Abstract
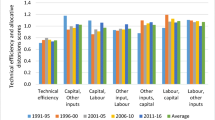
This contribution investigates the efficiency of water suppliers in rural areas of East and West Germany. A non-radial measure of input specific allocative inefficiency is used to reduce the distributional dependency with respect to the inefficiency parameters. It is based on the demand system of a flexible cost function for the variable inputs labour, energy and chemicals modelled by applying a modified symmetric generalized McFadden functional form. Concavity restrictions, as required by economic theory, are imposed. The analysis reveals that efforts towards increasing suppliers’ allocative efficiency should focus on the relatively inefficient usage of the input chemicals. The input specific allocative model specification was found to be superior to the overall allocative specification.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The problem of specifying an estimable input system that incorporates both technical and allocative inefficiency as well as the satisfactorily derivation of the relationship between allocative inefficiency in the input demand equations and economic inefficiency in the cost function has come to be known as the ‘Greene problem’ (see e.g. Kumbhakar, 1997).
Opting for empirical results with a very high significance one probably would have estimated an error components model by applying a translog functional form and using an easy to handle ‘black box’ estimation tool as e.g. FRONTIER provides.
References
Alchian AA (1965) Some economics of property rights. Il Polit 30:816–829
Arrow K (1985) The economics of agency. In: Pratt JW (ed) Principles and agents: the structure of business, pp 37–51
Bhattacharayya A, Harries TR, Narayanan R, Raffiee K (1995) Technical efficiency of rural water utilities. J Agric Resour Econ 20:373–391
Briscoe J (1995) Der Sektor Wasser und Abwasser in Deutschland – Qualität seiner Arbeit. Bedeutung für Entwicklungsländer gwf 136:422–432
Christopoulos D, Loizides J, Tsionas EG (2001) Efficiency in European railways: not as inefficient as one might think. J Appl Econ IV:63–88
Conrad K, Jorgenson DW (1977) Tests of a model of production for the Federal Republic of Germany. Eur Econ Rev 10:51–57
Craig SG, Airola J, Tipu M (2003) The effect of institutional form on airport governance efficiency. Working Papers. Department of Economics, University of Houston, Houston, USA
Diewert WE, Wales TJ (1987) Flexible functional form and global curvature conditions. Econometrica 55:43–68
Estache A, Rossi MA (2002) How different is the efficiency of public and private water companies in Asia? World Bank Econ Rev 16:139–148
Ewers H-J, Botzenhart K, Jekel M (2001) Optionen, Chancen und Rahmenbedingungen einer Marktöffnung für eine nachhaltige Wasserversorgung, Endbericht zum BMWI-Forschungsvorhaben 11/00
Hanusch H, Cantner U (1991) Produktion öffentlicher Leistungen - Effizienz und technischer Fortschritt. Jahrbuch für Nationalökonomie und Statistik 208:369–384
Kumbhakar SC (1989) Estimation of technical efficiency using flexible functional form and panel data. J Business Econ Stat 7:253–258
Kumbhakar SC (1997) Modeling allocative inefficiency in a translog cost function and cost share equations: an exact relationship. J Econometr 76:351–356
Kumbhakar SC, Lovell CA (2000) Stochastic frontier analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lau LJ (1978) Testing and imposing monotonicity, convexity and quasi-convexity constraints. In: Fuss M, McFadden D (eds) Production economics: a dual approach to theory and applications, volume I: the theory of production. pp 409–453
Lau LJ (1986) Functional forms in econometric model building. In: Griliches Z, Intriligator MD (eds) Handbook of econometrics, Vol III. pp 1515–1565
Niskanen WA (1971) Bureaucracy and representative government. Chicago, New York
O’Donnell CJ (2002) Parametric estimation of technical and allocative efficiency in U.S. agriculture. In: Ball E, Norton GW (eds) Agricultural productivity: measurement and sources of growth. Boston/Dordrecht/London
Pierani P, Rizzi PL (1999) Technology and efficiency in a panel of italian dairy farms: a SGM restricted cost function approach. Working Paper. Department of Economics, University of Siena
Rask K (1995) The structure of technology in Brazilian sugarcane production, 1975–87 – an application of a modified symmetric generalized McFadden cost function. J Appl Econmetr 10:221–232
Sauer J, Strecker D (2003) Enhancing the supply efficiency on firm and sector level – corporate strategies in the water market. J Public Nonprofit Serv 26:259–282
Sauer J (2005a) The optimal organisation of the water supplying industry – an economic perspective. J Econ Stat 225:225–244
Sauer J (2005b) Economies of scale and firm size optimum in rural water supply. Water Resour Res 41:1–13
Sauer J (2006) Economic theory and econometric practice: parametric efficiency analysis. Empirical Economics, online 7/2006
Vest P (1998) Die formelle Privatisierung öffentlicher Unternehmen – Eine Effizienzanalyse anhand betriebswirtschaftlicher Kriterien der Rechtsformwahl. J Public Nonprofit Serv 21:189–202
Wang H-J, Schmidt P (2002) One-step and two-step estimation of the effects of exogenous variables on technical efficiency levels. Working Paper. Michigan State University
Wiley DE, Schmidt WH, Bramble WJ (1973) studies of a class of covariance structure models. J Am Stat Assoc 68:317–323
Williamson OE (1985) The economic institutions of capitalism. The Free Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sauer, J., Frohberg, K. Allocative efficiency of rural water supply – a globally flexible SGM cost frontier. J Prod Anal 27, 31–40 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11123-006-0024-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11123-006-0024-4