Abstract
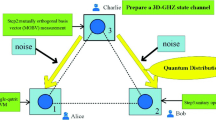
We present a scheme for implementing deterministic joint remote preparation of the Knill–Laflamme–Milburn state with two GHZ states as the quantum channel. Assuming that four of the six involved qubits collectively suffer the same type of noise, we first investigate the effects of four typical types of noises on the protocol by means of Kraus operators. It is shown that the bit-flip and amplitude damping noise are the severe noises for decoherence rate \(\chi <0.5\), followed by the depolarizing and phase-flip channel, respectively. Interestingly, the efficiency of the scheme can be restored by adding decoherence when \(\chi >0.5\) in bit-flip and phase-flip noise channel. Afterward, we investigate the dynamics of deterministic joint remote state preparation for dissipative environments. Analytical and numerical calculations show that the quality of our scheme can be enhanced by adjusting the system detuning no matter whether the non-Markovian effect is applicable or not.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., et al.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Lo, H.K.: Classical-communication cost indistributed quantum information processing: a generalization of quantum communication complexity. Phys. Rev. A 62(1), 012313 (2000)
Bennett, C.H., Divincenzo, D.P., Shor, P.W., Smolin, J.A., Terhal, B.M., Wootters, W.K.: Remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 077902 (2001)
Pati, A.K.: Minimum classical bit for remote preparation and measurement of a qubit. Phys. Rev. A 63(1), 014302 (2001)
Shi, B.S., Tomita, T.: Remote state preparation of an entangled state. J. Opt. B Quantum Semiclass. Opt. 4, 380 (2002)
Leung, D., Shor, P.W.: Oblivious remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 197901 (2003)
Berry, D.W., Sanders, B.C.: Optimal remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90(5), 057901 (2003)
Ye, M.Y., Zhang, Y.S., Guo, G.C.: Faithful remote state preparation using finite classical bits and a nonmaximally entangled state. Phys. Rev. A 69(2), 22310 (2004)
Peters, N.A., Barreiro, J.T., Goggin, M.E., Wei, T., Kwiat, P.G.: Remote state preparation: arbitrary remote control of photon polarization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(15), 150502 (2005)
Dai, H., Chen, P., Liang, L., Li, C.: Classical communication cost and remote preparation of the four-particle GHZ class state. Phys. Lett. A 355(4), 285–288 (2006)
Liu, J.M., Feng, X.L., Oh, C.H.: Remote preparation of arbitrary two- and three-qubit states. EPL 87(3), 30006 (2009)
Luo, M.X., Chen, X.B., Yang, Y.X., Niu, X.X.: Experimental architecture of joint remote state preparation. Quantum Inf. Process. 11(3), 751–767 (2012)
Wang, D., Hu, Y.D., Wang, Z.Q., Ye, L.: Efficient and faithful remote preparation of arbitrary three- and four-particle W-class entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(6), 2135–2151 (2015)
Chen, X.B., Sun, Y.R., Xu, G., Jia, H.Y., Qu, Z., Yang, Y.X.: Controlled bidirectional remote preparation of three-qubit state. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(10), 244 (2017)
Le, J.H., Cavailles, A., Raskop, J., Huang, K., Laurat, J.: Remote preparation of continuous-variable qubits using loss-tolerant hybrid entanglement of light. Optica 5(8), 1012 (2018)
Li, Y.H., Qiao, Y., Sang, M.H., Nie, Y.Y.: Bidirectional controlled remote state preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state. Internat. J. Theoret. Phys. 58(7), 2228 (2019)
Nikaeen, M., Ramezani, M., Bahrampour, A.: Optimal exploitation of resource in remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. A 102, 012416 (2020)
Wei, D.X., Luo, J., Yang, X.D.: Experimental realization of information transmission between not-directly-coupled spins on NMR quantum computers. Chin. Phys. 13, 817 (2004)
Liu, W.T., et al.: Experimental remote preparation of arbitrary photon polarization states. Phys. Rev. A 76, 022308 (2007)
Barreiro, J.T., Wei, T.C., Kwiat, P.G.: Remote preparation of single-photon hybrid entangled and vector-polarization states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 030407 (2010)
Dakic, B., et al.: Quantum discord as resource for remote state preparation. Nat. Phys 8(9), 666 (2012)
Xiang, G.Y., Li, J., Yu, B., Guo, G.C.: Remote preparation of mixed states via noisy entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 72, 012315 (2015)
Jiang, Y.F., et al.: Remote blind state preparation with weak coherent pulses in the field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 123(10), 100503 (2019)
An, N.B., Bich, C.T., Don, N.V.: Deterministic joint remote state preparation. Phys. Lett. A 375(41), 3570–3573 (2011)
Zhan, Y.B., Ma, P.C.: Deterministic joint remote preparation of arbitrary two- and three-qubit entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(2), 997–1009 (2013)
Xia, Y., Song, J., Song, H.S.: Multiparty remote state preparation. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 40(18), 3719 (2007)
An, N.B., Kim, J.: Joint remote state preparation. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 41(9), 095501 (2008)
Wu, W., Liu, W.T., Chen, P.X., Li, C.Z.: Deterministic remote preparation of pure and mixed polarization states. Phys. Rev. A 81(4), 042301 (2010)
Zhan, Y.B., Ma, P.C.: Deterministic remote preparation of arbitrary two- and three-qubit states. EPL 98(4), 40005 (2012)
Wang, Y., Ji, W.: Deterministic joint remote state preparation of arbitrary two- and three-qubit states. Chin. Phys. B 22(2), 020306 (2013)
Chen, Q.Q., Xia, Y., Song, J.: Deterministic joint remote preparation of an arbitrary three-qubit state via EPR pairs. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 45(5), 055303 (2012)
Ma, P.C., Chen, G.B., Zhan, Y.B.: Schemes for deterministic joint remote preparation of an arbitrary tripartite four-qubit entangled state. Laser Phys. 26(10), 105201 (2016)
Bich, C.T., et al.: Deterministic joint remote preparation of an equatorial hybrid state via high-dimensional Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pairs: active versus passive receiver. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(4), 1–12 (2018)
Du, Z.L., Li, X.L.: Deterministic joint remote state preparation of four-qubit cluster type with tripartite involvement. Quantum Inf. Process. 19, 39 (2020)
Wang, M.M., Qu, Z.G.: Effect of quantum noise on deterministic joint remote state preparation of a qubit state via a GHZ channel. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(11), 4805 (2016)
Qian, Y.J., Xue, S.B., Jiang, M.: Deterministic remote preparation of arbitrary single-qubit state via one intermediate node in noisy environment. Phys. Lett. A 384, 126204 (2020)
Guan, X.W., Chen, X.B., Wang, L.C., Yang, Y.X.: Joint remote preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state in noisy environments. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(7), 2236 (2014)
Adepoju, A.G., Falaye, B.J., Sun, G.H., Camacho-Nieto, O., Dong, S.H.: Joint remote state preparation(JRSP) of two-qubit equatorial state in quantum noisy channels. Phys. Lett. A 381(6), 581 (2017)
Wang, M.M., Qiu, Z.G., Wang, W., Chen, J.G.: Effect of noise on deterministic joint remote preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 140 (2017)
Dash, T., Sk, R., Panigrahi, P.K.: Deterministic joint remote state preparation of arbitrary two-qubit state through noisy cluster-GHZ channel. Opt. Commun. 464, 125518 (2020)
Zhang, Z.H., Zhao, C.R., Wang, J.W., Shu, L.: Joint remote state preparation of mixed states. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 53(2), 025501 (2020)
Nguyen, V.H., Cao, T.B., Nguyen, B.A.: Optimal joint remote state preparation in the presence of various types of noises. Adv. Nat. Sci.: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8, 015012 (2017)
Chen, Z.F., Liu, J.M., Ma, L.: Deterministic joint remote preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state in the presence of noise. Chin. Phys. B 23(2), 020312 (2014)
Zhang, Z.H., Sun, M.: Enhanced deterministic joint remote state preparation under Pauli channels with memory. Phys. Scr. 95(5), 055107 (2020)
Li, J.F., Liu, J.M., Feng, X.L., Oh, C.H.: Deterministic remote two-qubit state preparation in dissipative environments. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(5), 2155–2168 (2016)
Knill, E., Laflamme, R., Milburn, G.: A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46 (2001)
Modlawska, J., Grudka, A.: Adaptive quantum teleportation. Phys. Rev. A 79, 064302 (2009)
Franson, J.D., Donegan, M.M., Fitch, M.J., Jacobs, B.C., Pittman, T.B.: High-fidelity quantum logic operations using linear optical elements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 137901 (2002)
Lemr, K., Fiurášek, J.: Preparation of states of two photons in several spatial modes. Phys. Rev. A 77, 023802 (2008)
Cheng, L.Y., Wang, H.F., Zhang, S., Yeon, K.H.: Generation of two-atom knill-laflamme-milburn states with cavity quantum electrodynamics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29, 1584–1588 (2012)
Li, D.X., et al.: Engineering steady Knill-Laflamme-Milburn state of Rydberg atoms by dissipation. Opt. Express 26(3), 2292 (2018)
Fortes, R., Rigolin, G.: Fighting noise with noise in realistic quantum teleportation. Phys. Rev. A 92, 012338 (2015)
Badziag, P., Horodecki, M., Horodecki, P., Horodecki, R.: Local environment can enhance fidelity of quantum teleportation. Phys. Rev. A 62, 012311 (2000)
Breuer, H.P., Petruccione, F.: The Theory of Open Quantum Systems. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2002)
Garraway, B.M.: Nonperturbative decay of an atomic system in a cavity. Phys. Rev. A 55, 2290 (1997)
Bellomo, B., Franco, R.L., Compagno, G.: Non-Markovian effects on the dynamics of entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 160502 (2007)
Vacchini, B., Breuer, H.P.: Exact master equations for the non-Markovian decay of a qubit. Phys. Rev. A 81, 042103 (2010)
Xiao, X., Fang, M.F., Li, Y.L.: Wu, Chao: Robust entanglement preserving by detuning in non-Markovian regime. J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 42, 235502 (2009)
Zhang, Y.L., Zhou, Q.P., Kang, G.D., Zhou, F., Wang, X.B.: Remote state preparation in non-Markovian environment. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 10, 1250030 (2012)
Xu, Z.Y., Liu, C., Luo, S., Zhu, S.: Non-Markovian effect on remote state preparation. Ann. Phys. 356, 29–36 (2015)
Chruscinski, D., Kossakowski, A.: arXiv:1006.2764
Dijkstra, A.G., Tanimura, Y.: Non-Markovian entanglement dynamics in the presence of system-bath coherence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 250401 (2010)
Breuer, H.P., Laine, E.M., Piilo, J., Vacchini, B.: Colloquium: Non-Markovian dynamics in open quantum systems. Rev. Mod. Phys 88, 021002 (2006)
Rajagopal, A.K., Usha Devi, A.R., Rendell, R.W.: Kraus representation of quantum evolution and fidelity as manifestations of Markovian and non-Markovian forms. Phys. Rev. A 82, 042107 (2010)
Jozsa, R.: Fidelity for mixed quantum states. J. Mod. Opt. 41, 2315 (1994)
Rivas, A., Huelga, S.F., Plenio, S.F.: Entanglement and non-Markovianity of quantum evolutions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 050403 (2010)
Zou, W.J., et al.: Protecting entanglement from finite-temperature thermal noise via weak measurement and quantum measurement reversal. Phys. Rev. A 95, 042342 (2017)
Liu, B.H., et al.: Experimental control of the transition from Markovian to non-Markovian dynamics of open quantum systems. Nat. Phys. 7, 931 (2011)
Smirne, A., Brivio, D., Cialdi, S., Vacchini, B., Paris, M.G.A.: Experimental investigation of initial system-environment correlations via trace-distance evolution Phys. Rev. A 84, 032112 (2011)
Gessner, M., et al.: Local detection of quantum correlations with a single trapped ion. Nat. Phys. 10, 105 (2014)
Liu, J., Lu, X.M., Wang, X.G.: Nonunital non-Markovianity of quantum dynamics. Phys. Rev. A 87, 042103 (2013)
Acknowledgements
K. Hou and M. Shi thank the support the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11805004) and the Doctor Foundation of Anhui Jianzhu University(Grant No. 2020QDZ21). Z.Y. Chen thanks the support of the Higher Education Quality Engineering Project of Anhui Jianzhu University (Grant No. 2020XSXX01). X.Y.Zhang thanks the support of the Natural Science Fundation of Education Department of Anhui Province (Grant No. KJ2020A0484).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, K., Chen, ZY., Shi, M. et al. Effective deterministic joint remote preparation of the Knill–Laflamme–Milburn state in collective noise environment. Quantum Inf Process 20, 225 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03163-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03163-4