Abstract
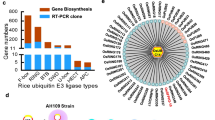
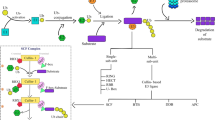
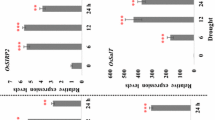
Nitrogen is the most critical nutrient for plant growth. To find potential strategies for enhancing both nitrogen use and tolerance to nitrogen deficiency in rice plants, we used the rice Full-length-cDNA OvereXpressor (FOX)-hunting system, a high-throughput phenotyping screen. After screening 3229 rice FOX lines, we identified 82 FOX-hunting lines that responded differently to nitrogen starvation. Among them, 11 FOX-hunting lines overexpressed putative E3 ligases, of which 6 were RING-type and 5 were F-box type E3 ligases. Of these, two lines overexpressed the same F-box type E3 ligase, OsFBL15. In vitro ubiquitination assay confirmed the auto-ubiquitination activity of OsFBL15. The overexpression of these E3 ligases altered the rice response to nitrogen deficiency and suggests a way to develop rice that is tolerant to nitrogen-deficient field conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMT:
-
AMmonium Transporter
- FOX:
-
Full-length cDNA OvereXpressor
- NRT:
-
NitRate Transporter
- RING:
-
Really Interesting New Gene
- −N:
-
Nitrogen deficiency
- +N:
-
Nitrogen sufficiency
- N:
-
Nitrogen
References
Abe K, Ichikawa H (2016) Gene overexpression resources in cereals for functional genomics and discovery of useful genes. Front Plant Sci 7:1359
Araus V, Vidal EA, Puelma T, Alamos S, Mieulet D, Guiderdoni E, Gutierrez RA (2016) Members of BTB gene family of scaffold proteins suppress nitrate uptake and nitrogen use efficiency. Plant Physiol 171:1523–1532
Bae H, Kim WT (2014) Classification and interaction modes of 40 rice E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes with 17 rice ARM-U-box E3 ubiquitin ligases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 444:575–580
Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M, Harper JW, Elledge SJ (1996) SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell 86:263–274
Cai H, Lu Y, Xie W, Zhu T, Lian X (2012) Transcriptome response to nitrogen starvation in rice. J Biosci 37:731–747
Callis J, Vierstra RD (2000) Protein degradation in signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:381–386
Chen L, Hellmann H (2013) Plant E3 ligases: flexible enzymes in a sessile world. Mol Plant 6:1388–1404
Cho SK et al (2006) Heterologous expression and molecular and cellular characterization of CaPUB1 encoding a hot pepper U-Box E3 ubiquitin ligase homolog. Plant Physiol 142:1664–1682
Du Z, Zhou X, Li L, Su Z (2009) PlantsUPS: a database of plants’ Ubiquitin Proteasome System. BMC Genomics 10:227
Fu H, Goring DR, Genschik P (2014) Reversible ubiquitylation in plant biology. Front Plant Sci 5:707
Gomi K, Sasaki A, Itoh H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2004) GID2, an F-box subunit of the SCF E3 complex, specifically interacts with phosphorylated SLR1 protein and regulates the gibberellin-dependent degradation of SLR1 in rice. Plant J 37:626–634
Good AG, Shrawat AK, Muench DG (2004) Can less yield more? Is reducing nutrient input into the environment compatible with maintaining crop production? Trends Plant Sci 9:597–605
Hakata M et al (2010) Production and characterization of a large population of cDNA-overexpressing transgenic rice plants using Gateway-based full-length cDNA expression libraries. Breeding Sci 60:575–585
Hong JP, Takeshi Y, Kondou Y, Schachtman DP, Matsui M, Shin R (2013) Identification and characterization of transcription factors regulating Arabidopsis HAK5. Plant Cell Physiol 54:1478–1490
Ichikawa T et al (2006) The FOX hunting system: an alternative gain-of-function gene hunting technique. Plant J 48:974–985
Jeong DH et al (2002) T-DNA insertional mutagenesis for activation tagging in rice. Plant Physiol 130:1636–1644
Jeong DH et al (2006) Generation of a flanking sequence-tag database for activation-tagging lines in japonica rice. Plant J 45:123–132
Jiang L et al (2013) DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice. Nature 504:401–405
Kant S, Bi YM, Rothstein SJ (2011) Understanding plant response to nitrogen limitation for the improvement of crop nitrogen use efficiency. J Exp Bot 62:1499–1509
Kazama Y, Hirano T, Saito H, Liu Y, Ohbu S, Hayashi Y, Abe T (2011) Characterization of highly efficient heavy-ion mutagenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 11:161
Kichey T, Hirel B, Heumez E, Dubois F, Le Gouis J (2007) In winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), post-anthesis nitrogen uptake and remobilisation to the grain correlates with agronomic traits and nitrogen physiological markers. Field Crop Res 102:22–32
Kim SM, Suh JP, Lee CK, Lee JH, Kim YG, Jena KK (2014) QTL mapping and development of candidate gene-derived DNA markers associated with seedling cold tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Mol Gen Genomics 289:333–343
Kumar A, Paietta JV (1998) An additional role for the F-box motif: gene regulation within the Neurospora crassa sulfur control network. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:2417–2422
Kuroda H, Takahashi N, Shimada H, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Matsui M (2002) Classification and expression analysis of Arabidopsis F-box-containing protein genes. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1073–1085
Kwon T et al (2012) Fine mapping and identification of candidate rice genes associated with qSTV11(SG), a major QTL for rice stripe disease resistance. Theor Appl Genet 125:1033–1046
Lechner E, Achard P, Vansiri A, Potuschak T, Genschik P (2006) F-box proteins everywhere. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:631–638
Li M et al (2011) Mutations in the F-box gene LARGER PANICLE improve the panicle architecture and enhance the grain yield in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 9:1002–1013
Liu Q, Chen X, Wu K, Fu X (2015) Nitrogen signaling and use efficiency in plants: what’s new? Curr Opin Plant Biol 27:192–198
Long TA, Tsukagoshi H, Busch W, Lahner B, Salt DE, Benfey PN (2010) The bHLH transcription factor POPEYE regulates response to iron deficiency in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell 22:2219–2236
Lorick KL, Jensen JP, Fang S, Ong AM, Hatakeyama S, Weissman AM (1999) RING fingers mediate ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2)-dependent ubiquitination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:11364–11369
Lyzenga WJ, Stone SL (2012) Abiotic stress tolerance mediated by protein ubiquitination. J Exp Bot 63:599–616
Marathi B et al (2012) QTL analysis of novel genomic regions associated with yield and yield related traits in new plant type based recombinant inbred lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.) BMC Plant Biol 12:137
McGinnis KM, Thomas SG, Soule JD, Strader LC, Zale JM, Sun TP, Steber CM (2003) The Arabidopsis SLEEPY1 gene encodes a putative F-box subunit of an SCF E3 ubiquitin ligase. Plant Cell 15:1120–1130
Mori M et al (2007) Isolation and molecular characterization of a Spotted leaf 18 mutant by modified activation-tagging in rice. Plant Mol Biol 63:847–860
Nakamura H et al (2007) A genome-wide gain-of function analysis of rice genes using the FOX-hunting system. Plant Mol Biol 65:357–371
Peng M, Hannam C, Gu H, Bi YM, Rothstein SJ (2007) A mutation in NLA, which encodes a RING-type ubiquitin ligase, disrupts the adaptability of Arabidopsis to nitrogen limitation. Plant J 50:320–337
Rice Full-Length cDNA Consortium (2003) Collection, mapping, and annotation of over 28,000 cDNA clones from japonica rice. Science 301:376–379
Sakamoto T, Matsuoka M (2008) Identifying and exploiting grain yield genes in rice. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:209–214
Sato T et al (2009) CNI1/ATL31, a RING-type ubiquitin ligase that functions in the carbon/nitrogen response for growth phase transition in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J 60:852–864
Shin R, Berg RH, Schachtman DP (2005) Reactive oxygen species and root hairs in Arabidopsis root response to nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium deficiency. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1350–1357
Smalle J, Vierstra RD (2004) The ubiquitin 26S proteasome proteolytic pathway. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:555–590
Socolow RH (1999) Nitrogen management and the future of food: lessons from the management of energy and carbon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:6001–6008
Sonoda Y, Ikeda A, Saiki S, von Wiren N, Yamaya T, Yamaguchi J (2003) Distinct expression and function of three ammonium transporter genes (OsAMT1;1-1;3) in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 44:726–734
Stone SL (2014) The role of ubiquitin and the 26S proteasome in plant abiotic stress signaling. Front Plant Sci 5:135
Stone SL, Callis J (2007) Ubiquitin ligases mediate growth and development by promoting protein death. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:624–632
Stone SL, Hauksdottir H, Troy A, Herschleb J, Kraft E, Callis J (2005) Functional analysis of the RING-type ubiquitin ligase family of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 137:13–30
Sujatha K et al (2011) Inheritance of bacterial blight resistance in the rice cultivar Ajaya and high-resolution mapping of a major QTL associated with resistance. Genet Res (Camb) 93:397–408
Tabuchi M, Abiko T, Yamaya T (2007) Assimilation of ammonium ions and reutilization of nitrogen in rice (Oryza sativa L.) J Exp Bot 58:2319–2327
Tsuchida-Mayama T, Nakamura H, Hakata M, Ichikawa H (2010) Rice transgenic resources with gain-of-function phenotypes. Breeding Sci 60:493–501
Vierstra RD (2009) The ubiquitin-26S proteasome system at the nexus of plant biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:385–397
Wan S et al (2009) Activation tagging, an efficient tool for functional analysis of the rice genome. Plant Mol Biol 69:69–80
Wang T, Uauy C, Till B, Liu CM (2010) TILLING and associated technologies. J Integr Plant Biol 52:1027–1030
Wang X, Bian Y, Cheng K, Zou H, Sun SS, He JX (2012) A comprehensive differential proteomic study of nitrate deprivation in Arabidopsis reveals complex regulatory networks of plant nitrogen responses. J Proteome Res 11:2301–2315
Wang H et al (2015) OsSIZ1, a SUMO E3 ligase gene, is involved in the regulation of the responses to phosphate and nitrogen in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 56:2381–2395
Yao N et al (2016) QTL mapping in three rice populations uncovers major genomic regions associated with African rice gall midge resistance. PLoS One 11:e0160749
Yee D, Goring DR (2009) The diversity of plant U-box E3 ubiquitin ligases: from upstream activators to downstream target substrates. J Exp Bot 60:1109–1121
Zeng LR, Park CH, Venu RC, Gough J, Wang GL (2008) Classification, expression pattern, and E3 ligase activity assay of rice U-box-containing proteins. Mol Plant 1:800–815
Zhang Y, Tan L, Zhu Z, Yuan L, Xie D, Sun C (2015) TOND1 confers tolerance to nitrogen deficiency in rice. Plant J 81:367–376
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. Tsuzumi Mito for taking care of rice plants, and Ms. Keiko Iida-Okada and Ms. Etsuko Sugai for their subdivision work of FOX-rice seeds. This work was supported by a grant from the Japan Society for Promotion of Science bilateral joint program to R.S. and under the framework of the International Cooperation Program (2015K2A2A4000129) managed by the National Research Foundation of Korea to C.-J.P. The production of FOX-rice lines was supported by grants from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan (Green Technology Project EF-1004 and Genomics for Agricultural Innovation, AMR-0001) and a funding for the biological resources from National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences (Tsukuba, Japan) to H.I.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
Representative FOX-hunting lines selected during the primary screening in nitrogen deficient condition (-N). The left side of each photo is Nipponbare control plants (WT) grown in -N. The right side of each photo is a tested FOX line. AD157 (A), AR013 (B), BI246 (C) and BM107 (D) show a tolerance phenotype to nitrogen deficiency, and AY004 (E) and BM137 (F) show a more susceptible phenotype to nitrogen deficiency condition compared to the control. The selected lines were transferred to soil for phenotypic analysis and seed production (DOCX 685 kb)
Fig. S2
The deduced amino acid sequence of OsFBL15 protein. The grey highlight indicates a predicted F-box motif. The lines indicate five leucine-rich repeats, which are numbered in superscript numbers (DOCX 226 kb)
Fig. S3
In vitro auto-ubiquitination assay for OsFBL15. Recombinant GST-OsFBL15 and GST proteins were incubated with ubiquitin and rice total protein extracts for 0 or 2 hours at 37 ºC. The total protein was prepared from rice plants grown in -N conditions for 7 days. Reaction mixtures were separated on 8% SDS-PAGE gel and the blotted proteins were detected with anti-Ub antibodies. The red line indicates the ubiquitinated protein (line) (DOCX 144 kb)
Table S1
(DOCX 20 kb)
Table S2
(DOCX 18 kb)
Table S3
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takiguchi, H., Hong, JP., Nishiyama, H. et al. Discovery of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases That Alter Responses to Nitrogen Deficiency Using Rice Full-Length cDNA OvereXpressor (FOX)-Hunting System. Plant Mol Biol Rep 35, 343–354 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-017-1027-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-017-1027-1