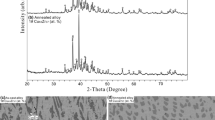
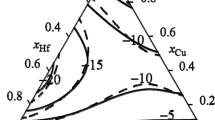
The thermodynamic assessment of the Cu-Ti-Zr system is carried out in the framework of the CALPHAD method. The Gibbs energy of the liquid alloys is described by the ideal associated solution model. The excess Gibbs energy of the solid solutions is described using the Redlich-Kister-Muggianu model. The Gibbs energy of intermetallic compounds with homogeneity region is described in the framework of the Compound Energy Formalism. A set of self-consistent parameters of models is obtained taking into account data on phase equilibria and thermodynamic properties of the liquid phase. The calculated isothermal and vertical sections of the phase diagram and liquidus and solidus surfaces are in satisfactory agreement with corresponding experimental data. Metastable transformations with participation of the supercooled liquid melts are calculated. Predicted concentration ranges of amorphization are in satisfactory agreement with experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. F. Bunshah, D. Osterberg, E. Ence, and H. Margolin, “Further studies on active-eutectoid alloys of titanium,” in: Technical Report of United States Department of Commerce (WADD TR 60-95), New York (1960), p.73.
E. Ence and H. Margolin, “A study of the Ti-Cu-Zr system and the structure of Ti2Cu,” Trans. Metal. Soc. AIME, 221, 320–322 (1961).
J. Dutkiewicz and T. B. Massalski, “Search for new amorphous materials in ternary metal systems, ” in: Proc. of the Regional Conference on Metallurgical Processes, Czestochowa, Poland (1983), pp. 308–312.
C. G. Woychik and T. B. Massalski, “Phase diagram relationships in the system copper-titanium-zirconium,” Z. Metallkd., 79, No. 3, 149–153 (1988).
V. N. Chebotnikov and V. V. Molokanov, “Structure and properties of amorphous and crystalline alloys in section Ti2Cu-Zr2Cu in the Ti-Zr-Cu system,” Izv. AN SSSR, Neorg. Mater., 26, No. 5, 960–964 (1990).
Yu. K. Kovneristyi and A. G. Pashkovskaya, “Bulk amorphization of alloys in the intermetallic-containing Ti-Cu-Zr system,” in: Amorphous (Glass Forming) Metal Materials [in Russian], Inst. Metallurg. RAN, Moscow (1992), pp. 153–157.
U. E. Klotz, C. Liu, P. J. Uggowitzer, et al., “Experimental investigation of the Cu-Ti-Zr system at 800°C,” Intermetallics, 15, 1666–1671 (2007).
A. M. Storchak-Fedyuk, V. M. Petyukh, and L. V. Artyukh, “Investigation of cast alloys of the Cu-Ti-Zr system,” in: Modern Material Science Problems [in Russian], Ser. Fiz. Khim. Osnovy Tekhnol. Poroshk. Mater., Kiev (2007), pp. 22–26.
A. R. Abdulov, M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, and A. A. Solorev, “Enthalpy of mixing of liquid Cu-Ti-Zr alloys,” Metally, No. 1, 28–34 (2007).
M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, A. N. Fesenko, and A. R. Abdulov, “Thermodynamics of liquid alloys and metastable phase transformations in the copper-titanium system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 44, No. 5–6, 259–270 (2005).
A. A. Turchanin, I. A. Tomilin, M. A, Turchanin, et al., “Enthalpies of formation of liquid and amorphous Zr-Cu alloys,” J. Non-Crystal. Sol., 250-252, 582–585 (1999).
U. Thiedermann, M. Rosner-Kuhn, K. Drewes, et al., “Mixing enthalpy measurements of liquid Ti-Zr, Fe-Ti-Zr and Fe-Ni-Zr alloys,” J. Steel Research, 70, No. 1, 3–8 (1999).
R. Arroyave, T. W. Eagar, and L. Kaufman, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Cu-Ti-Zr system, ” J. All. Compd., 351, No. 1–2, 158–170 (2003).
H. Kumar, I. Ansara, P. Wollants, and L. Delaey, “Thermodynamic optimization of the Cu-Ti system, ” Z. Metallkd., 87, No. 8, 666–672 (1996).
K.-J. Zeng, M. Haemaelaeinen, and H. L. Lukas, “A new thermodynamic description of the Cu-Zr system,” J. Phase Equilibria, 15, No. 6, 577–586 (1994).
H. Kumar, P. Wollants, and L. Delaey, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Ti-Zr system and calculation of the Nb-Ti-Zr phase diagram,” J. All. Compd., 205, No. 1, 121–127 (1994).
T. Velikanova and M. A. Turchanin, “Cu-Ti-Zr,” in: G. Effenberg and S. Ilyenko (eds.) Ternary Alloy Systems. Phase Diagrams, Crystallographic and Thermodynamic Data, Vol. 11C3, Springer-Verlag, Germany, Heidelberg, Berlin (2006), pp. 436–464.
D. Kim, B.-J. Lee, and N. J. Kim, “Thermodynamic approach for predicting the glass forming ability of amorphous alloys,” Intermetallics, 12, No. 10–11, 1103–1107 (2004).
A. T. Dinsdale, “SGTE data for pure elements,” CALPHAD, 15, No. 4, 317–425 (1991).
M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, and A. R. Abdulov, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Cu-Ti-Zr system. I. Cu-Ti system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 47, No. 5–6, 344–360 (2008).
M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, and A. R. Abdulov, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Cu-Ti-Zr system. II. Cu-Zr and Ti-Zr systems,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 47, 2008, No. 7–8, 428–446 (2008).
Y. M. Muggianu, M. Gambino, and J. P. Bros, “Enthalpies of formation of liquid alloys bismuth-gallium-tin at 723 K. Choice of an analytical representation of integral and partial excess functions of mixing,” J. Chimie Phys., 72, No. 1, 83–88 (1975).
M. A. Turchanin, I. V. Belokonenko, and P. G. Agraval, “The application of the theory of ideal associated solution for description of the temperature-concentration dependence of the thermodynamic properties of binary melts,” Rasplavy, No. 1, 58–69 (2001).
M. Hillert, “The compound energy formalism,” J. All. Compd., 320, 161–176 (2001).
I. Ansara, T. G. Chart, A. Fernandez Guillermet, et. al., “Group 2: Alloy system I. Thermodynamic modeling of selected topologically close-packed intermetallic compounds,” CALPHAD, 21, No. 2, 171–218 (1997).
X. Yan, X.-Q. Chen, A. Gritsiv, et al., “Crystal structure, phase stability and elastic properties of the Laves phase ZrTiCu2,” Intermetallics, 16, 651–657 (2008).
M. A. Turchanin, A. R. Abdulov, and P. G. Agraval, “Thermodynamic modeling of concentration ranges of amorphization of ternary metal melts,” in: Proc. Int. Conf. HighMatTech 2007 [in Russian] (October 15–19, 2007, Kiev, Ukraine), Kiev (2007), p. 87.
M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, and A. A. Turchanin, “Modeling of the temperature-concentration dependence of thermodynamic properties and metastable phase equilibria in the binary Ni-(Ti, Zr, Hf) systems,” in: Proc. 6th Int. School-Conference on Phase Diagrams in Materials Science (October 14–20, 2001, Kiev, Ukraine), Kiev (2001), p. 39.
M. A. Turchanin and P. G. Agraval, “Calculation of metastable phase equilibria with participation of supercooled liquid and assessment of concentration ranges of melt amorphization in the (Co, Ni, Cu)-IVAMe systems, ” in: Physics and Chemistry of Condensed Systems and Phase Boundaries (Collected Scientific Papers) [in Ukrainian], Vyd. Poligraf. Tsenter Kyiv Univ., Kiev (2003), pp. 134–141.
M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, and A. R. Abdulov, “Thermodynamic properties and glass forming ability of (Co, Ni, Cu)-(Ti, Zr, Hf) binary liquid alloys,” in: Proc. Int. Conf. on Modern Materials Science: Achievements and Problems (September 26–30, 2005, Kiev, Ukraine), Vol. 1, Kiev (2005), p. 146.
R. B. Schwarz, P. Nash, and D. Turnbull, “The use of thermodynamic models in the prediction of the glass-forming range of binary alloys,” J. Mater. Res., 2, No. 4, 456–460 (1987).
R. Borman, “Thermodynamics of undercooled liquids and its application to amorphous phase formation, ” Mater. Sci. Eng., A178, 55–60 (1994).
M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, and A. R. Abdulov, “Thermodynamic assessment of the copper-hafnium system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 47, No. 3–4, 223–233 (2008).
D. Xu, B. Lohwongwatana, G. Duan, et al., “Bulk metallic glass formation in binary Cu-rich alloy series — Cu100−x Zrx (x = 34, 36, 38.2, 40 at.%) and mechanical properties of bulk Cu64Zr36 glass,” Acta Materialia, 52, 2621–2624 (2004).
T. Shindo, Y. Waseda, A. Inoue, “Prediction of critical compositions for bulk glass formation in La-based, Cu-based and Zr-based ternary alloys,” Mater. Trans. JIM, 44, No. 3, 351–357 (2003).
A. Inoue, W. Zhang, T. Zhang, and K. Kurosaka, “High-strength Cu-based bulk glassy alloys in Cu-Zr-Ti and Cu-Hf-Ti ternary systems,” Acta Mater., 49, Issue 14, 2645–2652 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 47, No. 9–10 (463), pp. 106–129, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turchanin, M.A., Velikanova, T.Y., Agraval, P.G. et al. Thermodynamic assessment of the Cu-Ti-Zr system. III. Cu-Ti-Zr system. Powder Metall Met Ceram 47, 586–606 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-008-9062-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-008-9062-y