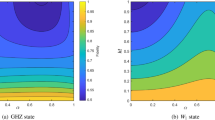
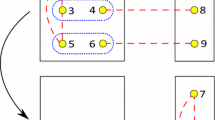
Abstract
In this paper we propose a tripartite teleportation protocol to teleport an unknown quantum state via noisy quantum channels with fidelity equal to one even with a non-maximally entangled state. In our protocol we utilize environment-assisted measurement during entanglement distribution and further modify the standard teleportation protocol to apply weak measurement reversal in the last step of teleportation. We design the weak measurement reversal operators to make the teleportation fidelity equal to one, independent of the magnitude of decoherence or the shared entangled state parameters. Since the teleportation fidelity is always equal to one, we can optimize the teleportation success probability without affecting the fidelity. Moreover, we give the detailed procedure of the standard tripartite teleportation protocol in the presence of amplitude damping and derive the final expression of the average standard teleportation fidelity.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability and materials
Not applicable. For all requests relating to the paper, please contact the first author.
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Shi, B.S., Tomita, A.: Teleportation of an unknown state by W state. Phys. Lett. Sect. A Gen. At. Solid State Phys. 296, 161–164 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-9601(02)00257-8
Bartlett, S.D., Munro, W.J.: Quantum teleportation of optical quantum gates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 117901 (2003)
Karlsson, A., Bourennane, M.: Quantum teleportation using three-particle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A. 58, 4394 (1998)
Zounia, M., Shamirzaie, M., Ashouri, A.: Quantum teleportation via noisy bipartite and tripartite accelerating quantum states: beyond the single mode approximation. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 50, 395302 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8121/aa812b
Guan, S.Y., Jin, Z., Wu, H.J., Zhu, A.D., Wang, H.F., Zhang, S.: Restoration of three-qubit entanglements and protection of tripartite quantum state sharing over noisy channels via environment-assisted measurement and reversal weak measurement. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 1–15 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1584-0
Kumar, S.A.: Quantum teleportation of a tripartite entangled coherent state. Mod. Phys. Lett. A. 36, 2150217 (2021)
Bhatia, P.S.: Elementary tripartite quantum communication photonic network at the telecom wavelength. Laser Phys. 31, 95203 (2021)
Joy, D., Sabir, M.: Efficient schemes for the quantum teleportation of a sub-class of tripartite entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 1–11 (2018)
Fedrizzi, A., Ursin, R., Herbst, T., Nespoli, M., Prevedel, R., Scheidl, T., Tiefenbacher, F., Jennewein, T., Zeilinger, A.: High-fidelity transmission of entanglement over a high-loss free-space channel. Nat. Phys. 5, 389–392 (2009)
Gyongyosi, L., Imre, S.: Entanglement concentration service for the quantum Internet. Quantum Inf. Process. 19, 1–28 (2020)
Jiang, L., Taylor, J.M., Nemoto, K., Munro, W.J., Van Meter, R., Lukin, M.D.: Quantum repeater with encoding. Phys. Rev. A. 79, 32325 (2009)
Yi, X.-F., Xu, P., Yao, Q., Quan, X.: Quantum repeater without Bell measurements in double-quantum-dot systems. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 82 (2019)
Behera, B.K., Seth, S., Das, A., Panigrahi, P.K.: Demonstration of entanglement purification and swapping protocol to design quantum repeater in IBM quantum computer. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 1–13 (2019)
Harraz, S., Cong, S., Member, S., Nieto, J.J.: Protected quantum teleportation through noisy channel by weak measurement and environment-assisted measurement. IEEE Commun. Lett. 26(3), 528–531 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3138854
Jung, E., Hwang, M.-R., Park, D., Tamaryan, S.: Three-party entanglement in tripartite teleportation scheme through noisy channels. Quantum Inf. Comput. 10, 377–397 (2010)
Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Özdemir, ŞK., Imoto, N.: Experimental extraction of an entangled photon pair from two identically decohered pairs. Nature 421, 343–346 (2003)
Li, M., Fei, S.-M., Li-Jost, X.: Quantum entanglement: separability, measure, fidelity of teleportation, and distillation. Math. Phys, Adv (2010). https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/301072
Devetak, I., Winter, A.: Distillation of secret key and entanglement from quantum states. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 461, 207–235 (2005)
Lee, S.-W., Ralph, T.C., Jeong, H.: Fundamental building block for all-optical scalable quantum networks. Phys. Rev. A. 100, 52303 (2019)
Azuma, K., Tamaki, K., Lo, H.-K.: All-photonic quantum repeaters. Nat. Commun. 6, 1–7 (2015)
Dias, J., Ralph, T.C.: Quantum repeaters using continuous-variable teleportation. Phys. Rev. A. 95, 22312 (2017)
Barasiński, A., Černoch, A., Lemr, K.: Demonstration of controlled quantum teleportation for discrete variables on linear optical devices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 170501 (2019)
Pan, J.-W., Gasparoni, S., Ursin, R., Weihs, G., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental entanglement purification of arbitrary unknown states. Nature 423, 417–422 (2003)
Zhang, Q., Goebel, A., Wagenknecht, C., Chen, Y.-A., Zhao, B., Yang, T., Mair, A., Schmiedmayer, J., Pan, J.-W.: Experimental quantum teleportation of a two-qubit composite system. Nat. Phys. 2, 678–682 (2006)
Im, D., Lee, C., Kim, Y., Nha, H., Kim, M.S., Lee, S.-W., Kim, Y.-H.: Optimal teleportation via noisy quantum channels without additional qubit resources. npj Quantum Inf. 7, 86 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-021-00426-x
Lee, S.-W., Im, D.-G., Kim, Y.-H., Nha, H., Kim, M.S.: Quantum teleportation is a reversal of quantum measurement. Phys. Rev. Res. 3(3), 033119 (2021)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Harraz, S., Cong, S.: Comparison of quantum state protection against decoherence, a survey. Int. J. Quantum Information, 2250007 (2022)
Kim, Y.S., Lee, J.C., Kwon, O., Kim, Y.H.: Protecting entanglement from decoherence via weak quantum measurement. Pacific Rim Conf. Lasers Electro-Optics, CLEO - Tech. Dig. 8, 117–120 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/CLEOPR.2013.6600351
Harraz, S., Cong, S.: N-qubit state protection against amplitude damping by quantum feed-forward control and its reversal. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 26, 1–8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2020.2969574
Harraz, S., Cong, S., Li, K.: Two-qubit state recovery from amplitude damping based on weak measurement. Quantum Inf. Process. 19, 1–22 (2020)
Harraz, S., Cong, S., Nieto, J.J.: Quantum state and entanglement protection in finite temperature environment by quantum feed-forward control. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 136, 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01861-7
Wang, K., Zhao, X., Yu, T.: Environment-assisted quantum state restoration via weak measurements. Phys. Rev. At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 89, 1–6 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.89.042320
Gregoratti, M., Werner, R.F.: Quantum lost and found. J. Mod. Opt. 50–6, 915–933 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1080/09500340308234541
Zhao, X., Hedemann, S.R., Yu, T.: Restoration of a quantum state in a dephasing channel via environment-assisted error correction. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 88, 1–8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.88.022321
Wang, Q., Li, W.J.: Restoring distribution entanglement for two-qubit transmission using environment-assisted measurement and quantum measurement reversal. Laser Phys. 29, 115201 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1555-6611/ab41ed
Wang, Q., Xu, L., Li, W.J., He, Z.: Environment-assisted high-dimensional quantum entanglement restoration via weak measurement reversal. Laser Phys. 30, 065202 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1555-6611/ab8124
Li, Y.L., Sun, F., Yang, J., Xiao, X.: Enhancing the teleportation of quantum Fisher information by weak measurement and environment-assisted measurement. Quantum Inf. Process. 20, 1–19 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-02998-1
Cunha, M., Fonseca, A., Silva, E.O.: Tripartite entanglement: Foundations and applications. Universe. 5, 209 (2019)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61973290 and Ministry of Science and Technology of P. R. China Program under the grant no. QN2022200007L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SH conceived and developed the idea of EA-WMR, performed the experiments and analyzed the results. SC conceived and supervised the project. JJN discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Harraz, S., Cong, S. & Nieto, J.J. Optimal tripartite quantum teleportation protocol through noisy channels. Quantum Inf Process 22, 83 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03830-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03830-8