Abstract
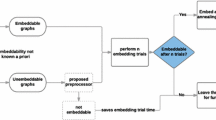
In Choi (Quantum Inf Process, 7:193–209, 2008), we introduced the notion of minor-embedding in adiabatic quantum optimization. A minor-embedding of a graph G in a quantum hardware graph U is a subgraph of U such that G can be obtained from it by contracting edges. In this paper, we describe the intertwined adiabatic quantum architecture design problem, which is to construct a hardware graph U that satisfies all known physical constraints and, at the same time, permits an efficient minor-embedding algorithm. We illustrate an optimal complete-graph-minor hardware graph. Given a family \({\mathcal{F}}\) of graphs, a (host) graph U is called \({\mathcal{F}}\)-minor-universal if for each graph G in \({\mathcal{F}, U}\) contains a minor-embedding of G. The problem for designing a \({{\mathcal{F}}}\)-minor-universal hardware graph U sparse in which \({{\mathcal{F}}}\) consists of a family of sparse graphs (e.g., bounded degree graphs) is open.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonov, D., van Dam, W., Kempe, J., Landau, Z., Lloyd, S., Regev, O.: Adiabatic quantum computation is equivalent to standard quantum computation. In: Proceedings of the 45th FOCS, pp. 42–51 (2004)
Alon, N., Capalbo, M.: Optimal universal graphs with deterministic embedding. In: Proceedings of the 19th SODA (2008)
Bodlaender H.L.: A partial k-arboretum of graphs with bounded treewidth. Theoretical Computer Science 209, 1–45 (1998)
Boros E., Hammer P.: Pseudo-boolean optimization. Discrete Appl. Math 123, 155–225 (2002)
Boros, E., Hammer, P.L., Tavares, G.: Preprocessing of quadratic unconstrained binary optimization. Technical report RRR 10-2006, RUTCOR research report (2006)
Choi, V.: Minor-embedding in adiabatic quantum computation: I. The parameter setting problem. Quantum Inf. Process. 7, 193–209, (2008). Available at arXiv:quant-ph/0804.4884
Choi, V.: Systems, devices and methods for analog processing. US Patent Application US2009/0121215, May 14, (2009)
Das A., Chakrabarti B.K.: Quantum annealing and analog quantum computations. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 1061–1081 (2008)
Diestel R.: Graph Theory. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
D-Wave Systems Inc.: 100-4401 Still Creek Dr., Burnaby, V5C 6G9, BC, Canada. http://www.dwavesys.com/
Farhi, E., Goldstone, J., Gutmann, S., Sipser, M.: Quantum Computation by Adiabatic Evolution. arXiv:quant-ph/0001106 (2000)
Farhi E., Goldstone J., Gutmann S., Lapan J., Lundgren A., Preda D.: A quantum adiabatic evolution algorithm applied to random instances of an NP-complete problem. Science 292(5516), 472–476 (2001)
Harris, R., Johansson, J., Berkley, A.J., Johnson, M.W., Lanting, T., Han, S. et al.: Experimental Demonstration of a Robust and Scalable Flux Qubit. arXiv:quant-ph/0909.4321, (2009)
Kaminsky, W.M., Lloyd, S.: Scalable architecture for adiabatic quantum computing of NP-hard problems. Quantum Computing and Quantum Bits in Mesoscopic Systems, (2004)
Kaminsky, W.M., Lloyd, S., Orlando, T.P.: Scalable Superconducting Architecture for Adiabatic Quantum Computation. arXiv.org:quant-ph/0403090, (2004)
Kleinberg, J.M., Rubinfeld, R.: Short paths in expander graphs. In: Proceedings of the 37th FOCS (1996)
Markov, I.L., Shi, Y.: Simulating quantum computation by contracting tensor networks. SIAM J. Comput. 38(3), 963–981 (2008)
Mizel A., Lidar D.A., Mitchell M.: Simple proof of equivalence between adiabatic quantum computation and the circuit model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 070502 (2007)
Rezakhani A.T., Kuo W.-J., Hamma A., Lidar D.A., Zanardi P.: Quantum adiabatic brachistochrone. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 080502 (2009)
Robertson N., Seymour P.D.: Graph minors. xiii: the disjoint paths problem. J. Comb. Theory Ser. B 63(1), 65–110 (1995)
Rose, G., Bunyk, P., Coury, M.D., Macready, W., Choi, V.: Systems, Devices, and Methods For Interconnected Processor Topology. US Patent Application US2008/0176750, July 24, (2008)
Thomson L.F.: Introduction to Parallel Algorithms and Architectures: Arrays, Trees, Hypercubes. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, V. Minor-embedding in adiabatic quantum computation: II. Minor-universal graph design. Quantum Inf Process 10, 343–353 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-010-0200-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-010-0200-3