Abstract
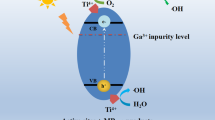
The properties of ZnO nanoparticles doped with titanium ions (Ti4+) and gallium ions (Ga3+) were modified by sol–gel method. Considering the ion radius of doped metal elements, the radius of Zn ions and the doping limit of ZnO, the doping rate of Ti is fixed at 1 atom%, and the optimal doping amount of Ga is discussed. The Ga/Ti co-doped ZnO nanoparticles were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), ultraviolet/visible spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and infrared spectroscopy. XRD results show that Ga/Ti co-doped ZnO has hexagonal wurtzite phase structure. With the increase of Ga doping concentration, the particle size of ZnO decreases. Through photoluminescence analysis, it is found that the absorption of Ga/Ti co-doped ZnO in the visible region moves to the long wave direction. In addition, with the increase of Ga doping, the particle size of GTZ powder first decreases and then increases, the band gap also decreases and then increases. When the doping amount of Ga is 1.5 atom%, the photocatalytic activity is the best. The degradation rate of MB was 90% within 2.5 h. Ga/Ti co-doped ZnO nanoparticles have good photocatalytic properties and low cost. They are a promising catalyst for wastewater treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu X, Yan L, Yin W, Zhou L, Zhao Y (2014) A magnetic graphene hybrid functionalized with beta-cyclodextrins for fast and efficient removal of organic dyes. J Mater Chem A 2(31):12296–12303
Lei C, Meng P, Jiang C, Bei C, Yu J (2017) Synthesis of hierarchical porous zinc oxide (zno) microspheres with highly efficient adsorption of congo red. J Colloid Interface Sci 490:242–251
Zhu YG, Johnson TA, Su JQ, Qiao M, Guo GX, Stedtfeld RD, Hashsham SA, Tiedje JM (2013) Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes in Chinese swine farms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:3435–3440
Hao R, Xiao X, Zuo X, Nan J, Zhang W (2012) Efficient adsorption and visible-light photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride using mesoporous BiOI microspheres. J Hazard Mater 209–210:137–145
Le-Minh N, Khan SJ, Drewes JE, Stuetz RM (2010) Fate of antibiotics during municipal water recycling treatment processes. Water Res 44:4295–4323
Chen H, Wang XX, Li J, Wang XK (2015) cotton derived carbonaceous aerogels for the efficient removal of organic pollutants and heavy metal ions. J Mater Chem A 3:6073–6081
Gao P, Mao D, Luo Y, Wang L, Xu B, Xu L (2012) Occurrence of sulfonamide and tetracycline-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in aquaculture environment. Water Res 46:2355–2364
He D, Sun Y, Xin L, Feng J (2014) Aqueous tetracycline degradation by non-thermal plasma combined with nano-TiO2. Chem Eng J 258:18–25
Chen R, Wang W, Zhao X, Zhang Y, Wu S, Li F (2014) Rapid hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic coxNi1-xFe2O4 nanoparticles and their application on removal of congo red. Chem Eng J 242:226–233
Alila S, Boufi S (2009) Removal of organic pollutants from water by modified cellulose fibres. Ind Crops Prod 30:93–104
Sun H, Cao L, Lu L (2011) Magnetite/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites: one step solvothermal synthesis and use as a novel platform for removal of dye pollutants. Nano Res 4:550–562
Zhao G, Ren X, Gao X, Tan X, Li J, Chen C, Huang Y, Wang X (2011) Removal of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions on few layered graphene oxide nanosheets. Dalton Trans 40:10945–10952
Yang ST, Chen S, Chang Y, Cao A, Liu Y, Wang H (2011) Removal of methylene Blue from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. J colloid Interface Sci 359:24–29
Huang ZH, Zheng X, Lv W, Wang M, Yang QH, Kang F (2011) Adsorption of lead(II) ions from aqueous solution on LowTemperature exfoliated graphene nanosheets. Langmuir 27:7558–7562
Wang J, Jiang Z, Zhang L, Kang P, Xie Y, Lv Y, Xu R, Zhang X (2009) Sonocatalytic degradation of some dyestuffs and comparison of catalytic activities of nanosized TiO2, nano-sized ZnO and composite TiO2/ZnO powders under ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason Sonochem 16:225–231
Hao Y, Deng S, Wang R et al (2022) Development of dual-enhancer biocatalyst with photothermal property for the degradation of cephalosporin. J Hazardous Mater 429:128294
Li ZJ, Zhang FH, Meng AL, Xie CC, Xing J (2015) ZnO/Ag micro/nanospheres with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial properties synthesized by a novel continuous synthesis method. RSC Adv 5:612–620
Meng AL, Shao J, Fan XY, Wang JH, Li ZJ (2014) Rapid synthesis of a flower-like ZnO/rGO/Ag micro/nano-composite with enhanced photocatalytic performance by a one-step microwave method. RSC Adv 4:60300–60305
Shi BY, Li GH, Wang DS, Feng CH, Tang HX (2007) Removal of direct dyes by coagulation: the performance of preformed polymeric aluminum species. J Hazard Mater 143:567–574
Xu YY, Zhou M, Geng HJ, Hao JJ, Ou QQ, Qi SD, Chen HL, Chen XG (2012) A simplified method for synthesis of Fe3O4@PAA nanoparticles and its application for the removal of basic dyes. Appl Surf Sci 258:3897–3902
Gupta VK, Agarwal S, Saleh TA (2011) Synthesis and characterization of aluminacoated carbon nanotubes and their application for lead removal. J Hazard Mater 185:17–23
Gupta VK, Saleh TA (2013) Sorption of pollutants by porous carbon, carbon nanotubes and fullerene–an overview. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2828–2843
Chang X, Li Z, Zhai X et al (2016) Efficient synthesis of sunlight-driven ZnO-based heterogeneous photocatalysts. Mater Des 98(15):324–332
Rokhsat E, Akhavan O et al (2016) Improving the photocatalytic activity of graphene oxide/ZnO nanorod films by UV irradiation. Appl Surf Sci 371:590–595
Doost HA, Ara MM, Koushki E (2016) Synthesis and complete mie analysis of different sizes of TiO2 nanoparticles. Optik 127:1946–1951
Seyedi M, Haratian S, Vahdati Khaki J (2015) Mechanochemical synthesis of Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Procedia Mater Sci 11:309–313
Sedlák J, Kuřitka I, Machovský M, Šuly P, Bažant P, Sedláček T (2015) Zinc oxide nanoparticles with surface modified by degradation of capping polymers in situ during microwave synthesis. Adv Powder Technol 26(4):1064–1071
Sedlák J (2015) Zinc oxide nanoparticles with surface modified by degradation of capping polymers in situ during microwave synthesis. Adv Powder Technol 26:1064–1071
Yan H, Tian X, Ma F, Sun J (2015) CuO nanoparticles fabricated by direct thermo-oxidation of sputtered Cu film for VOCs detection. Sens Actuators B 221:599–605
Wang X, Zhang Y, Hao C et al (2014) Solid-phase synthesis of mesoporous ZnO using lignin-amine template and its photocatalytic properties. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(16):6585–6592
Bijanzad K, Tadjarodi A, Akhavan O (2015) Photocatalytic activity of mesoporous microbricks of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by the thermal decomposition of bis(2-aminonicotinato) zinc (II). Chin J Catal 36(005):742–749
Wang Y, Zhu S, Chen X, Tang Y, Jiang Y, Peng Z, Wang H (2014) One-step template-free fabrication of mesoporous ZnO/TiO2 hollow microspheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 307:263–271
Nirmala M, Anukaliani A (2011) Synthesis and characterization of undoped and TM (co, Mn) doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater Lett 65:2645–2648
Rasouli S, Moeen SJ (2011) combustion synthesis of co-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles using mixture of citric acid–glycine fuels. J Alloys Compds 509:1915–1919
Thongsuriwong K, Amornpitoksik P, Suwanboon S (2013) Structure, morphology photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of ZnO thin film prepared by sol–gel dip-coating method. Adv Powder Technol 204:2557–3280
Glasgow A, Glasgow J, Limonta D et al (2020) Engineered ACE2 receptor traps potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci 117(45):28046–28055
Päivänranta B, Pudas M, Pitkänen O, Leinonen K, Kuittinen M, Baroni P-Y, Scharf T, Herzig H-P (2009) Liquid phase deposition of polymers on arbitrary shaped surfaces and their suitability for e-beam patterning. Nanotechnology 20(22):225305
Ekambaram S, Iikubo Y, Kudo A (2007) combustion synthesis and photocatalytic properties of transition metal-incorporated ZnO. J Alloys Compds 433:237–240
Lu JF, Zhang QW (2006) Synthesis of N-doped ZnO by grinding and subsequent heating ZnO-urea mixture. Powder Technol 162:33–37
Sepehr MN, Sivasankar V, Zarrabi M, Kumar MS (2013) Surface modification of pumice enhancing its fluoride adsorption capacity: an insight into kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 228:192–204
Akhavan O, Azimirad R, Safa S (2011) Functionalized carbon nanotubes in ZnO thin films for photoinactivation of bacteria. Mater Chem Phys 130(1–2):598–602
Suresh M, Sivasamy A (2020) Fabrication of graphene nanosheets decorated by nitrogen-doped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced visible photocatalytic activity for the degradation of Methylene Blue dye. J Mol Liq 317:114112
Zou CW, Rao YF, Alyamani A et al (2010) Heterogeneous Lollipop-like V2O5/ZnO Array: A Promising Composite Nanostructure for Visible Light Photocatalysis. Langmuir 26(14):11615–11620
Zirak M, Akhavan O, Moradlou O et al (2014) Vertically aligned ZnO@CdS nanorod heterostructures for visible light photoinactivation of bacteria. J Alloy Compds 590:507–513
Ahmed G, Hanif M, Zhao L et al (2016) Defect engineering of ZnO nanoparticles by graphene oxide leading to enhanced visible light photocatalysis. J Mol Catal A 15:310–321
Chiu HM, Wu JM et al (2013) Opto-electrical properties and chemisorption reactivity of Ga-doped ZnO nanopagodas. J Mater Chem A 1(18):5524–5534
Akhavan O (2010) Graphene nanomesh by ZnO nanorod photocatalysts. ACS Nano 4(7):4174–4180
Yang S, Ge C, Liu Z, Fang Y, Li Z, Kuang D et al (2011) Novel ga-doped, self-supported, independent aligned zno nanorods: one-pot hydrothermal synthesis and structurally enhanced photocatalytic performance. RSC Adv 1(9):1691–1694
Park GC, Hwang SM, Lim JH et al (2014) Growth behavior and electrical performance of Ga-doped ZnO nanorod/p-Si heterojunction diodes prepared using a hydrothermal method. Nanoscale 6:18
Thambidurai M, Kim JY, Kang CM et al (2014) Enhanced photovoltaic performance of inverted organic solar cells with In-doped ZnO as an electron extraction layer. Renewable Energy 66(6):433–442
Ra A, Ssk B, Sv B et al (2021) Enhanced optoelectronic properties of Ti-doped ZnO nanorods for photodetector applications. Ceram Int 47(17):24031–24038
Thongsuriwonga K, Amornpitoksuk P, Suwanboon S (2013) Structure, morphology, photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel dip-coating method. Adv Powder Technol 24:275–280
Risbud AS, Spaldin NA, Chen ZQ, Stemmer S, Seshadri R (2003) Magnetism in polycrystalline cobalt-substituted zinc oxide. Phys Rev B 68:205202-1-205202–7
Chen Y, Bagnall DM, Koh HJ, Park KT, Hiraga K, Zhu Z, Yao T (1998) Plasma assisted molecular beam epitaxy of ZnO on c-plane sapphire: growth and characterization. J Appl Phys 84:3912–3918
Fierro JLG, Arrua LA, Lopez Nieto JM, Kremenic G (1988) Surface properties of coprecipitated Vsingle bond Ti single bond O catalysts and their relation to the selective oxidation of isobutene. Appl Catal 37:323–338
Biesinger MC, Lau L, Gerson AR et al (2012) (2012) The role of the Auger parameter in XPS studies of nickel metal, halides and oxides. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:15
Mazaheri H, Ghaedi M, Azqhandi MHA, Asfaram A (2017) Application of machine/statistical learning, artificial intelligence and statistical experimental design for the modeling and optimization of methylene blue and Cd(II) removal from a binary aqueous solution by natural walnut carbon. Phys Chem 19:11299–11317
Asfaram A, Ghaedi M, Goudarzi A, Rajabi M (2015) Response surface methodology approach for optimization of simultaneous dye and metal ion ultrasound-assisted adsorption onto Mn doped Fe3O4-NPs loaded on AC: kinetic and isothermal studies. Dalton Trans 44:14707–14723
Gao Y, Li Y, Zhang L, Huang H, Hu J, Shah SM, Su X (2012) Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 368:540–546
Asfaram A, Ghaedi M et al (2017) Ultrasound-assisted binary adsorption of dyes onto Mn@ CuS/ZnS-NC-AC as a novel adsorbent: application of chemometrics for optimization and modeling. J Ind Eng Chem 54:377–388
Ungula J, Dejene BF, Swart HC (2018) Band gap engineering, enhanced morphology and photoluminescence of un-doped, Ga and/or Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles by reflux precipitation method. J Lumin 195:54–60
Yatskiv R, Grym J (2016) Luminescence properties of hydrothermally grown ZnO nanorods. Superlattices Microstruct 99:214–220
Ahmed AS, Singla ML, Tabassum S, Naqvi AH, Azam A (2011) Band gap narrowing and fluorescence properties of nickel doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J Lumin 131(1):1–6
Qiao XQ et al (2018) In situ synthesis of n–n Bi2MoO6 & Bi2S3 heterojunctions for highly efficient photocatalytic removal of Cr (vi). J Mater Chem A 6:22580–22589
Lente G (2018) Facts and alternative facts in chemical kinetics: remarks about the kinetic use of activities, termolecular processes, and linearization techniques. Curr Opin Chem Eng 21:76–83
Mahdavi R et al (2017) Sol-gel synthesis, structural and enhanced photocatalytic performance of Al doped ZnO nanoparticles. Adv Powder Technol 28:1418–1425
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61604087) and the Chinese Ministry of Education (111 Project D20015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Q., Sun, Y., Guo, J. et al. Enhancement of ZnO catalytic activity under visible light by co-doping with Ga and Ti for efficient decomposition of methylene blue. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 135, 2231–2246 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02239-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02239-1