Abstract
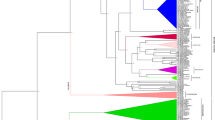
Analysis of evolving microRNA repertoires within the plant domain can further corroborate our understanding of genome evolution and plasticity. An extensive collection of relatively unbiased miRBase-registered plant miRNAs and predicted unlisted MIRs from 23 plant ESTs were examined. As a result, 4324 pre-miRNAs were predicted and classified in 656 miRNA gene families with mostly being transposons (57.81%). From 216 newly identified pre-miRNAs, 103 distinct types belonged to reduced complexity/repeated regions. Collinearity between the numbers of miRNAs in each species with the relevant sizes of genomes was absent. Duplications of MIRs were evident, with higher MIR paralogs in Liliopsida compared with dicots. Due to the lack of an apparent pattern of phylogeny, Dollo maximum parsimony was used that established the acceleration of gains and potential losses of miRNA gene families within Mesangiospermae during the last 200 million years ago. Phylogenetic analysis of Liliopsida in contrast to Eudicotyledons agreed with the reconstructed tree based on the possible expansion of distinguished MIR families. In marked contrast to dicots, the degrees of resemblance in Liliopsida were higher than their direct predecessors. Analyses of recent monophyletic lineages were illustrative of miRNA horizontal genes transfer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Sung GH, Spatafora JW, Carrington JC (2004) Evolution of microRNA genes by inverted duplication of target gene sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 36(12):1282–1290
Alptekin B, Badak H (2016) Wheat miRNA ancestors evident by transcriptome analysis of A, B, and D genome donors. Funct Integr Genomics 17:171–187
Ambros V, Bartel B, Bartel DP, Burge CB, Carrington JC, Chen X, Dreyfuss G, Eddy SR, Griffiths-Jones S, Marshall M, Matzke M, Ruvkun G, Tuschl T (2003) A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA 9(3):277–279
Arteaga-Vázquez M, Caballero-Pérez J, Vielle-Calzada JP (2006) A family of microRNAs present in plants and animals. Plant Cell 18:3355–3369
Axtell MJ (2013) Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:137–196
Axtell MS, Meyers BC (2018) Revisiting criteria for plant micro RNA annotation in the era of big data. Plant Cell 30:272–284
Axtell MJ, Westholm J, Lai EC (2011) Vive la difference: biogenesis and evolution of micro RNA in plants and animals. Genome Biol 12:221–234
Babashpour S, Aminzadeh S, Farrokhi N, Karkhane A, Haghbeen K (2012) Characterization of a chitinase (Chit62) from Serratia marcescens B4A and its efficacy as a bioshield against plant fungal pathogens. Biochem Genet 50:722–735
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics biogenesis mechanism and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bladrich P, Beric A, Meyers BC (2018) Despacito: the slow evolutionary changes in plant microRNAs. Curr Opin Plant Biol 42:10–22
Bonnet E, De Peer YV, Rouze P (2006) The small RNA world of plants. New Phytopathologist 171:451–458
Borges F, Martienssen RA (2015) The expanding world of small RNAs in plants. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm4085
Budak H, Akpinar BA (2015) Plant miRNAs: biogenesis organization and origins. Funct Integr Genomics 15:523–531
Budak H, Bulut R, Kantar M, Alptekin B (2015) MicroRNA nomenclature and the need for a revised naming prescription. Brief Funct Genomics:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/elv026
Charostecki U et al (2017) Evolutionary footprints reveal insights into plant biogenesis. Plant Cell 29:1248–1261
Cui J, You C, Chen X (2017) The evolution of microRNAs in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 35:61–67
Cuperus JT, Fahlgren N, Carrington JC (2011) Evolution and functional diversification of miRNA genes. Plant Cell 23:431–442
De-Felippes FF et al (2008) Evolution of Arabidopsis thaliana microRNAs from random sequences. RNA 14:2455–2459
Ehrenreich IM, Purugganan MD (2008) Sequence variation of microRNAs and their binding sites in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 146(4):1974–1982
Fahlgren N, Howell MD, Kasschau KD, Chapman EJ, Sullivan CM, Cumbie JS, Givan SA, Law TF, Grant SR, Dangl JL, Carrington JC (2007) High-throughput sequencing of Arabidopsis microRNAs: evidence for frequent birth and death of miRNA genes. PLoS One 2:e219
Farris JS (1977) Phylogenetic analysis under Dollo’s law. Syst Zool 26:77–88
Fei Q, Zhang Y, Xia R, Meyers BC (2016) Small RNAs add zing to the zig-zag-zig modeled of plant defenses. MPMI 29(3):165–169
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP - Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 32). Cladistics 5:164–166
Fortune PM, Roulin A, Panaud O (2008) Horizontal transfer of transposable elements in plants. Comm Integ Biol 1(1):74–77
Fromm B, Billipp T, Peck LE, Johansen M, Tarver JE, King BL, Newcomb JM, Sempere LF, Flatmark K, Hovig E, Peterson KJ (2015) A uniform system for the annotation of vertebrate microRNA genes and the evolution of the human microRNAome. Annu Rev Genet 49(1):213–242
Gao D et al (2014) Annotation and sequence diversity of transposable elements in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Front Plant Sci 5:339
Griffiths-Jones S (2004) The microRNA registry. Nucleic Acids Res 32(D):109–111
Griffiths-Jones S et al (2006) MIRBase: microRNA sequences targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 34D:140–144
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, Van Dongen S, Enright AJ (2008) miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 36 D:154–158
Guerra-Assunção JA, Enright AJ (2012) Large-scale analysis of microRNA evolution. BMC Genomics 13:218
Hajieghrari B, Farrokhi N, Goliaei B, Kavousi K (2015) Computational identification characterization and analysis of conserved miRNAs and their targets in Amborella Trichopoda. J Data Mining Genomics Proteomics 6:2
Hajieghrari B, Farrokhi N, Goliaei B, Kavousi K (2016) Identification and characterization of novel miRNAs in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by computational methods. MicroRNA 5:66–77
Hajieghrari B, Farrokhi N, Goliaei B, Kavousi K (2017) Computational identification of microRNAs and their transcript target(s) in field mustard (Brassica rapa L). Iranian J Biotech 15(1):22–32
Hajieghrari B, Farrokhi N, Goliaei B, Kavousi K (2019a) The role of microRNAs in defense against viral phytopathogens. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 107:8–13
Hajieghrari B, Farroki N, Goliaei B, Kavousi K (2019b) In silico identification of conserved miRNAs from Physcomitrella patens ESTs and their target characterization. Curr Bioinform 14(1):33-42
Hausser J, Zavolan M (2014) Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions- beyond repression of gene expression. Nat Rev Genet 15:599–612
Hedges SB, Marin J, Suleski M, Paymer M, Kumar S (2015) Tree of life reveals clock-like speciation and diversification. Mol Biol Evol 32:835–845
Hertel J, Stadler PF (2015) The expansion of animal microRNA families revisited. Life 5:905–920
Hou J et al (2019) Non-coding RNAs and transposable elements in plant genomes: emergence regulatory mechanisms and roles in plant development and stress response. Planta. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-os1667/sw
Jiu S, Zhu X, Wang J, Zhang C, Mu Q, Wang C, Fang J (2015) Genome-Wide Mapping and Analysis of Grapevine MicroRNAs and Their Potential Target Genes. The Plant Genome 8(2):plantgenome2014.12.0091
Jones-Rhoades MW (2012) Conservation and divergence in plant microRNAs. Plant Mol Biol 80(1):3–16
Li A, Mao L (2007) Evolution of plant microRNA gene families. Cell Res 17(3): 212-218
Li Y, Li C, Xia J, Jin Y (2011) Domestication of transposable elements into MicroRNA genes in plants. PLoS One 6:e19212
Liu H, Yu H, Tang G, Huang T (2018) Small but powerful: the function of micro RNA in plant development. Plant Cell Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2246-5
Marco A, Ninova M, Ronshaugen M, Griffiths-Jones S (2013) Clusters of microRNAs emerge by new hairpins in existing transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res 41(16):7745–7752
Miyoshi K, Miyoshi T, Siomi H (2010) Many ways to generate microRNA-like small RNAs: non-canonical pathways for microRNA production. Mol Genet Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-010-0556-1
Mohammad J, Siepel A, Lia EC (2014) Diverse modes of evolutionary emergence and flux of conserved microRNA clusters. RNA 20:1850–1863
Mukherjee K, Campos H, Kolaczkowski B (2013) Evolution of animal and plant dicers: early parallel duplications and recurrent adaptation of antiviral RNA binding in plants. Mol Biol Evol 30:627–641
Nozawa M, Miura S, Nei M (2012) Origins and evolution of microRNA genes in plant species. Genome Biol Evol 4(3):230–239
Nozawa M et al (2016) Evolutionary transitions of microRNA-target pairs. Genome Biol Evol. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evw092
Obbard DJ, Gordon KHJ, Buck AH, Jiggins FM (2009) The evolution of RNAi as a defense against viruses and transposable elements. Phil Trans Soc B 364:99–115
Pelaez P, Sanchez F (2013) Small RNAs in plant defense responses during viral and bacterial interactions: similarities and differences frontiers in plant. Science 4:343
Piednoel M, Carrete-Vega G, Renner SS (2013) Characterization of the LTR retrotransposon repertoire of a plant clade of six diploids and one tetraploid species. Plant Cell J 75:699–709
Piriyapongsa J, Jordan IK (2008) Dual coding of siRNAs and miRNAs by plant transposable elements. RNA 14:814–821
Robinson DF, Foulds LR (1981) Comparison of phylogenetic trees. Math Biosci 53:131–147
Sarilar V (2013) Allopolyploidy has a moderate impact on restructuring at three contrasting transposable element insertion sites in resynthesized Brassica napus allotetraploids. New Phytol 198:593–604
Shabalina SA, Koonin EV (2008) Origins and evolution of eukaryotic RNA interference. Trends Ecol Evol 23(10):578–587
Caballero J, Smit AF, Hood L, Glusman G (2014) Realistic artificial DNA sequences as negative controls for computational genomics. Nucl. Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku356
Smith LM (2015) Rapid divergence and high diversity of miRNAs and MIRNA targets in the Camelineae. Plant J 81:597–610
Soltis PS, Marchant DB, Van de Peer Y, Soltis DE (2015) Polyploid and genome evolution in plants. Curr Opin Genetics Dev 35:119–125
Springer NM, Li Q, Lisch D (2016) Creating order from chaos: epigenome organization dynamics in plants with complex genomes. Plant Cell 28:314–325
Sun J, Zhou M, Mao Z, Li C (2012) Characterization and evolution of microRNA genes derived from repetitive elements and duplication events in plants. PLoS One 7:e340
Tarver JE, Donoghue PCJ, Peterson KJ (2012) Do miRNAs have a deep evolutionary history? BioEssay 34(10):857–866
Tarver JE, Sperling EA, Nailor A, Heimberg AM, Robinson JM, King BL, Pisani D, Donoghue PCJ, Peterson KJ (2013) miRNAs: small genes with big potential in metazoan phylogenetics. Mol Biol Evol 30(11):2369–2384
Tarver JE et al (2018) Well-annotated microRNAomes do not evidence pervasive miRNA loss. Genome Biol 10(6):1457–1470
Taylor RS, Tarver JE, Hiscock SJ, Donoghue PCJ (2014) Evolutionary history of plant microRNAs. Trends Plant Sci 19(3):175–182
Taylor RS, Tarver JE, Foroozani A, Donoghue PC (2017) MicroRNA annotation of plant genomes-do it right or not at all. BioEssays 39(2):1600113
Thampson RC, Platchetzki DC, Mahler DL, Moore BR (2014) A critical appraisal of the use of microRNA data in phylogenetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(35):E3659–E3668
Vicient CM, Casacubrta JM (2017) Impact of transposable elements on polyploid plant genomes. Ann Bot 120:195–207
Voinnet O (2009) Origin biogenesis and activity of plant microRNAs. Cell 136:669–687
Wang S, Adam KL (2015) Duplicate gene divergence by changes in microRNA binding sites Genome. Biol Evol. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evvo23
Wang Y, Luo J, Zhang H, Lu J (2016) MicroRNAs in the same clusters evolve to coordinately regulate functionally related genes. Mol Biol Evol 33(9):2232–2247
Wang J, Mei J, Ren G (2019) Plant microRNAs: biogenesis homeostasis and degradation. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls201900360
Weber JM (2005) New human and mouse microRNA genes found by homology search. FEBS 272:59–73
Will CL, Luhrmann R (2011) Spliceosome structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:a003707
Yaakov B, Kashkush K (2011) Massive alterations of the methylation patterns around DNA transposons in the first four generations of a newly formed wheat allohexaploids. Genome 54:42–49
You C et al (2017) Conservation and divergence of small RNA pathways and micro RNAs in land plants. Genome Biol 18:158. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-017-1291-2
Zealy RW (2017) microRNA-binding proteins: specificity and function. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 8(5). https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna1414
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb P, Anderson TA (2006a) Plant micro RNA: a small regulatory molecule with big impact. Dev Biol 289:3–16
Zhang B, Pan X, Cannon CH, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2006b) Conservation and divergence of plant micro RNA genes. Plant J 46:243–259
Zhou Z, Wang Z, Li W, Fang C, Shen Y, Li C, Wu Y, Tian Z (2013) Comprehensive analyses of microRNA gene evolution in the paleopolyploid soybean genome. Plant J 76:332–344
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The data analysis and preparation of the first draft was carried out by B.H and N.F checked the data and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hajieghrari, B., Farrokhi, N. Investigation on the Conserved MicroRNA Genes in Higher Plants. Plant Mol Biol Rep 39, 10–23 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-020-01228-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-020-01228-9