Abstract
The security of quantum key distribution protocols is guaranteed by the laws of quantum mechanics. However, a precise analysis of the security properties requires tools from both classical cryptography and information theory. Here, we employ recent results in non-asymptotic classical information theory to show that one-way information reconciliation imposes fundamental limitations on the amount of secret key that can be extracted in the finite key regime. In particular, we find that an often used approximation for the information leakage during information reconciliation is not generally valid. We propose an improved approximation that takes into account finite key effects and numerically test it against codes for two probability distributions, that we call binary–binary and binary–Gaussian, that typically appear in quantum key distribution protocols.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
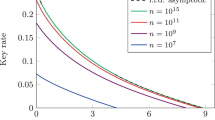
Consider, for example, BB84 with asymmetric basis choice [25] on a channel with quantum bit error rate Q. Here, contributions (1) and (2) vanish asymptotically while contributions (3) and (4) converge to h(Q).
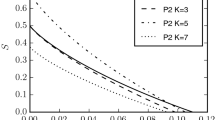
We here apply Theorem 1 to distributions that are continuous in Y. Note that the proofs leading to Theorem 1 can easily be generalized to this setting.
References
Abruzzo, S., Mertz, M., Kampermann, H., Bruss. D.: Finite-key analysis of the six-state protocol with photon number resolution detectors. In: Proceedings of SPIE, pp. 818917. Prague (2011)
Altug, Y., Wagner, A. B.: The third-order term in the normal approximation for singular channels. In: IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), 2014, pp. 1897–1901. IEEE, (2014)
Beigi, S., Gohari, A.: Quantum achievability proof via collision relative entropy. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 60(12), 7980–7986 (2014)
Bennett, C. H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer System Signal Processing, pp. 175–179, IEEE, Bangalore (1984)
Bratzik, S., Mertz, M., Kampermann, H., Bruß, D.: Min-entropy and quantum key distribution: nonzero key rates for small numbers of signals. Phys. Rev. A 83(2), 022330 (2011)
Bruß, D.: Optimal eavesdropping in quantum cryptography with six states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81(14), 3018–3021 (1998)
Cai, R.Y.Q., Scarani, V.: Finite-key analysis for practical implementations of quantum key distribution. New J. Phys. 11(4), 045024 (2009)
Chung, S.-Y., Forney, G.D., Richardson, T.J., Urbanke, R.: On the design of low-density parity-check codes within 0.0045 dB of the Shannon limit. IEEE Commun. Lett. 5(2), 58–60 (2001)
Dupuis, F., Kraemer, L., Faist, P., Renes, J. M., Renner, R.: Generalized entropies. In: Proceedings of XVIIth International Congress on Mathematical Physics, pp. 134–153, Aalborg, Denmark (2012)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67(6), 661–663 (1991)
Elkouss, D., Martinez-Mateo, J., Martin, V.: Information reconciliation for quantum key distribution. Quantum Inf. Comput. 11(3), 226–238 (2011)
Elkouss, D., Martinez-Mateo, J., Martin, V.: Untainted puncturing for irregular low-density parity-check codes. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 1(6), 585–588 (2012)
Han, T.S.: Information-Spectrum Methods in Information Theory. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Hayashi, M.: Practical evaluation of security for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 74(2), 022307 (2006)
Hayashi, M.: Second-order asymptotics in fixed-length source coding and intrinsic randomness. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 54(10), 4619–4637 (2008)
Hayashi, M.: Information spectrum approach to second-order coding rate in channel coding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 55(11), 4947–4966 (2009)
Hayashi, M., Tsurumaru, T.: Concise and tight security analysis of the Bennett–Brassard 1984 protocol with finite key lengths. New J. Phys. 14(9), 093014 (2012)
Hu, X.-Y., Eleftheriou, E., Arnold, D.-M.: Regular and irregular progressive edge-growth tanner graphs. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 51(1), 386–398 (2005)
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Leverrier, A.: Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a Gaussian modulation. Phys. Rev. A 84(6), 062317 (2011)
Leverrier, A.: Theoretical study of continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Ph.D. thesis, Telecom ParisTech, Paris, France, (2009)
Leverrier, A., Alléaume, R., Boutros, J., Zémor, G., Grangier, P.: Multidimensional reconciliation for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 77, 042325 (2008)
Leverrier, A., Grangier, P.: Unconditional security proof of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution with discrete modulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102(18), 180504 (2009)
Leverrier, A., Grangier, P.: Continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution protocols with a non-Gaussian modulation. Phys. Rev. A 83(4), 042312 (2011)
Lim, C.C.W., Portmann, C., Tomamichel, M., Renner, R., Gisin, N.: Device-independent quantum key distribution with local Bell test. Phys. Rev. X 3(3), 031006 (2013)
Lo, H.-K., Chau, H., Ardehali, M.: Efficient quantum key distribution scheme and a proof of its unconditional security. J. Cryptol. 18(2), 133–165 (2004)
Martinez-Mateo, J., Elkouss, D., Martin, V.: Key reconciliation for high performance quantum key distribution. Sci. Rep. 3(1576), 1–6 (2013)
Mayers, D.: Unconditional security in quantum cryptography. J. ACM 48(3), 351–406 (2001)
Morelos-Zaragoza, R.H.: The Art of Error Correcting Coding. Wiley, Hoboken (2006)
Moroder, T., Curty, M., Lütkenhaus, N.: One-way quantum key distribution: simple upper bound on the secret key rate. Phys. Rev. A 74(5), 052301 (2006)
Pacher, C., Lechner, G., Portmann, C., Maurhart, O., Peev, M.: Efficient QKD Postprocessing Algorithms. In: QCrypt 2012, Singapore, (2012)
Pfister, C., Coles, P. J., Wehner, S., Lütkenhaus, N.: Sifting attacks in finite-size quantum key distribution. arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.07502 (2015)
Polyanskiy, Y., Poor, H.V., Verdú, S.: Channel coding rate in the finite blocklength regime. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 56(5), 2307–2359 (2010)
Renner, R.: Security of Quantum Key Distribution. Ph.D. thesis, ETH Zurich, (2005)
Scarani, V., Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H., Cerf, N., Dušek, M., Lütkenhaus, N., Peev, M.: The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81(3), 1301–1350 (2009)
Scarani, V., Renner, R.: Quantum cryptography with finite resources: unconditional security bound for discrete-variable protocols with one-way postprocessing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100(20), 200501 (2008)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(2), 441–444 (2000)
Slepian, D., Wolf, J.: Noiseless coding of correlated information sources. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 19(4), 471–480 (1973)
Strassen, V.: Asymptotische Abschätzungen in Shannons Informationstheorie. In: Transactions of the Third Prague Conference on Information Theory, pp. 689–723. Prague (1962)
Tan, V., Tomamichel, M.: The third-order term in the normal approximation for the AWGN channel. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 61(5), 2430–2438 (2015)
Tan, V.Y., Kosut, O.: On the dispersions of three network information theory problems. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 60(2), 881–903 (2014)
Tomamichel, M., Hayashi, M.: A hierarchy of information quantities for finite block length analysis of quantum tasks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 59(11), 7693–7710 (2013)
Tomamichel, M., Leverrier, A.: A rigorous and complete proof of finite key security of quantum key distribution. arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.08458 (2015)
Tomamichel, M., Lim, C.C.W., Gisin, N., Renner, R.: Tight finite-key analysis for quantum cryptography. Nat. Commun. 3, 634 (2012)
Tomamichel, M., Martinez-Mateo, J., Pacher, C., Elkouss, D.: Fundamental finite key limits for information reconciliation in quantum key distribution. In: IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), 2014, pp. 1469–1473. IEEE (2014)
Tomamichel, M., Tan, V.Y.F.: A tight upper bound for the third-order asymptotics for most discrete memoryless channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 59(11), 7041–7051 (2013)
Tyurin, I.: A refinement of the remainder in the Lyapunov theorem. Theory Probab. Appl. 56(4), 693–696 (2010)
Varodayan, D., Aaron, A., Girod, B.: Rate-adaptive codes for distributed source coding. Signal Process. 86(11), 3123–3130 (2006)
Walenta, N., Burg, A., Caselunghe, D., Constantin, J., Gisin, N., Guinnard, O., Houlmann, R., Junod, P., Korzh, B., Kulesza, N., Legré, M., Lim, C.W., Lunghi, T., Monat, L., Portmann, C., Soucarros, M., Thew, R.T., Trinkler, P., Trolliet, G., Vannel, F., Zbinden, H.: A fast and versatile quantum key distribution system with hardware key distillation and wavelength multiplexing. New J. Phys. 16(1), 013047 (2014)
Wang, L., Colbeck, R., Renner, R.: Simple channel coding bounds. In: Proceedings of IEEE ISIT, pp.1804–1808. IEEE, (2009)
Yassaee, M.H., Aref, M.R., Gohari, A.: A technique for deriving one-shot achievability results in network information theory. In: Proceedings of IEEE ISIT, (2013)
Acknowledgements
MT thanks N. Beaudry, S. Bratzik, F. Furrer, M. Hayashi, C.C.W. Lim, and V.Y.F. Tan for helpful comments and pointers to related work. MT is supported by an Australian Research Council Discovery Early Career Researcher Award (DECRA) fellowship. JM has been funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness through project Continuous Variables for Quantum Communications (CVQuCo), TEC2015-70406-R. CP has been funded by the Vienna Science and Technology Fund (WWTF) through project ICT10-067 (HiPANQ). DE was supported via STW and the NWO Vidi grant “Large quantum networks from small quantum devices”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Part of these results without the technical derivations were published in the proceedings of the International Symposium on Information Theory, Honolulu (2014) [44].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomamichel, M., Martinez-Mateo, J., Pacher, C. et al. Fundamental finite key limits for one-way information reconciliation in quantum key distribution. Quantum Inf Process 16, 280 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1709-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1709-5