Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to analyze and compare the quality of life of renal replacement therapy patients undergoing hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis and those with renal transplantation in Brazil. In addition, we aimed to verify factors associated with patients’ quality of life and the relationship between quality of life and treatment modality, socioeconomic and demographic conditions as well as aspects related to the disease and health services.
Methods
A representative sample of the dialysis units and transplant centers was obtained. Structured questionnaires were used to interview 3,036 patients in one of three treatment modalities: hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis and renal transplant. Information was collected about socioeconomic and demographic characteristics and quality of life measures.
Results
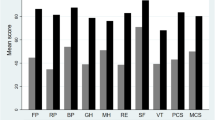
There were significant differences between renal transplants and both forms of dialysis for all dimensions of the SF-36. Hemodialysis patients showed better results in the dimensions of functional capacity, physical aspects and social aspects, compared to peritoneal dialysis patients. Renal transplant patients had the best mean score in the physical component of quality of life. There were no significant differences among treatment groups regarding the mental component of quality of life. The physical and mental components were associated with comorbidities and age; however, older patients had better mental quality of life but worse physical quality of life. Patients in a higher socioeconomic class and patients that were not hospitalized also reported better quality of life. Unmarried and male patients presented better physical quality of life. The dialysis units and transplant centers influenced the patients’ quality of life.
Conclusions
Renal transplant patients have the best quality of life of the three treatment modalities. It is necessary to increase access to renal transplants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- QOL:
-
Quality of life
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- RRT:
-
Renal replacement therapies
- HD:
-
Hemodialysis
- PD:
-
Peritoneal dialysis
- RT:
-
Renal transplantation
- NHS:
-
National health system
- SF-36:
-
Medical outcome survey—short form 36
- IRT:
-
Item response theory
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
References
Griva, K., Jayasena, D., Davenport, A., et al. (2009). Illness and treatment cognitions and health related quality of life in end stage renal disease. British Journal of Health Psychology, 14(1), 17–34.
Morsch, C. M., Gonçalves, L. F., & Barros, E. (2006). Health-related quality of life among haemodialysis patients–relationship with clinical indicators, morbidity and mortality. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 15(4), 498–504.
Hayashino, Y., Fukuhara, S., Akiba, T., et al. (2009). Low health-related quality of life is associated with all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes on haemodialysis: The Japan Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Pattern Study. Diabetic Medicine, 26(9), 921–927.
Kuyken, W., Orley, J., Power, M., et al. (1995). The world health organization Quality of Life assessment (WHOQOL): Position paper from the world health organization. Social Science and Medicine, 41, 1403–1409.
Kimmel, P. L., & Patel, S. S. (2006). Quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease: Focus onend-stage renal disease treated with hemodialysis. Seminars in Nephrology, 26, 68.
Perovic, S., & Jankovic, S. (2009). Renal transplantation vs hemodialysis: Cost-effectiveness analysis. Vojnosanitetski Pregled, 66(8), 639–644.
White, S. L., Chadban, S. J., Jan, S., Chapman, J. R., & Cass, A. (2008). How can we achieve global equity in provision of renal replacement therapy? Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 86(3), 229–237.
Franke, G. H., Heemann, U., Kohnle, M., et al. (2000). Quality of life in patients before and after kidney transplantation. Psychology Health, 14, 1037–1049.
Wight, J. P., Edwards, L., Brazier, J., et al. (1998). The SF36 as an outcome measure of services for end stage renal failure. Quality Health Care, 7, 209–221.
Sesso, R., Neto, J. F. R., & Ferraz, M. B. (2003). Impact of socioeconomic status on the quality of life of ESRD patients. American Journal of Kidney Disease, 41(1), 186–195.
Bohlke, M., Nunes, D. L., Marini, S. S., et al. (2008). Predictors of quality of life among patients on dialysis in Southern Brazil. São Paulo Medical Journal, 126(5), 252–256.
Brazilian Society of Nephrology. (2008). Profile of chronic kidney disease. The Brazilian challenge. Available in: http://www.sbn.org.br/noticias/DossieFinal.pdf. Accessed June 13, 2008.
Sayin, A., Mutluay, R., & Sindel, S. (2007). Quality of life in hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis and transplantation patients. Transplantation Proceedings, 39, 3047–3053.
Fujisawa, M., Ichikawa, Y., Yoshiya, K., et al. (2000). Assesment of health-related quality of life in renal transplant and hemodialysis patients using the SF-36 health survey. Urology, 56, 201.
Noshad, H., Sadreddini, S., Nezami, N., et al. (2009). Comparison of outcome and quality of life: Haemodialysis versus peritoneal dialysis patients. Singapore Medical Journal, 50(2), 185–192.
Ware, J. E., Kosinski, M., Bjorner, J. B., et al. (2008). SF-36v2 ® health survey: A primer for healthcare providers. Lincoln, RI: QualityMetric Incorporated.
Ciconelli, R. M., Ferraz, M. B., Santos, W., et al. (1999). Translation into Portuguese and validation of the generic questionnaire for assessing quality of life SF-36 (Brazil SF-36). Brazilian Journal of Rheumatology, 39(3), 143–150.
Neto, J. R. F., Ferraz, M., Cendoroglo, S., et al. (2000). Quality of life at initiation of maintenance dialysis treatment—a comparison between the SF-36 and the KDQ questionnaires. Quality of Life Research, 9, 1001–1107.
Rizopoulos, D. (2006). ltm: An R package for latent variable modeling and item response theory analyses. Journal of Statistical Software, 17(5), 1–25.
Senna, E.R. (2002). Study of the prevalence of rheumatic disease in the city of Montes Claros. Master of sciences thesis, Federal University of São Paulo, Medicine School, Brazil.
Overbeck, I., Bartels, M., Decker, O., et al. (2005). Changes in quality of life after renal transplantation. Transplantation Proceedings, 37, 1618–1621.
Alavi, N. M., Aliakbarzadeh, Z., & Sharifi, K. (2009). Depression, anxiety, activities of daily living, and quality of life scores in patients undergoing renal replacement therapies. Transplantation Proceedings, 41(9), 3693–3696.
Zhang, A., Cheng, L., Zhu, N., et al. (2007). Comparison of quality of life and causes of hospitalization between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients in China. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 5(49), 2–6.
Wu, A. W., Fink, N. E., Marsh-Manzi, J. V. R., et al. (2004). Changes in quality of life during hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis treatment: Generic and disease specific measures. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 15, 743–753.
Andrade, M. V., Junoy, J. P., Andrade, E. I. G., Acurcio, F. A., Sesso, R., Queiroz, O. V., et al. (2010). Allocation of initial modality for renal replacement therapy in Brazil. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 5, 637–644.
Mittal, S. K., Ahern, L., Flaster, E., et al. (2001). Self-assessed physical and mental function of haemodialysis patients. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 16(7), 2152–2159.
Baiardi, F., Esposit, E. D., Cocechi, R., Fabri, A., Sturani, A., Valpiani, G., et al. (2002). Effects of clinical and individual variables on quality of life in chronic renal failure patients. Journal of Nephrology, 15(1), 61–67.
Mucsi, I., Kovacs, A. Z., Molnar, M. Z., & Novak, M. (2008). Co-morbidity and quality of life in chronic kidney disease patients. Journal of Nephrology, 21(suppl13), S84–S91.
Bossola, M., Giungi, S., Luciani, G., & Tazza, L. (2009). Body mass index, comorbid conditions and quality of life in hemodialysis patients. Journal of Nephrology, 22(4), 508–514.
Valderrábano, F., Jofre, R., & Lopez-Gomez, J. M. (2001). Quality of life in end-stage renal disease patients. American Journal of Kidney Disease, 38, 443–464.
Rosenberger, J., Dijk, J. P., Nagyova, I., et al. (2005). Do dialysis—and transplantation—related medical factors affect perceived health status? Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 20, 2153–2158.
Lopes, G. B., Martins, M. T. S., Matos, C. M., et al. (2007). Comparisons of measures of quality of life among women and men on hemodialysis. Brazilian Journal of Medical Association, 53(6), 506–509.
Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Kopple, J. D., Block, G., et al. (2001). Association among SF36 quality of life measures and nutrition, hospitalization, and mortality in hemodialysis. Journal of American Society of Nephrology, 12, 2797–2806.
Kutner, N. G., Zhang, R., & Brogan, D. (2005). Race, gender, an incident dialysis patients’ reported health status and quality of life. Journal of American Society of Nephrology, 16, 1440–1448.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Brazilian Health Ministry and the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Álvares, J., Cesar, C.C., de Assis Acurcio, F. et al. Quality of life of patients in renal replacement therapy in Brazil: comparison of treatment modalities. Qual Life Res 21, 983–991 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-011-0013-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-011-0013-6