through a common receptor composed by two chains (IFNAR-1 and IFNAR-2). Several in vitro and in vivo studies underline the fact that type I IFNs are involved in the regulation of the immune-endocrine circuitry. Treatment with type I IFNs of patients affected by chronic viral hepatitis, multiple sclerosis and tumors influences the secretion of pituitary hormones. This article reviews the current knowledge about the effects of IFN-α and IFN-β on hypothalamic–pituitary function and describes the potential role of type I IFNs in the treatment of pituitary adenomas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pestka S. Interferons, interferon-like cytokines and their receptors. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:8–32.
Borden EC, Sen GC, Uze G, Silverman RH, Ransohoff RM, Foster GR, et al. Interferons at age 50: past, current and future impact on biomedicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:975–90.
Bekisz J, Schmeisser H, Hernandez J, Goldman ND, Zoon KC. Human interferons alpha, beta and omega. Growth Factors. 2004;22:243–51.
De Maeyer E, De Maeyer-Guignard J. Type I interferons. Int Rev Immunol. 1998;17:53–73.
Pestka S. The interferon receptors. Semin Oncol. 1997;24:S9–18–S9-40.
Domanski P, Witte M, Kellum M, Rubinstein M, Hackett R, Pitha P, et al. Cloning and expression of a long form of the beta subunit of the interferon alpha beta receptor that is required for signaling. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:21606–11.
Cohen B, Novick D, Barak S, Rubinstein M. Ligand-induced association of the type I interferon receptor components. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:4208–14.
Schindler C, Darnell JE Jr. Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: the JAK-STAT pathway. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:621–51.
Ihle JN. STATs: signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell 1996;84:331–34.
Darnell JE Jr. STATs and gene regulation. Science 1997;277:1630–5.
Imada K, Leonard WJ. The Jak–STAT pathway. Mol Immunol. 2000;37:1–11.
Takeda K, Akira S. STAT family of transcription factors in cytokine-mediated biological responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000;11:199–207.
Darnell JE, Kerr IM, Stark GR. Jak–STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994;264:1415–21.
Meinke A, Barahmand-Pour F, Wohrl S, Stoiber D, Decker T. Activation of different Stat5 isoforms contributes to cell type-restricted signaling in response to interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:6937–45.
Janick PK. Binding of human alpha-interferon in the brain tissue membranes of rat. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1992;75:117–20.
Khan NUD, Pulford KAF, Farquharson MA, Howatson A, Stewart C, Jackson R, et al. The distribution of immunoreactive interferon-alpha in normal human tissues. Immunology 1989;66:201–6.
Gisslinger H, Svoboda T, Clodi M, Gilly B, Ludwig H, Havelec L, et al. Interferon-alpha stimulates the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in vivo and in vitro. Neuroendocrinology 1993;57:489–95.
Raber J, Koob GF, Bloom FE. Interferon-alpha and transforming growth factor-beta 1 regulate corticotropin-releasing factor release from the amygdala: comparison with the hypothalamic response. Neurochem Int. 1997;30:455–63.
Felger JC, Alagbe O, Hu F, Mook D, Freeman AA, Sanchez MM, et al. Effects of interferon-alpha on rhesus monkeys: a nonhuman primate model of cytokine-induced depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;62:1324–33.
Dafny N, Yang PB. Interferon and central nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005;523:1–15.
Corssmit EP, Heijligenberg R, Endert E, Ackermans MT, Saverwein HP, Romijn JA. Endocrine and metabolic effects of interferon-alpha in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:3265–9.
Goebel MU, Baase J, Pithan V, Exton M, Saller B, Schedlowski M, et al. Acute interferon b-1b administration alters hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis activity, plasma cytokines and leukocyte distribution in healthy subjects. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2002;27:881–92.
Ohno Y, Fujimoto M, Nishimura A, Aoki N. Change of peripheral levels of pituitary hormones and cytokines after injection of interferon (IFN)-b in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:3681–7.
Barbarino A, Colasanti S, Corsello SM, Satta M, Della Casa S, Rota CA, et al. Dexamethasone inhibition of interferon-alpha 2-induced stimulation of cortisol and growth hormone secretion in chronic myeloproliferative syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995;80:1329–32.
Asnis GM, De La Garza R II. Interferon-induced depression in chronic hepatitis C: a review of its prevalence, risk factors, biology, and treatment approaches. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40:322–35.
Taylor JL, Grossberg SE. The effects of interferon-alpha on the production and action of other cytokines. Semin Oncol. 1998;25(Suppl 1):23–9.
Shimizu H, Ohtani K, Sato N, Nagamine T, Mori M. Increase in serum interleukin-6, plasma ACTH and serum cortisol levels after systemic interferon-alpha administration. Endocr J. 1995;42:551–6.
Wichers MC, Kenis G, Koek GH, Robaeys G, Nicolson NA, Maes M. Interferon-a-induced depressive symptoms are related to changes in the cytokine network but not to cortisol. J Psychosom Res. 2007;62:207–14.
John CD, Buckingham JC. Cytokines: regulation of the hypothalamopituitary–adrenocortical axis. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003;3:78–84.
Turnbull AV, Rivier CL. Regulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary adrenal axis by cytokines: actions and mechanisms of action. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:1–71.
Ericsson A, Kovacs KJ, Sawchenko PE. A functional anatomical analysis of central pathways subserving the effects of interleukin-1 on stress-related neuroendocrine neurons. J Neurosci. 1994;14:897–913.
Buller KM, Xu Y, Day TA. Indomethacin attenuates oxytocin and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis responses to systemic interleukin-1b. J Neuroendocrinol. 1998;10:519–28.
Lacroix S, Rivest S. Functional circuitry in the brain of immune-challenged rats: partial involvement of prostaglandins. J Comp Neurol. 1997;387:307–24.
Bergh FT, Kümpfel T, Yassouridis A, Lechner C, Holsboer F, Trenkwalder C. Acute and chronic neuroendocrine effects of interferon-b1a in multiple sclerosis. Clin Endocrinol. 2007;66:295–303.
Capuron L, Raison CL, Musselman DL, Lawson DH, Nemeroff CB, Miller AH. Association of exaggerated HPA axis response to the initial injection of interferon-alpha with development of depression during interferon-alpha therapy. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:1342–5.
Romanowski W, Braczkowski R, Kosiewicz J, Korzonek I, Nowakowska-Zajdel E, Muc-Wierzgon M, et al. Changes in growth hormone (GH) messenger RNA (GH mRNA) expression in the rat anterior pituitary after single interferon (IFN) alfa administration. Endokrynol Pol. 2006;57:482–6.
Plockinger U, Kruger D, Bergk A, Weich V, Wiedenmann B, Berg T. Hepatitis-C patients have reduced growth hormone (GH) secretion which improves during long-term therapy with pegylated interferon-a. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:2724–31.
Stjernholm MR, Alsever RN, Beck P. Growth hormone release after synthetic 1-24 ACTH: effects of estrogen and sex. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975;40:516–8.
Casanueva FF, Burguera B, Tome MA, Lima L, Tresguerres JA, Devesa J, et al. Depending on the time of administration, dexamethasone potentiates or blocks growth hormone-releasing hormone-induced growth hormone release in man. Neuroendocrinology 1988;47:46–9.
Muller H, Hiemke C, Hammes E, Hess G. Sub-acute effects of interferon-alpha 2 on adrenocorticotrophic hormone, cortisol, growth hormone and prolactin in humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1992;17:459–65.
Baudin E, Marcellin P, Pouteau M, Colas-Linhart N, Le Floch JP, Lemmonier C, et al. Reversibility of thyroid dysfunction induced by recombinant alpha interferon in chronic hepatitis C. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1993;39:657–61.
Mazziotti G, Sorvillo F, Stornaiuolo G, Rotondi M, Morisco F, Ruberto M, et al. Temporal relationship between the appearance of thyroid autoantibodies and development of destructive thyroiditis in patients undergoing treatment with two different type-1 interferons for HCV-related chronic hepatitis: a prospective study. J Endocrinol Invest. 2002;25:624–30.
Lisker-Melman M, Di Bisceglie AM, Usala SJ, Weintraub B, Murray LM, Hoofnagle H. Development of thyroid disease during therapy of chronic viral hepatitis with interferon alfa. Gastroenterology 1992;102:2155–60.
Carella C, Mazziotti G, Amato G, Braverman LE, Roti E. Interferon-a-related thyroid disease: pathophysiological, epidemiological, and clinical aspects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:3656–61.
Caraccio N, Dardano A, Manfredonia F, Manca L, Pasquali L, Iudice A, et al. Long-term follow-up of 106 multiple sclerosis patients undergoing interferon-beta 1a and 1b therapy: predictive factors of thyroid disease development and duration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:4133–7.
Tebben PJ, Atkinson JL, Scheithauer BW, Erickson D. Granulomatous adenohypophysitis after interferon and ribavirin therapy. Endocr Pract. 2007;13(2):169–75.
Ridruejo E, Chritiensen AF, Mando OG. Central hypothyroidism and hypophysitis during treatment of chronic hepatitis C with pegylated interferon alpha and ribavirin. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepat. 2006;18:693–4.
Barros CM, Betts JG, Thatcher WW, Hansen PJ. Possible mechanisms for reduction of circulating concentrations of progesterone by interferon-a in cows: effects on hyperthermia, luteal cells, metabolism of progesterone and secretion of LH. J Endocrinol. 1992;133:175–82.
Corssmit EPM, Endert E, Sauerwein HP, Romijn JA. Acute effects of interferon-a administration on testosterone concentrations in healthy men. Eur J Endocrinol. 2000;143:371–4.
Orava M, Cantell K, Vihko R. Treatment with preparations of human leukocyte interferon decreases serum testosterone concentrations in men. Int J Cancer. 1986;38:295–6.
Piazza M, Tosone G, Borgia G, Orlando R, Fenzi G, Vitale M, et al. Long-term interferon-alpha therapy does not affect sex hormones in males with chronic hepatitis C. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1997;17:525–9.
Barreca T, Picciotto A, Franceschini R, Varagona G, Garibaldi A, Valle F, et al. Sex hormones and sex-hormone binding globulin in males with chronic viral hepatitis during recombinant interferon-alpha 2b therapy. J Interferon Res. 1993;13:209–11.
Yamaguchi M, Koike K, Matsuzaki N, Yoshimoto Y, Taniguchi T, Miyake A, et al. The interferon family stimulates the secretions of prolactin and interleukin-6 by the pituitary gland in vitro. J Endocrinol Invest. 1991;14:457–61.
Bohnet SC, Traynor TR, Majde JA, Kacsoh B, Krueger JM. Mice deficient in the interferon type I receptor have reduced REM sleep and altered hypothalamic hypocretin, prolactin and 2', 5'-oligoadenylate synthetase expression. Brain Res. 2004;1027:117–25.
Kumai TTT, Tanaka M, Watanabe M, Shimizu H, Kobayashi S. Effect of interferon-alpha on tyrosine hydorxylase and catecholamine levels in the brain of rats. Life Sci. 2000;67:663–9.
Gillam MP, Molitch ME, Lombardi G, Colao A. Advances in the treatment of prolactinomas. Endocr Rev. 2006;27:485–534.
Colao A, Pivonello R, Cappabianca P, Vitale G, Lombardi G. The treatment algorithm of acromegaly. J Endocrinol Invest. 2003;26(8 Suppl):39–45.
Colao A, Arnaldi G, Beck-Peccoz P, Cannavò S, Cozzi R, degli Uberti E, et al. Pegvisomant in acromegaly: why, when, how. J Endocrinol Invest. 2007;30:693–9.
Melmed S. Medical progress. Acromegaly. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2558–73.
Murray RD, Melmed S. A critical analysis of clinically available somatostatin analog formulations for therapy of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008, (in press).
Jaffe CA. Clinically non-functioning pituitary adenoma. Pituitary 2006;9:317–21.
Labeur M, Theoodoropoulou M, Sievers C, Paez-Pereda M, Castillo V, Aret E, et al. New aspects in the diagnosis and treatment of Cushing disease. Front Horm Res. 2006;35:169–78.
Morris D, Gorssman A. The medical management of Cushing's syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;970:119–33.
Katahira M, Iwasaki Y, Aoki Y, Oiso Y, Saito H. Cytokine regulation of the rat proopiomelanocortin gene expression in AtT-20 cells. Endocrinology 1998;139:2414–22.
Zennaro R, Petracca EG, Paolini R, Ramazzina E. Normalization of the prolactin values during alfa-interferon therapy: the considerations with a female patient with anti-HCV-positive chronic hepatitis and prolactin-secreting hypophyseal microadenoma. Clin Ter. 1996;147:169–71.
Hofland LJ, de Herder WW, Zuijderwijk J, Uitterlinden P, van Koetsveld PM, Lamberts SW. Interferon-alpha-2a is a potent inhibitor of hormone secretion by cultured human pituitary adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84:3336–43.
Vitale G, van Eijck CH, van Koetsveld PM, Erdmann JJ, Speel EJ, van der Wansem K, et al. Type I interferons in the treatment of pancreatic cancer: mechanisms of action and role of related receptors. Ann Surg. 2007;246:259–68.
Vitale G, de Herder WW, van Koetsveld PM, Waaijers M, Schoordijk W, Croze E, et al. Interferon-beta is a highly potent inhibitor of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor cell growth in vitro. Cancer Res. 2006;66:554–62.
van Koetsveld PM, Vitale G, de Herder WW, Feelders RA, van der Wansem K, Waaijers M, et al. Potent inhibitory effects of type i interferons on human adrenocortical carcinoma cell growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:4537–43.
Johns TG, Mackay IR, Callister KA, Hertzog PJ, Devenish RJ, Linnane AW. Antiproliferative potencies of interferons on melanoma cell lines and xenografts: higher efficacy of interferon beta. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992;84:1185–90.
Buchwalder PA, Buclin T, Trinchard I, Munafo A, Biollaz J. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of IFN-beta 1a in healthy volunteers. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2000;20:857–66.
Mager DE, Neuteboom B, Jusko WJ. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of PEGylated IFN-beta 1a following subcutaneous administration in monkeys. Pharm Res. 2005;22:58–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vitale, G., Caraglia, M., van Koetsveld, P.M. et al. Potential role of type I interferons in the treatment of pituitary adenomas. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 10, 125–133 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-008-9083-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-008-9083-3