Abstract
Aims
Belowground carbon (C) input is a key component of the global C cycle. However, how does fencing affect Belowground net primary production (BNPP) and the contribution of root derived C to belowground C input remains poorly studied.
Methods
In this study, the in-growth soil cores-13C method was used to quantify net root C input. Five different plant communities of different fencing years (1 year, 5 years, 10 years, 25 years, 30 years) in the Loess Plateau of China, characterized by herbs and shrubs were investigated.
Results
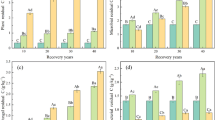
BNPP was increased with the increase of fencing years: 61.54~140.23 gC·m− 2·yr− 1. Root derived C in soil represented a considerable contribution to BNPP varying from 57 to 81 %, and the proportion of root derived C to BNPP was decreased with the fencing years. The contribution of root derived C to soil organic carbon (SOC) was 3 %~5 % during one-year growth.
Conclusions
Our results underline the fact that fencing is an effective means to improve the BNPP and plant community. Root derived C rather than root biomass contributes to the SOC sequestration in grassland soils with different fencing years. Fencing increases the contribution of root derived C to SOC mainly by increasing root C content.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
31 October 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-05173-8
References
Adamczyk B et al (2019) Plant roots increase both decomposition and stable organic matter formation in boreal forest soil. Nat Commun 10:3982. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11993-1
Alberti G et al (2015) Soil C:N stoichiometry controls carbon sink partitioning between above-ground tree biomass and soil organic matter in high fertility forests . iForest - Biogeosci For 8:195–206. https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1196-008
Amelung W, Brodowski S, Sandhage-Hofmann A, Bol R (2008) Chap. 6 combining biomarker with stable isotope analyses for assessing the transformation and turnover of soil organic matter. In: Advances in Agronomy. pp 155–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-2113(08)00606-8
An SS, Huang YM, Zheng FL (2009) Evaluation of soil microbial indices along a revegetation chronosequence in grassland soils on the Loess Plateau. Northwest China Appl Soil Ecol 41:286–292
Bai X, Guo Z, Huang Y, An S (2020) Root cellulose drives soil fulvic acid carbon sequestration in the grassland restoration process. Catena 191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104575
Bai X, Yang X, Zhang S, An S (2021) Newly assimilated carbon allocation in grassland communities under different grazing enclosure times. Biol Fertil Soils 57:563–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-021-01549-1
Balesdent J, Balabane M (1996) Major contribution of roots to soil carbon storage inferred from maize cultivated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 28:1261–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(96)00112-5
Bradford MA, Keiser AD, Davies CA, Mersmann CA, Strickland MS (2013) Empirical evidence that soil carbon formation from plant inputs is positively related to microbial growth. Biogeochemistry 113:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.02.012
Chang R, Fu B, Liu G, Wang S, Yao X (2012) The effects of afforestation on soil organic and inorganic carbon: A case study of the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 95:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.02.01
Chen H, Dong Y, Xu T, Wang Y, Wang H, Duan B (2017) Root order-dependent seasonal dynamics in the carbon and nitrogen chemistry of poplar fine roots. New For 48:587–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-017-9587-3
Cheng JM, Jing ZB, Jin JW, Gao Y (2014) Restoration and utilization mechanism of degraded grassland in the semi-arid region of Loess Plateau. Sci Sin Vitae 044:267–279. https://doi.org/10.1360/052013-280
Cong WF, van Ruijven J, Mommer L, De Deyn GB, Berendse F, Hoffland E (2014) Plant species richness promotes soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in grasslands without legumes. J Ecol 102:1163–1170. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12280
Cotrufo MF et al (2011) Decreased summer drought affects plant productivity and soil carbon dynamics in a Mediterranean woodland. Biogeosciences 8:2729–2739. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-8-2729-2011
De Kauwe MG et al (2014) Where does the carbon go? A model-data intercomparison of vegetation carbon allocation and turnover processes at two temperate forest free-air CO2 enrichment sites. New Phytol 203:883–899. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12847
Deng L (2016) Soil organic carbon dynamics following natural vegetation restoration: Evidence from stable carbon isotopes (δ13C). Agric Ecosyst Environ 221:235–244
Deng L, Sweeney S, Shangguan ZP (2013) Grassland responses to grazing disturbance: plant diversity changes with grazing intensity in a desert steppe. Grass Forage Sci 69:524–533. https://doi.org/10.1111/gfs.12065
Deng L, Zhang Z, Shangguan Z (2014) Long-term fencing effects on plant diversity and soil properties in China. Soil Tillage Res 137:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2013.11.002
Deng L, Liu GB, Shangguan ZP (2015) Land-use conversion and changing soil carbon stocks in China’s ‘Grain‐for‐Green’ Program: a synthesis. Glob Chang Biol 20:3544–3556
Derrien D, Amelung W (2011) Computing the mean residence time of soil carbon fractions using stable isotopes: impacts of the model framework European. J Soil Sci 62:237–252. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2010.01333.x
Fornara DA, Tilman D (2008) Plant functional composition influences rates of soil carbon and nitrogen accumulation. J Ecol 96:314–322. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2007.01345.x
Fransen B, de Kroon H, Berendse F (1998) Root morphological plasticity and nutrient acquisition of perennial grass species from habitats of different nutrient availability. Oecologia 115:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050527
Freschet GT et al (2013) Linking litter decomposition of above- and below-ground organs to plant-soil feedbacks worldwide. J Ecol 101:943–952. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12092
Gao YZ, Giese M, Lin S, Sattelmacher B, Zhao Y, Brueck H (2008) Belowground net primary productivity and biomass allocation of a grassland in Inner Mongolia is affected by grazing intensity. Plant Soil 307:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9579-3
Ge TD et al (2012) Biological carbon assimilation and dynamics in a flooded rice -. Soil Syst Soil Biol Biochem 48:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.01.009
Gill RA, Jackson RB (2000) Global patterns of root turnover for terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytologist 147:13–31
Golodets C, Kigel J, Sternberg M (2010) Recovery of plant species composition and ecosystem function after cessation of grazing in a Mediterranean grassland. Plant Soil 329:365–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0164-1
Gong L, Liu GH, Wang M, Ye X, Wang H, Li ZS (2017) Effects of vegetation restoration on soil organic carbon in China: A meta-analysis. Chin Geogr Sci 27:188–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-017-0858-x
Grace J, Rayment M (2000) Respiration in the balance. Nature 404:819–820. https://doi.org/10.1038/35009170
Guo Q (2007) The diversity–biomass–productivity relationships in grassland management and restoration . Basic Appl Ecol 8:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.baae.2006.02.005
He Y et al (2020) Soil DOC release and aggregate disruption mediate rhizosphere priming effect on soil C decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107787
Jackson RB, Canadell J, Ehleringer JR, Mooney HA, Sala OE, Schulze ED (1996) A global analysis of root distributions for terrestrial biomes. Oecologia 108:389–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/Bf00333714
Janssens IA et al (2001) Productivity overshadows temperature in determining soil and ecosystem respiration across European forests. Glob Change Biol 7:269–278. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2001.00412.x
Jones DL, Hodge A, Kuzyakov Y (2004) Plant and mycorrhizal regulation of rhizodeposition. New Phytol 163:459–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01130.x
Kell DB (2012) Large-scale sequestration of atmospheric carbon via plant roots in natural and agricultural ecosystems: why and how. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367:1589–1597. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2011.0244
King WL et al (2021) The hierarchy of root branching order determines bacterial composition, microbial carrying capacity and microbial filtering. Commun Biol 4:483. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-01988-4
Kuzyakov Y, Domanski G (2000) Carbon input by plants into the soil. Review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 163:421–431. 10.1002/1522-2624(200008)163:4<421::Aid-Jpln421>3.0.Co;2-R
Laganire J, Angers DA, Par D (2010) Carbon accumulation in agricultural soils after afforestation: a meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol 16:439–453
Lal R (2004) Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 304:1623–1627. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1097396
Li Q, Zhou D, Jin Y, Wang M, Song Y, Li G (2014) Effects of fencing on vegetation and soil restoration in a degraded alkaline grassland in northeast China. J Arid Land 6:478–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-013-0207-6
Li C, Li Q, Zhao L, Ge S, Chen D, Dong Q, Zhao X (2016a) Land-use effects on organic and inorganic carbon patterns in the topsoil around Qinghai Lake basin, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Catena 147:345–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.07.040
Li Z, Xu X, Pan G, Smith P, Cheng K (2016) Irrigation regime affected SOC content rather than plow layer thickness of rice paddies: A county level survey from a river basin in lower Yangtze valley, China. Agric Water Manag 172:31–39
Litton CM, Raich JW, Ryan MG (2007) Carbon allocation in forest ecosystems. Glob Change Biol 13:2089–2109. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01420.x
Ma W, Yang Y, He J, Zeng H, Fang J (2008) Above- and belowground biomass in relation to environmental factors in temperate grasslands. Inner Mongolia. Sci China C Life Sci 51:263–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-008-0029-5
Martinez C et al (2016) Belowground carbon allocation patterns as determined by the in-growth soil core 13C technique across different ecosystem types. Geoderma 263:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.08.043
Novara A, Gristina L, La Mantia T, Ruhl J (2013) Carbon dynamics of soil organic matter in bulk soil and aggregate fraction during secondary succession in a Mediterranean environment. Geoderma 193:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.08.036
Paterno GB, Siqueira JA, Ganade G (2016) Species-specific facilitation, ontogenetic shifts and consequences for plant community succession. J Veg Sci 27:606–615. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvs.12382
Pausch J, Kuzyakov Y (2018) Carbon input by roots into the soil: Quantification of rhizodeposition from root to ecosystem scale. Glob Chang Biol 24:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13850
Prommer J et al (2020) Increased microbial growth, biomass, and turnover drive soil organic carbon accumulation at higher plant diversity. Glob Chang Biol 26:669–681. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14777
Qiu L, Wei X, Zhang X, Cheng J (2013) Ecosystem carbon and nitrogen accumulation after grazing exclusion in semiarid grassland. PLoS ONE 8:e55433. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055433
Ravenek JM et al (2014) Long-term study of root biomass in a biodiversity experiment reveals shifts in diversity effects over time. Oikos 123:1528–1536. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.01502
Scandellari F, Tonon G, Thalheimer M, Ceccon C, Gioacchini P, Aber JD, Tagliavini M (2007) Assessing nitrogen fluxes from roots to soil associated to rhizodeposition by apple (Malus domestica) trees. Trees-Struct Funct 21:499–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-007-0141-3
Schmidt MWI et al (2011) Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 478:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10386
Shi Y, Baumann F, Ma Y, Song C, Kühn P, Scholten T, He JS (2012) Organic and inorganic carbon in the topsoil of the Mongolian and Tibetan grasslands: pattern, control and implications. Biogeosciences (2012-06-27) 9:2287–2299
Shi S, Zhang W, Zhang P, Yu Y, Ding F (2013) A synthesis of change in deep soil organic carbon stores with afforestation of agricultural soils. For Ecol Manag 296:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2013.01.026
Solly EF et al (2018) Unravelling the age of fine roots of temperate and boreal forests. Nat Commun 9:3006. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05460-6
Song ZL, Liu GB, Zhang C (2019) Response of rhizosphere microbial communities to plant succession along a grassland chronosequence in a semiarid area. J Soils Sediments 19:2496–2508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02241-6
Spivak AC, Sanderman J, Bowen JL, Canuel EA, Hopkinson CS (2019) Global-change controls on soil-carbon accumulation and loss in coastal vegetated ecosystems. Nat Geosci 12:685–692. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-019-0435-2
Tang S et al (2019) Heavy grazing reduces grassland soil greenhouse gas fluxes: A global meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 654:1218–1224
Vandandorj S, Eldridge DJ, Travers SK, Delgado-Baquerizo M (2017) Contrasting effects of aridity and grazing intensity on multiple ecosystem functions and services in australian woodlands. Land Degradation & Development 28:2098-2108. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2736
Walkley AJ, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff Method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the Chromic Acid Titration Method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Wang F et al (2020) Vegetation restoration in Northern China: A contrasted picture. Land Degrad Dev 31:669–676. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3314
Wang H et al (2020b) Vegetation and species impacts on soil organic carbon sequestration following ecological restoration over the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114389
Wu G-L, Du G-Z, Liu Z-H, Thirgood S (2009) Effect of fencing and grazing on a Kobresia-dominated meadow in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Plant Soil 319:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9854-3
Wu G-L, Liu Z-H, Zhang L, Chen J-M, Hu T-M (2010) Long-term fencing improved soil properties and soil organic carbon storage in an alpine swamp meadow of western China. Plant Soil 332:331–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0299-0
Wynn JG (2007) Carbon isotope fractionation during decomposition of organic matter in soils and paleosols: Implications for paleoecological interpretations of paleosols. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl 251:437–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.04.009
Wynn JG, Bird MI (2008) Environmental controls on the stable carbon isotopic composition of soil organic carbon: implications for modelling the distribution of C-3 and C-4 plants, Australia. Tellus B 60:604–621. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0889.2008.00361.x
Xia MX, Talhelm AF, Pregitzer KS (2015) Fine roots are the dominant source of recalcitrant plant litter in sugar maple-dominated northern hardwood forests. New Phytol 208:715–726. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13494
Yang Y, Tilman D, Furey G, Lehman C (2019) Soil carbon sequestration accelerated by restoration of grassland biodiversity. Nat Commun 10:718. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08636-w
Yunbin Q, Zhongbao X, Xinxiao Y, Yuling X, Manuel R (2014) Influence of vegetation restoration on topsoil organic carbon in a small catchment of the loess hilly region, China. PLoS One 9:e94489
Zanotelli D, Montagnani L, Manca G, Tagliavini M (2013) Net primary productivity, allocation pattern and carbon use efficiency in an apple orchard assessed by integrating eddy covariance biometric continuous soil chamber measurements. Biogeosciences 10:3089–3108. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-10-3089-2013
Zhang K, Dang H, Tan S, Cheng X, Zhang Q (2010) Change in soil organic carbon following the ‘Grain-for-Green’ programme in China. Land Degradation & Development 21:13-23. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.954
Zhang K, Dang H, Zhang Q, Cheng X (2015) Soil carbon dynamics following land-use change varied with temperature and precipitation gradients: evidence from stable isotopes. Glob Chang Biol 21:2762–2772. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12886
Zhao W, Zhang R, Huang C, Wang B, Cao H, Koopal LK, Tan W (2016) Effect of different vegetation cover on the vertical distribution of soil organic and inorganic carbon in the Zhifanggou Watershed on the loess plateau. Catena 139:191-198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.01.003
Zhu Z et al (2016) Belowground carbon allocation and dynamics under rice cultivation depends on soil organic matter content. Plant Soil 410:247–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-3005-z
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [42077072, 41871280, 41671280]. Xuan Yang performed experiments, conducted fieldwork, analysed data, and wrote the manuscript; Baorong Wang did writing- reviewing and editing; Shaoshan An did supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, writing- reviewing and Editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans Lambers.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.31 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Wang, B. & An, S. Root derived C rather than root biomass contributes to the soil organic carbon sequestration in grassland soils with different fencing years. Plant Soil 469, 161–172 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-05144-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-05144-z