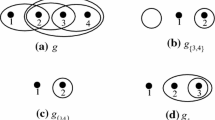
Abstract
We investigate some properties of the entanglement of hypergraph states in purely hypergraph theoretical terms. We first introduce an approach for computing local entropic measure on qubit \(t\) of a hypergraph state by using the Hamming weight of the so-called \(t\)-adjacent subhypergraph. Then, we quantify and characterize the entanglement of hypergraph states in terms of local entropic measures obtained by using the above approach. Our results show that full-rank hypergraph states of more than two qubits can not be converted into any graph state under local unitary transformations.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In fact, the local entropic measure \(E_2^t \left( {\left| \phi \right\rangle } \right) \) is usually given by the smallest eigenvalue of the reduced density matrix \(\rho _t \).
References
Horodecki, R., et al.: Quantum entanglement. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 865 (2009)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Hein, M., Eisert, J., Briegel, H.J.: Multiparty entanglement in graph states. Phys. Rev. A 69, 062311 (2004)
Aschauer, H., Dur, W., Briegel, H.J.: Multiparticle entanglement purification for two-colorable graph states. Phys. Rev. A 71, 012319 (2005)
Raussendorf, R., Browne, D.E., Briegel, H.J.: Measurement-based quantum computation on cluster states. Phys. Rev. A 68, 022312 (2003)
Raussendorf, R., Briegel, H.J.: A one-way quantum computer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5188 (2001)
Briegel, H.J., Raussendorf, R.: Persistent entanglement in arrays of interacting particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 910 (2001)
Gottesman, D.: Class of quantum error-correcting codes saturating the quantum Hamming bound. Phys. Rev. A 54, 1862 (1996)
Gottesman, D.: Theory of fault-tolerant quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 57, 127 (1998)
Ionicioiu, R., Spiller, T.P.: Encoding graphs into quantum states: an axiomatic approach. Phys. Rev. A 85, 062313 (2012)
Looi, S.Y., et al.: Quantum-error-correcting codes using qudit graph states. Phys. Rev. A 78, 042303 (2008)
Menicucci, N.C., Flammia, S.T., van Loock, P.: Graphical calculus for Gaussian pure states. Phys. Rev. A 83, 042335 (2011)
Verstraete, F., et al.: Criticality, the area law, and the computational power of projected entangled pair states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 220601 (2006)
Pérez-García, D., et al.: Quantum Inf. Comput. 8, 650 (2008); N. Schuch et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 140506 (2007)
Perseguers, S., et al.: Quantum random networks. Nat. Phys. 6, 539 (2010)
Qu, R., et al.: Encoding hypergraphs into quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 87, 022311 (2013)
Rossi et al.: arXiv:1211.5554[quant-ph]
Qu, R., et al.: Multipartite entanglement and hypergraph states of three qubits. Phys. Rev. A 87, 032329 (2013)
Vidal, G.: Entanglement monotones. J. Mod. Opt. 47, 355 (2000)
Eisert, J., Briegel, H.J.: Schmidt measure as a tool for quantifying multiparticle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 64, 022306 (2001)
Bruß, D., Macchiavello, C.: Multipartite entanglement in quantum algorithms. Phys. Rev. A 83, 052313 (2011)
Kruszynska, C., Kraus, B.: Local entanglability and multipartite entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 79, 052304 (2009)
Qu, R., et al.: Relationship among locally maximally entangleable states, W states, and hypergraph states under local unitary transformations. Phys. Rev. A 87, 052331 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Chinese National Program on Key Basic Research Project (973 Program, Grant Nos. 2014CB744605 and 2013CB329304), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants Nos. 61170178, 61272254 and 61272265), and the European Union Framework 7 Marie-Curie International Research Staff Exchange Programme (Grant No. 247590). This work is completed during our academic visit at the Department of Computing, the Open University, United Kingdom.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, R., Ma, Yp., Bao, Yr. et al. Entropic measure and hypergraph states. Quantum Inf Process 13, 249–258 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0646-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0646-1