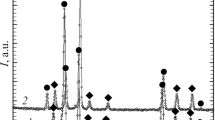
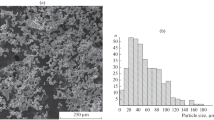
The mechanical behavior of porous titanium compacts is analyzed. Four-point bending, compression, and Brazilian tests of the samples are conducted. The influence of the porosity and particle size of the initial powder on Young's modulus, ultimate strength, and strain-to-failure of porous titanium is examined. The dependence of the strength and plasticity of compacts on their porosity is analyzed using different tests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. K. Radchenko, “Mechanical properties of unsintered pressing. I. Phenomenological relations for unsintered pressing strength,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 43, No. 9–10, 447–460 (2004).
A. K. Radchenko, “Mechanical properties of green compacts. II. Effect of powder relative bulk density on the strength of compacts with different forming temperature conditions,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 43, No. 11–12, 552–563 (2004).
M. Yu. Bal'shin, Powder Metallurgy [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1948), p. 332.
V. V. Pokropivnyi and V. V. Skorokhod, Cohesion (Adhesion, Seizure, Connection, Welding) of Interparticle Surfaces and Formation of Grain Boundaries in Sintering, Return, Recrystallization, Superplasticity, Friction, and Failure [in Russian], Preprint No. 95-2, Inst. Probl. Materialoved. NAN Ukrainy, Kiev (1995), p. 60.
S. A. Firstov, Yu. N. Podrezov, N. I. Danilenko, et al., “Role of relaxation in hardening of nanocrystalline materials produced by severe plastic deformation,” Fiz. Tekh. Vys. Davl., 13, No. 3, 37–47 (2003).
E. M. Borisovskaya, V. A. Nazarenko, Yu. N. Podrezov, et al., “Mechanical properties of powder titanium at different production stages. I. Densification curves for powder titanium billets,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 47, No. 7–8, 406–413 (2008).
A. V. Vdovichenko and Yu. N. Podrezov, “Evolution of dynamic Young's modulus and damping capability of porous iron,” Metallofiz. Noveish. Tekhnol., 27, No. 11, 1429–1440 (2005).
A. V. Vdovichenko, L. A. Ivanchenko, and N. D. Pinchuk, “Determining the elastic characteristics of calcium-based composites with ultrasonic resonance spectroscopy,” Metallofiz. Noveish. Tekhnol., 26, No. 9, 1215–1226 (2004).
O. V. Vdovychenko, V. S. Voropaev, and A. N. Slipenyuk, “Effect of microstructure on Young's modulus of extruded Al-SiC composites studied by resonant ultrasound spectroscopy,” J. Mater. Sci., 41, No. 24, 8329–8338 (2006).
J. Gerland and N. M. Parich, “Microstructural aspects of failure of two-phase alloys,” in: Failure of Nonmetals and Composite Materials [Russian translation], Vol. 7, Part 1, Mir, Moscow (1976), pp. 473–512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 47, No. 9–10 (463), pp. 46–54, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borisovskaya, E.M., Nazarenko, V.A., Podrezov, Y.N. et al. Mechanical properties of powder titanium at different production stages. II. Mechanical behavior of porous titanium compacts. Powder Metall Met Ceram 47, 538–545 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-008-9056-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-008-9056-9