Abstract
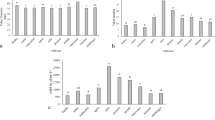
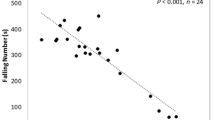
The radish (Raphanus sativus) is a root vegetable of the Brassicaceae family which shows amylolytic activity in the taproot. However, there is little information about differences in these amylolytic activities among radish cultivars. We analyzed the amylase activities and starch contents of 7 kinds of radish cultivars. The Koshin cultivar showed the highest amylase activity, with a level approximately 6 times higher than that of the Sobutori cultivar, which had the lowest. Cultivars with higher amylase activities showed higher starch contents. These results suggest that there are intraspecies variations in amylolytic activities in radishes, and positive correlations between amylase activity and starch content.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DNSA:
-
3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid
- IgG:
-
immunoglobulin G
- RsBAMY1:
-
Raphanus sativus β-amylase 1
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
References
Talalay P, Fahey JW (2001) Phytochemicals from cruciferous plants protect against cancer by modulating carcinogen metabolism. J Nutr 131:3027S–3033S
Khanum F, Siddalinga Swamy M, Sudarshana Krishna KR, Santhanam K, Viswanathan KR (2000) Dietary fiber content of commonly fresh and cooked vegetables consumed in India. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 55:207–218
Ben Salah-Abbès J, Abbès S, Houas Z, Abdel-Wahhab MA, Oueslati R (2008) Zearalenone induces immunotoxicity in mice: possible protective effects of radish extract (Raphanus sativus). J Pharm Pharmacol 60:761–770
Chaturvedi P (2008) Inhibitory response of Raphanus sativus on lipid peroxidation in albino rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 5:55–59
Barillari J, Cervellati R, Paolini M, Tatibouët A, Rollin P, Iori R (2005) Isolation of 4-methylthio-3-butenyl glucosinolate from Raphanus sativus sprouts (Kaiware Daikon) and its redox properties. J Agric Food Chem 53:9890–9896
Ippoushi K, Takeuchi A, Ito H, Horie H, Azuma K (2007) Antioxidative effects of daikon sprout (Raphanus sativus L.) and ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) in rats. Food Chem 102:237–242
Papi A, Orlandi M, Bartolini G, Barillari J, Iori R, Paolini M, Ferroni F, Grazia Fumo M, Pedulli GF, Valgimigli L (2008) Cytotoxic and antioxidant activity of 4-methylthio-3-butenyl isothiocyanate from Raphanus sativus L. (Kaiware Daikon) sprouts. J Agric Food Chem 56:875–883
Hanlon PR, Webber DM, Barnes DM (2007) Aqueous extract from Spanish black radish (Raphanus sativus L. Var. niger) induces detoxification enzymes in the HepG2 human hepatoma cell line. J Agric Food Chem 55:6439–6446
Suh SJ, Moon SK, Kim CH (2006) Raphanus sativus and its isothiocyanates inhibit vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and induce G1 cell cycle arrest. Int Immunopharmacol 6:854–861
Hara M, Sawada T, Ito A, Ito F, Kuboi T (2009) A major β-amylase expressed in radish taproots. Food Chem 114:523–528
Hara M, Oki K, Hoshino K, Kuboi T (2003) Enhancement of anthocyanin biosynthesis by sugar in radish (Raphanus sativus) hypocotyl. Plant Sci 164:259–265
Wang J, Zhang G, Chen J, Shen Q, Wu F (2003) Genotypic and environmental variation in barley beta-amylase activity and its relation to protein content. Food Chem 83:163–165
Saika H, Nakazono M, Ikeda A, Yamaguchi J, Masaki S, Kanekatsu M, Nemoto K (2005) A transposon-induced spontaneous mutation results in low β-amylase content in rice. Plant Sci 169:239–244
Adams CA, Broman TH, Rinne RW (1981) Starch metabolism in developing and germinating soya bean seeds is independent of ß-amylase activity. Ann Bot 48:433–440
Gana JA, Kalengamaliro NE, Cunningham SM, Volenec JJ (1998) Expression of beta-amylase from alfalfa taproots. Plant Physiol 118:1495–1506
Nakamura Y, Nakamura K, Asai Y, Wada T, Tanaka K, Matsuo T, Okamoto S, Meijer J, Kitamura Y, Nishikawa A, Park EY, Sato K, Ohtsuki K (2008) Comparison of the glucosinolate-myrosinase systems among daikon (Raphanus sativus, Japanese white radish) varieties. J Agric Food Chem 56:2702–2707
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hara, M., Ito, F., Asai, T. et al. Variation in Amylase Activities in Radish (Raphanus sativus) Cultivars. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 64, 188–192 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-009-0129-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-009-0129-9