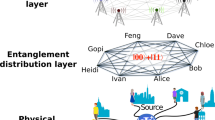
Abstract
Anonymity is a desirable yet challenging requirement of communication networks. In this paper, we present the first quantum anonymous notification (QAN) protocol that introduces anonymity for both sender and the receiver in practical quantum networks. Our QAN protocol features tracelessness, i.e., it is impossible to trace the encoding operations back to the encoding party even if all network communication including qubits and measurement results are made available to an adversary. Additionally, we demonstrate the QAN protocol in a four-node network using IBM quantum computer to benchmark its performance in practical settings. QAN protocol can be of independent interest as a powerful component of several applications ranging from multiparty quantum computation to quantum Internet. Security analysis shows that this protocol is robust against external adversaries and malicious participants.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K.: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(3), 648 (1999)
Bell, B., Markham, D., Herrera-Martí, D., Marin, A., Wadsworth, W., Rarity, J., Tame, M.: Experimental demonstration of graph-state quantum secret sharing. Nat. Commun. 5(1), 1–12 (2014)
Bao, N., Halpern, N.Y.: Quantum voting and violation of Arrow’s impossibility theorem. Phys. Rev. A 95(6), 062306 (2017)
Ribeiro, J., Murta, G., Wehner, S.: Fully device-independent conference key agreement. Phys. Rev. A 97(2), 022307 (2018)
Kimble, H.J.: The quantum internet. Nature 453(7198), 1023 (2008)
Wehner, S., Elkouss, D., Hanson, R.: Quantum internet: A vision for the road ahead. Science 362(6412) (2018)
Christandl, M., Wehner, S.: Quantum anonymous transmissions. In: International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Springer (2005) 217–235
Vaccaro, J.A., Spring, J., Chefles, A.: Quantum protocols for anonymous voting and surveying. Phys. Rev. A 75(1), 012333 (2007)
Brassard, G., Broadbent, A., Fitzsimons, J., Gambs, S., Tapp, A.: Anonymous quantum communication. In: Advances in Cryptology – ASIACRYPT 2007, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 460–473 (2007)
Bouda, J., Sprojcar, J.: Anonymous transmission of quantum information. In: 2007 first international conference on quantum, nano, and micro technologies (ICQNM’07), 12–12 (2007)
Jiang, L., He, G., Nie, D., Xiong, J., Zeng, G.: Quantum anonymous voting for continuous variables. Phys. Rev. A 85(4), 042309 (2012)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., Su, Q., Qin, S.J., Gao, F.: Quantum anonymous ranking. Phys. Rev. A 89(3), 032325 (2014)
Lipinska, V., Murta, G., Wehner, S.: Anonymous transmission in a noisy quantum network using the W state. Phys. Rev. A 98(5), 052320 (2018)
Unnikrishnan, A., MacFarlane, I.J., Yi, R., Diamanti, E., Markham, D., Kerenidis, I.: Anonymity for practical quantum networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122(24), 240501 (2019)
Yang, Y.G., Yang, Y.L., Lv, X.L., Zhou, Y.H., Shi, W.M.: Examining the correctness of anonymity for practical quantum networks. Phys. Rev. A 101(6), 062311 (2020)
Broadbent, A., Tapp, A.: Information-theoretic security without an honest majority. In: international conference on the theory and application of cryptology and information security, Springer (2007) 410–426
Hahn, F., de Jong, J., Pappa, A.: Anonymous quantum conference key agreement. PRX Quantum 1(2), 020325 (2020)
Preskill, J.: Quantum computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2, 79 (2018)
IBM-Quantum-team: IBM. ibmq-vigo v1.0.2 https://quantum-computing.ibm.com (2020)
Wilde, M.M.: From classical to quantum Shannon theory. arXiv preprint arXiv:1106.1445 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2019R1A2C2007037) and the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT) ITRC (Information Technology Research Center) support program (IITP-2021-0-02046) supervised by the IITP (Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation). We acknowledge the use of IBM Quantum services for this work. The views expressed are those of the authors, and do not reflect the official policy or position of IBM or the IBM Quantum team.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., ur Rehman, J. & Shin, H. Quantum anonymous notification for network-based applications. Quantum Inf Process 20, 397 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03339-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03339-y