Abstract
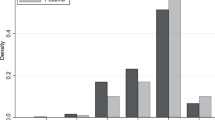
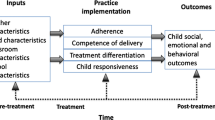
Although there is evidence that school-based prevention programs can produce positive effects on students’ academic and behavioral functioning, the ability of teachers to sustain high-quality implementation remains an open and vexing question. Because teachers are often the intervention agents in school-based prevention programs, assessing both their adherence to program procedures and their competence in program delivery is critical for ensuring student responsiveness to prevention programs, which in turn may impact their efficacy. The current study assessed treatment fidelity of implementation of the Olweus’ Bullying Prevention Program (OBPP) in two urban middle schools. Trained observers completed 280 observations of teachers’ delivery of the class meeting component of the OBPP and rated teachers’ instructional and procedural adherence and competence of delivery and students’ responsiveness. Analyses using multilevel modeling indicated that competence of delivery was significantly related to student responsiveness above and beyond teacher instructional behavior adherence, such that class meetings conducted with higher instructional adherence and procedural competence resulted in higher student responsiveness to the program after controlling for the clustered nature of teachers, and several observation-level and teacher-level covariates. This study highlights the need for strategies to increase teacher use of effective instructional practices and competence with program procedures to enhance the efficacy of prevention programming in schools.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkel, C., Mauricio, A. M., Schoenfelder, E., & Sandler, I. N. (2011). Putting the pieces together: An integrated model of program implementation. Prevention Science, 12, 22–33. doi:10.1007/s11121-010-0186-1.
Bierman, K. L. (2011). The promise and potential of studying the “invisible hand” of teacher influence on peer relations and student outcomes: A commentary. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 32, 297–303. doi:10.1016/j.appdev.2011.04.004.
Carroll, K. M., Nich, C., Sifry, R. L., Nuro, K. F., Frankforter, T. L., Ball, S. A., & Rounsaville, B. J. (2000). A general system for evaluating therapist adherence and competence in psychotherapy research in the addictions. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 57, 225–238. doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(99)00049-6.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Domitrovich, C. E., Moore, J. E., & Greenberg, M. T. (2012). Maximizing the effectiveness of social-emotional interventions for young children through high-quality implementation of evidence-based interventions. In B. Kelly & D. F. Perkins (Eds.), Handbook of implementation science for psychology in education (pp. 207–229). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Durlak, J. A. (2010). The importance of doing well in whatever you do: A commentary on the special section, “Implementation research in early childhood education”. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 25, 348–357. doi:10.1016/j.ecresq.2010.03.003.
Durlak, J. A., & DuPre, E. P. (2008). Implementation matters: A review of research on the influence of implementation on program outcomes and the factors affecting implementation. American Journal of Community Psychology, 41, 327–350. doi:10.1007/s10464-008-9165-0.
Durlak, J. A., Weissberg, R. P., Dymnicki, A. B., Taylor, R. D., & Schellinger, K. B. (2011). The impact of enhancing students’ social and emotional learning: A meta-analysis of school-based universal interventions. Child Development, 82, 405–432. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01564.x.
Ennett, S. T., Ringwalt, C. L., Thorne, J., Rohrbach, L. A., Vincus, A., Simons-Rudolph, A., et al. (2003). A comparison of current practice in school-based substance use prevention programs with meta-analysis findings. Prevention Sciences, 4, 1–14. doi:10.1023/A:1021777109369.
Farmer, T. W., Lines, M. M., & Hamm, J. V. (2011). Revealing the invisible hand: The role of teachers in children’s peer experiences. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 32, 247–256. doi:10.1016/j.appdev.2011.04.006.
Fixsen, D. L., Naoom, S. F., Blasé, K. A., Friedman, R. M., Wallace, F. (2005). Implementation research: A synthesis of the literature. Tampa, FL: University of South Florida, Louis de la Parte Florida Mental Health Institute, The National Implementation Research Network (FMHI Publication #231).
Forgatch, M. S., Patterson, G. R., & DeGarmo, D. S. (2005). Evaluating fidelity: Predictive validity for a measure of component adherence to the Oregon model of parent management training. Behavior Therapy, 36, 3–13. doi:10.1016/S0005-7894(05)80049-8.
Greenwood, C. R. (1996). The case for performance-based instructional models. School Psychology Quarterly, 11, 283–296. doi:10.1037/h0088935.
Hagermoser Sanetti, L. M., & Kratochwill, T. R. (2009). Toward developing a science of treatment integrity: Introduction to the special series. School Psychology Review, 38, 445–459.
Han, S. S., & Weiss, B. (2005). Sustainability of teacher implementation of school-based mental health programs. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 33, 665–679. doi:10.1007/s10802-005-7646-2.
Hedeker, D. (2014). Methods for multilevel ordinal data in prevention science. Prevention Science. doi:10.1007/s11121-014-0495-x.
Hirschstein, M. K., Van Schoiack Edstrom, L., Frey, K. S., Snell, J. L., & MacKenzie, E. P. (2007). Walking the talk in bullying prevention: Teacher implementation variables related to initial impact of the Steps to Respect program. School Psychology Review, 36, 3–21.
Humphrey, N., Lendrum, A., & Wigelsworth, M. (2013). Making the most out of school-based prevention: Lessons from the social and emotional aspects of learning (SEAL) programme. Emotional and Behavioural Difficulties, 18, 248–260. doi:10.1080/13632752.2013.819251.
Kelly, B., & Perkins, D. F. (2012). Handbook of implementation science for psychology in education. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Kern, L., & Clemons, N. H. (2007). Antecedent strategies to promote appropriate classroom behavior. Psychology in the Schools, 44, 65–75. doi:10.1002/pits.20206.
Limber, S. P. (2011). Development, evaluation, and future directions of the Olweus Bullying Prevention Program. Journal of School Violence, 10, 71–87. doi:10.1080/15388220.2010.519375.
Low, S., Van Ryzin, M. J., Brown, E. C., Smith, B. H., & Haggerty, K. P. (2014). Engagement matters: Lessons from assessing classroom implementation of Steps to Respect: A Bullying Prevention Program over a one-year period. Prevention Science, 15, 165–176. doi:10.1007/s11121-012-0359-1.
Matjasko, J. L., Vivolo-Kantor, A. M., Massetti, G. M., Holland, K. M., Holt, M. K., & Cruz, J. D. (2012). A systematic meta-review of evaluations of youth violence prevention programs: Common and divergent findings from 25 years of meta-analyses and systematic reviews. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 17, 540–552. doi:10.1016/j.avb.2012.06.006.
Olweus, D., & Limber, S. P. (2007). Olweus bullying prevention program: Teacher guide. Center City: Hazelden.
Sameroff, A. (2009). The transactional model of development: How children and contexts shape each other. Washington, D.C.: APA.
SAS Institute Inc. (2013). Configuration guide for SAS® 9.3 foundation for z/OS®. Cary: SAS Institute Inc.
Simonsen, B., Fairbanks, S., Breisch, A., Myers, D., & Sugai, G. (2008). Evidence-based practices in classroom management: Considerations for research to practice. Education and Treatment of Children, 31, 351–380. doi:10.1353/etc.0.0007.
Smith, P. K., Pepler, D., & Rigby, K. (2004). Bullying in schools: How successful can interventions be? Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Strambler, M. J., & McKown, C. (2013). Promoting student engagement through evidence-based action research with teachers. Journal of Educational & Psychological Consultation, 23, 87–114. doi:10.1080/10474412.2013.757153.
Sullivan, T. N., Sutherland, K. S., Farrell, A., & Taylor, K. (2014). Schools as venues for prevention programming. In K. Bosworth (Ed.), Prevention science in school settings: Complex relationships and processes. New York: Springer. In press
Sutherland, K. S., Wehby, J. H., & Copeland, S. R. (2000). Effect of varying rates of behavior-specific praise on the on-task behavior of students with EBD. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 8, 2–8. doi:10.1177/106342660000800101.
Sutherland, K. S., Alder, N., & Gunter, P. L. (2003). The effect of varying rates of opportunities to respond to academic requests on the classroom behavior of students with EBD. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 11, 239–248. doi:10.1177/10634266030110040501.
Sutherland, K. S., Lewis-Palmer, T., Stichter, J., & Morgan, P. L. (2008). Examining the influence of teacher behavior and classroom context on the behavioral and academic outcomes for students with emotional or behavioral disorders. The Journal of Special Education, 41, 223–233. doi:10.1177/0022466907310372.
Sutherland, K. S., McLeod, B. D., Conroy, M. A., Abrams, L., Smith, M. M. (2013). Preliminary psychometric properties of the BEST in CLASS Adherence and Competence Scale. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders. Advance online publication. doi:10.1177/1063426613493669
Virginia Department of Education. (2014). Virginia Department of Education Fall Membership. Retrieved February 26, 2014, fromhttp://www.doe.virginia.gov/statistics_reports/ enrollment/fall_membership/index.shtml.
Vo, A., Sutherland, K. S., & Conroy, M. A. (2012). BEST in CLASS: A classroom-based model for ameliorating problem behavior in early childhood settings. Psychology in the Schools, 49, 402–415. doi:10.1002/pits.21609.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Cooperative Agreement 1U01CE001956 from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goncy, E.A., Sutherland, K.S., Farrell, A.D. et al. Measuring Teacher Implementation in Delivery of a Bullying Prevention Program: the Impact of Instructional and Procedural Adherence and Competence on Student Responsiveness. Prev Sci 16, 440–450 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-014-0508-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-014-0508-9