Abstract
Purpose
To assess the predictive validity of the 15 components of the Tilburg Frailty Indicator (TFI), a self-report questionnaire, for quality of life domains physical health, psychological, social relations and environmental in community-dwelling older persons in a longitudinal study.
Methods
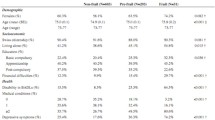
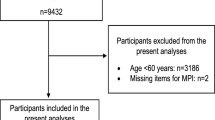
The predictive validity of the components of the TFI was tested in a sample of 484 community-dwelling persons aged 75 years and older in the Netherlands in 2008 (response rate 42 %). A subset of all respondents participated two years later, in 2010 (n = 261, 54 %), and a subset of these respondents participated again in 2012 (n = 196, 75 %). The WHOQOL-BREF was used for measuring four quality of life domains.
Results
Four physical frailty components (physical unhealthy, difficulty in maintaining balance, difficulty in walking and physical tiredness), one psychological frailty component (feeling down) and one social frailty component (lack of social support) predicted future scores on quality of life domains, even after controlling for background characteristics and diseases.
Conclusion
This longitudinal study showed that quality of life is predicted by physical as well as psychological and social frailty components. This finding emphasizes the relevance of a multidimensional assessment of frailty. To improve quality of life of older persons, special attention should go to the screening and subsequent interventions focusing on the frailty components difficulty in walking, feeling down and lack of social support.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abellan Van Kan, G., Rolland, Y., Bergman, H., et al. (2008). The I.A.N.A Task Force on frailty assessment of older people in clinical practice. The Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging, 12 (1), 29–37.
Fried, L. P., Tangen, C. M., Walston, J., et al. (2001). Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. Journal of Gerontology: Medical Sciences, 56(3), M146–M156.
Markle-Reid, M., & Browne, G. (2003). Conceptualizations of frailty in relation to older adults. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 44(1), 58–68.
Gobbens, R. J., Luijkx, K. G., Wijnen-Sponselee, M. T., & Schols, J. M. (2010). In search of an integral conceptual definition of frailty: Opinions of experts. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 11(5), 338–343.
Hogan, D. B., MacKnight, C., & Bergman, H. (2003). Models, definitions, and criteria of frailty. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research, 15(3 Suppl), 1–29.
Levers, M. J., Estabrooks, C. A., & Ross Kerr, J. C. (2006). Factors contributing to frailty: Literature review. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 56(3), 282–291.
De Witte, N., Gobbens, R., de Donder, L., et al. (2013). The comprehensive frailty assessment instrument: Development, validity and reliability. Geriatric Nursing, 34(4), 274–281.
Gobbens, R. J., Luijkx, K. G., Wijnen-Sponselee, M. T., & Schols, J. M. (2007). Frail elderly. Identification of a population at risk. Tijdschrift Gerontologie en Geriatrie, 38(2), 65–76.
Gobbens, R. J., Luijkx, K. G., Wijnen-Sponselee, M. T., & Schols, J. M. (2010). Toward a conceptual definition of frail community dwelling older people. Nursing Outlook, 58(2), 76–86.
Gobbens, R. J., Luijkx, K. G., Wijnen-Sponselee, M. T., & Schols, J. M. (2010). Towards an integral conceptual model of frailty. The Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging, 14(3), 175–181.
Gobbens, R. J., van Assen, M. A., Luijkx, K. G., & Schols, J. M. (2012). Testing an integral conceptual model of frailty. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 68(9), 2047–2060.
Gobbens, R. J., van Assen, M. A., Luijkx, K. G., Wijnen-Sponselee, M. T., & Schols, J. M. (2010). The Tilburg Frailty Indicator: Psychometric properties. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 11(5), 344–355.
Van Campen, C. (2011). Frail older persons in the Netherlands. The Hague: The Netherlands Institute for Social Research.
Boyd, C. M., Xue, Q. L., Simpson, C. F., Guralnik, J. M., & Fried, L. P. (2005). Frailty, hospitalization, and progression of disability in a cohort of disabled older women. The American Journal of Medicine, 118(11), 1225–1231.
Puts, M. T., Lips, P., & Deeg, D. J. (2005). Static and dynamic measures of frailty predicted decline in performance-based and self-reported physical functioning. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 58(11), 1188–1198.
Rockwood, K., Song, X., MacKnight, C., et al. (2005). A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 173(5), 489–495.
Jones, D. M., Song, X., & Rockwood, K. (2004). Operationalizing a frailty index from a standardized comprehensive geriatric assessment. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 52(11), 1929–1933.
Lin, C. C., Li, C. I., Chang, C. K., et al. (2011). Reduced health-related quality of life in elders with frailty: A cross-sectional study of community-dwelling elders in Taiwan. PLoS ONE,. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021841.
Bilotta, C., Bowling, A., Case, A., et al. (2010). Dimensions and correlates of quality of life according to frailty status: A cross-sectional study on community-dwelling older adults referred to an outpatient geriatric service in Italy. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes,. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-8-56.
Masel, M. C., Ostir, G. V., & Ottenbacher, K. J. (2010). Frailty, mortality, and health-related quality of life in older Mexican Americans. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 58(11), 2149–2153.
WHOQOL group. (1995). World Health Organization Quality of Life assessment (WHOQOL): Position paper from the World Health Organization. Social Science and Medicine, 41(10), 1403–1409.
WHOQOL Group. (1998). Development of the World Health Organization WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment. Psychological Medicine, 28(3), 551–558.
Paskulin, L. M., & Molzahn, A. (2007). Quality of life of older adults in Canada and Brazil. Western Journal of Nursing Research, 29(1), 10–26. discussion 7–35.
Bilotta, C., Bowling, A., Nicolini, P., et al. (2011). Older People’s Quality of Life (OPQOL) scores and adverse health outcomes at a one-year follow-up. A prospective cohort study on older outpatients living in the community in Italy. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-9-72.
Gobbens, R. J., Luijkx, K. G., & van Assen, M. A. (2013). Explaining quality of life of older people in the Netherlands using a multidimensional assessment of frailty. Quality of Life Research, 22(8), 2051–2061.
Gobbens, R. J., van Assen, M. A., Luijkx, K. G., & Schols, J. M. (2012). The predictive validity of the Tilburg frailty indicator: Disability, health care utilization, and quality of life in a population at risk. The Gerontologist, 52(5), 619–631.
Gobbens, R. J., van Assen, M. A., Luijkx, K. G., Wijnen-Sponselee, M. T., & Schols, J. M. (2010). Determinants of frailty. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 11(5), 356–364.
Central Committee on Research inv. Human Subjects. (2010). Does your study have to be reviewed? http://www.ccmo-online.nl (Home>For investigators>Review step plan RC>WMO) Accessed 15 June 2010.
Santiago, L. M., Luz, L. L., Mattos, I. E., Gobbens, R. J., & van Assen, M. A. (2013). Psychometric properties of the Brazilian version of the Tilburg frailty indicator (TFI). Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, 57(1), 39–45.
Huisman, M., & Deeg, D. (2011). The course of frailty. In Van Campen C (Ed.), Frail older persons in the Netherlands (pp. 83–90). The Hague: The Netherlands Institute for Social Research.
Skevington, S. M., Lotfy, M., & O’Connell, K. A. (2004). The World Health Organization’s WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment: Psychometric properties and results of the international field trial. A report from the WHOQOL group. Quality of Life Research, 13(2), 299–310.
Heo, S., Moser, D. K., Lennie, T. A., Zambroski, C. H., & Chung, M. L. (2007). A comparison of health-related quality of life between older adults with heart failure and healthy older adults. Heart and Lung, 36(1), 16–24.
Hlatky, M. A., Chung, S. C., Escobedo, J., et al. (2010). The effect of obesity on quality of life in patients with diabetes and coronary artery disease. American Heart Journal, 159(2), 292–300.
DiBonaventura, M., Paulose-Ram, R., Su, J., et al. (2012). The impact of COPD on quality of life, productivity loss, and resource use among the elderly United States workforce. Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, 9(1), 46–57.
Puts, M. T., Lips, P., & Deeg, D. J. (2005). Sex differences in the risk of frailty for mortality independent of disability and chronic diseases. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 53(1), 40–47.
Kriegsman, D. M., Penninx, B. W., van Eijk, J. T., Boeke, A. J., & Deeg, D. J. (1996). Self- reports and general practitioner information on the presence of chronic diseases in community dwelling elderly. A study on the accuracy of patients’ self-reports and on determinants of inaccuracy. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 49(12), 1407–1417.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc Inc.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A.-G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavioral Research Methods, 39(2), 175–191.
Maxwell, S. E., & Delaney, H. D. (2004). Designing experiments and analyzing data: a model comparison perspective (2nd ed.). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc Inc.
Lee, T. W., Ko, I. S., & Lee, K. J. (2006). Health promotion behaviors and quality of life among community-dwelling elderly in Korea: A cross-sectional survey. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 43(3), 293–300.
Paskulin, L., Vianna, L., & Molzahn, A. E. (2009). Factors associated with quality of life of Brazilian older adults. International Nursing Review, 56(1), 109–115.
Lubetkin, E. I., Jia, H., Franks, P., & Gold, M. R. (2005). Relationship among sociodemographic factors, clinical conditions, and health-related quality of life: Examining the EQ-5D in the U.S. general population. Quality of Life Research, 14(10), 2187–2196.
Hilleras, P. K., Jorm, A. F., Herlitz, A., & Winblad, B. (2001). Life satisfaction among the very old: A survey on a cognitively intact sample aged 90 years or above. International Journal of Aging and Human Development, 52(1), 71–90.
Raphael, D., Brown, I., Renwick, R., et al. (1997). Measuring the quality of life of older persons: A model with implications for community and public health nursing. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 34(3), 231–239.
Rijken, M., van Kerkhof, M., Dekker, J., & Schellevis, F. G. (2005). Comorbidity of chronic diseases: Effects of disease pairs on physical and mental functioning. Quality of Life Research, 14(1), 45–55.
Fortin, M., Bravo, G., Hudon, C., et al. (2006). Relationship between multimorbidity and health-related quality of life of patients in primary care. Quality of Life Research, 15(1), 83–91.
Hopman, W. M., Harrison, M. B., Coo, H., et al. (2009). Associations between chronic disease, age and physical and mental health status. Chronic Diseases in Canada, 29(3), 108–116.
Chang, Y. W., Chen, W. L., Lin, F. G., et al. (2012). Frailty and its impact on health-related quality of life: A cross-sectional study on elder community-dwelling preventive health service users. PLoS ONE,. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0038079.
Abellan van Kan, G., Rolland, Y., Andrieu, S., et al. (2009). Gait speed at usual pace as a predictor of adverse outcomes in community-dwelling older people an International Academy on Nutrition and Aging (IANA) Task Force. The Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging, 13(10), 881–889.
Shinkai, S., Watanabe, S., Kumagai, S., et al. (2000). Walking speed as a good predictor for the onset of functional dependence in a Japanese rural community population. Age and Ageing, 29(5), 441–446.
Woo, J., Ho, S. C., & Yu, A. L. (1999). Walking speed and stride length predicts 36 months dependency, mortality, and institutionalization in Chinese aged 70 and older. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 47(10), 1257–1260.
Rolland, Y., Lauwers-Cances, V., Cesari, M., et al. (2006). Physical performance measures as predictors of mortality in a cohort of community-dwelling older French women. European Journal of Epidemiology, 21(2), 113–122.
Baernholdt, M., Hinton, I., Yan, G., Rose, K., & Mattos, M. (2012). Factors associated with quality of life in older adults in the United States. Quality of Life Research, 21(3), 527–534.
Bilotta, C., Bowling, A., Nicolini, P., Case, A., & Vergani, C. (2012). Quality of life in older outpatients living alone in the community in Italy. Health and Social Care in the Community, 20(1), 32–41.
Bowling, A., Seetai, S., Morris, R., & Ebrahim, S. (2007). Quality of life among older people with poor functioning. The influence of perceived control over life. Age and Ageing, 36(3), 310–315.
Gabriel, Z., & Bowling, A. (2004). Quality of life from the perspectives of older people. Ageing & Society, 24(5), 675–691.
Puts, M. T., Shekary, N., Widdershoven, G., et al. (2007). What does quality of life mean to older frail and non-frail community-dwelling adults in the Netherlands? Quality of Life Research, 16(2), 263–277.
Metzelthin, S. F., Daniels, R., van Rossum, E., et al. (2010). The psychometric properties of three self-report screening instruments for identifying frail older people in the community. BMC Public Health,. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-10-176.
Verkleij, S. P., Adriaanse, M. C., Verschuren, W. M., et al. (2011). Five-year effect of community-based intervention Hartslag Limburg on quality of life: A longitudinal cohort study. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes,. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-9-11.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gobbens, R.J.J., van Assen, M.A.L.M. The prediction of quality of life by physical, psychological and social components of frailty in community-dwelling older people. Qual Life Res 23, 2289–2300 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-014-0672-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-014-0672-1