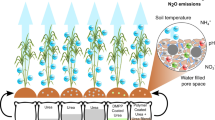
Abstract
Aims
Evaluate which nitrogen fertilizer alone or in combination with additives for enhanced efficiency can reduce N2O and CH4 emissions of soil cultivated with eucalyptus and also increase nitrogen uptake.
Methods
A pot experiment with eucalyptus seedlings was conducted with the application of urea or ammonium sulfate alone or in combination with polymer coatings, with nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide (DCD), or with urease inhibitor N-(n-butyl)-thiophosphoric triamide (NBPT, only with urea). The sampling of gases and soil parameters was carried out over a 163-day period, and at the end of this period plant attributes were evaluated.
Results
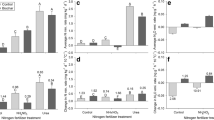
When added to urea or ammonium sulfate, DCD reduced N2O emission by >95%, increased CH4 uptake by 11–20%, and increased the nitrogen uptake by eucalyptus by 27–30%. Meanwhile, polymer coated urea, polymer coated ammonium sulfate, or NBPT added to urea did not change these parameters. Ammonium sulfate alone reduced N2O emission by 38% and increased nitrogen uptake by 23% relative to urea alone.
Conclusions
DCD mixed with urea or ammonium sulfate effectively reduced soil N2O emission and increased nitrogen uptake by eucalyptus plants; while polymer coatings or NBPT did not. Among the pure sources, ammonium sulfate was more efficient at reducing N2O emission and increasing nitrogen uptake compared with urea; but when DCD was added, N2O emissions were similarly low for both sources.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama H, Yan X, Yagi K (2010) Evaluation of effectiveness of enhanced-efficiency fertilizers as mitigation options for N2O e NO emissions from agricultural soil: meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol 16:1837–1846. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02031.x
Banerjee B, Pathak H, Aggarwal PK (2002) Effects of dicyandiamide, farmyard manure and irrigation on crop yields and ammonia volatilization from an alluvial soil under a rice (Oryzia sativa L.)-wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cropping system. Biol Fert Soils 36:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-002-0528-7
Barth G, Otto R, Almeida RF, Cardoso EJB, Cantarella H, Vitti GC (2020) Conversion of ammonium to nitrate and abundance of ammonium-oxidizing-microorganism in tropical soils with nitrification inhibitor. Sci Agric 77:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-992x-2018-0370
Bodelier PLE, Laanbroek HJ (2004) Nitrogen as a regulatory of methane oxidation in soils and sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47:265–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-6496(03)00304-0
Chien SH, Prochnow LI, Cantarella H (2009) Recent developments of fertilizer production and use to improve nutrient efficiency and minimize environmental impacts. Adv Agron 120:267–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(09)01008-6
Clayton H, Mctaggart IP, Parker J, Swan L, Smith KA (1997) Nitrous oxide emissions from fertilized grassland: a 2-year study of the effects of N fertiliser form and environmental conditions. Biol Fert Soils 25:252–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050311
Degaspari IAM, Soares JR, Montezano ZF, Del Grosso SJ, Vitti AC, Rossetto R, Cantarella H (2020) Nitrogen sources and application rates affect emissions of N2O and NH3 in sugarcane. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 116:329–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-019-10045-w
Ding WX, Chen ZM, Yu HY, Luo JF, Yoo GY, Xiang J, Zhang HJ, Yuan JJ (2015) Nitrous oxide emission and nitrogen use efficiency in response to nitrophosphate, N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide and dicyandiamide of wheat cultivated soil under sub-humid monsoon conditions. Biogeosciences 12:803–815. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-12-803-2015
EMBRAPA (1997) Manual de métodos de análise de solo. Embrapa Solos, Rio de Janeiro
Fan J, Xu Y, Chen Z, Xiao J, Liu D, Luo J, Bolan N, Ding W (2017) Sulfur deposition suppressed nitrogen-induced soil N2O emission from subtropical forestland in southeastern China. Agric For Meteorol 233:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2016.11.017
FAO (2020) Global Forest resources assessment 2020 - key findings. FAO, Rome
Forrestal PJ, Harty M, Carolan R, Laningan GJ, Watson CJ, Laughlin RJ, Mcneill G, Chambers BJ, Richards KG (2016) Ammonia emissions from urea, stabilized urea and calcium ammonium nitrate: insights into loss abatement in temperate grassland. Soil Use Manag 32:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12232
Fu Q, Abadie M, Blaud A, Carswell MTH, Clark IM, Hirsch PR (2020) Effects of urease and nitrification inhibitors on soil N, nitrifier abundance and activity in a sandy loam soil. Bio Fert Soils 56:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-019-01411-5
Gao Y, Chen H, Zeng X (2014) Effects of nitrogen and sulfur deposition on CH4 and N2O fluxes in high-altitude peatland soil under different water tables in the Tibetean plateau. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 60:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2014.893812
Garnett TP, Smethrust PJ (1999) Ammonium and nitrate uptake by Eucalyptus nitens: effects of pH and temperature. Plant Soil 214:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004740204876
Gilsanz C, Báez D, Misselbrook TH, Dhanoa MS, Cárdenas LM (2016) Development of emission factors and efficiency of two nitrification inhibitors, DCD and DMPP. Agric Ecosyst Environ 216:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2015.09.030
Gregorich E, Janzen HH, Helgason B, Ellert B (2015) Nitrogenous gas emissions from soil and greenhouse gas effects. Adv Agron 132:39–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2015.02.004
Halvorson AD, Snyder CS, Blaylock AD, Del Grosso SJ (2014) Enhanced-efficiency nitrogen fertilizer: potential role in nitrous oxide emission mitigation. Agron J 106:715–722. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2013.0081
Hou AX, Tsuruta H (2003) Nitrous oxide and nitric fluxes from an upland field in Japan: effect of urea type, placement and crop residues. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 65:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022149901586
Hütsch BW (1998) Methane oxidation in arable soil as inhibited by ammonium, nitrite, and organic manure with respect to soil pH. Biol Fert Soils 28:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050459
IBÁ (2019) Relatório 2019. IBÁ
IPCC (2006) N2O emissions from managed soil, and CO2 emissions from lime and urea application. In: Eggleston S, Buendia L, Miwa K, Ngara T, Tanabe K (eds) 2006 IPCC guidelines for National Greenhouse gas Inventories: agriculture, forestry and other land use. IGES, Hayama
IPCC (2013) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner K, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM (eds) Fifth assessment report. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
IUSS Working Group WRB (2015) World Reference Base for soil resources 2014: international soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps, World soil resources reports no. 106. FAO, Rome
Jiang C, Wang H, Lu D, Zhou J, Li D, Zu C (2017) Effects of fertilizer placement and nitrogen forms of soil nitrogen diffusion and migration of red-yellow soil in China. Agric Sci 8:1227–1238. https://doi.org/10.4236/as.2017.811088
Liu S, Wang JJ, Tian Z, Wang X, Harrison S (2017) Ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions from a subtropical wheat field under different nitrogen fertilization strategies. J Environ Sci 57:196–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.02.014
Maharjan B, Venterea RT (2013) Nitrite intensity explains N management effects on N2O emissions in maize. Soil Biol Biochem 66:229–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.07.015
Naz MY, Sulaiman SA (2016) Slow release coating remedy for nitrogen loss from conventional urea: a review. J Control Release 225:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.01.037
Pan B, Lam SK, Mosier A, Luo Y, Chen D (2016) Ammonia volatilization from synthetic fertilizers and its mitigation strategies: a global synthesis. Agric Ecosyst Environ 212:283–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.08.019
Parkin T, Venterea R (2010) Chamber- based trace gas flux measurements. In: Follett RF (ed) Sampling protocols. USDA-ARS GRACEnet, pp 1–39
Pasquali CEL, Hernando PF, Alegria JSD (2007) Spectrophotometric simultaneous determination of nitrite, nitrate and ammonium in soils by flow injection analysis. Anal Chim Acta 600:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.03.015
Ribeiro RH, Besen MR, Simon PL, Bayer C, Piva JT (2020) Enhanced-efficiency nitrogen fertilisers reduce winter losses of nitrous oxide, but not of ammonia, from no-till soil in a subtropical agroecosystem. Soil Use Manag 36:420–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12575
Roche L, Forrestal PJ, Lanigan GJ, Richards KG, Shaw LJ, Wall DP (2016) Impact of fertilizer nitrogen formulation, and N stabilizers on nitrous oxide emissions in spring barley. Agric Ecosyst Environ 233:229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.08.031
Ruser R, Schulz R (2015) The effect of nitrification inhibitors on the nitrous oxide (N2O) release from agricultural soils – a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 178:171–188. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201400251
Shrestha RK, Strahm BD, Sucre EB, Holub SM, Meehan N (2014) Fertilizer management, parent material, and stand age influence forest soil greenhouse gas fluxes. Soil Sci Soc America J 78:2041–2053. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2014.03.0118
Singh J, Kunhikrishnan A, Bolan NS, Saggar S (2013) Impact of urease inhibitor and nitrous oxide emissions from temperate pasture soil cores receiving urea fertilizer and cattle urine. Sci Total Environ 465:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.018
Soares JR, Cantarella H, Vargas VP, Carmo JB, Martins AA, Sousa RM, Andrade CA (2015) Enhanced-efficiency fertilizers in nitrous oxide emissions from urea applied to sugarcane. J Environ Qual 44:423–430. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2014.02.0096
Soares JR, Cassman NA, Kielak AM, Pijl A, Carmo JB, Lourenço KS, Laanbroek HJ, Cantarella H, Kurumae EE (2016) Nitrous oxide emission related to ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and mitigation options from N fertilization in a tropical soil. Nature 6:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30349
Tenuta M, Beauchamp EG (2003) Nitrous oxide production from granular nitrogen fertilizers applied to a silt loam soil. Can J Soil Sci 83:521–532. https://doi.org/10.4141/S02-062
Thapa R, Chatterjee A, Johnson JMF, Awale R (2015) Stabilized nitrogen fertilizers and application rate influence nitrogen losses under rainfed spring wheat. Agron J 107:1885–1894. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj15.0081
Tian Z, Wang JJ, Liu S, Zhang Z, Dodla SK, Myers G (2015) Application effects of coated urea and urease and nitrification inhibitors on ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions from a subtropical cotton field of the Mississippi delta region. Sci Total Environ 533:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.147
Tierling J, Kuhlmann H (2018) Emissions of nitrous oxide (N2O) affected by pH-related nitrite accumulation during nitrification of N fertilizers. Geoderma 310:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.08.040
Tong D, Xu R (2012) Effects of urea and (NH4)2SO4 on nitrification and acidification of Ultisols from southern China. J Environ Sci 24:682–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60832-2
Trenkel ME (2010) Slow- and controlled-release and stabilized fertilizers: an option for enhancing nutrient efficiency in agriculture. International Fertilizer Industry Association, Paris
Vilsmeier K, Bornnemisza E, Amberger A (1987) Urea, ammonium sulfate and dicyandiamide transformations in Costa Rican soils. Fert Res 12:255–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01315109
Wang Q, Hu H, Shen J, Du S, Zhang L, He J, Han L (2017) Effects of the nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide (DCD) in N2O emissions and the abundance of nitrifiers and denitrifiers in two contrasting agricultural soil. J Soils Sediments 17:1635–1643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1633-9
Wang W, Park G, Reeves S, Zahmel M, Heenan M, Salter B (2016) Nitrous oxide emission and fertilizer nitrogen efficiency in a tropical sugarcane cropping system applied with different formulations of urea. Soil Res 54:572–584. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR15314
Wang Y, Cheng S, Fang H, Yu G, Xu M, Dang X, Li L, Wang L (2014) Simulated nitrogen deposition reduces CH4 uptake and increases N2O emission from a subtropical plantation forest soil in southern China. PLoS One 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093571
Warren CR, Adams PR (2007) Uptake of nitrate, ammonium and glycine by plants of Tasmanian wet eucalypt forests. Tree Physiol 27:413–419. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/27.3.413
Wilcken CF, Lima ACV, Dias TKR, Masson MV, Ferreira Filho PJ, Pogetto MHFAD (2008) Guia prático de manejo de plantações de eucalipto. FEPAF, Botucatu
Wrage N, Velthof GL, van Beusichem ML, Oenema O (2001) Role of nitrifier denitrification in the production of nitrous oxide. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1723–1732. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00096-7
Yang M, Fang Y, Sun D, Yaunliang S (2016) Efficiency of two nitrification inhibitors (dicyandiamide and 3,4-dimethypyrazole phosphate) on soil nitrogen transformations and plant productivity: a meta-analysis. Nature 6:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22075
Zanatta JA, Alves BJR, Bayer C, Tomazi M, Fernandes AHBM, Costa FS, Carvalho AM (2014) Protocolo para medição de fluxos de gases de efeito estufa do solo. Embrapa Florestas, Colombo
Zanatta JA, Bayer C, Vieira FCB, Gomes J, Tomazi M (2010) Nitrous oxide and methane fluxes in south Brazilian Gleysol as affected by nitrogen fertilizers. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 34:1653–1665. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832010000500018
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel, Brazil) for the financial support and the doctorate scholarship; CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, Brazil) for the financial support (Edital Universal) and the research scholarships; and R.A. Taverna for support during the experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Paul Bodelier.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 362 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibarr, M.A., Zanatta, J.A., Dieckow, J. et al. Nitrous oxide and methane emissions from soil and nitrogen uptake by eucalyptus fertilized with enhanced efficiency fertilizers. Plant Soil 463, 615–630 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-04938-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-04938-5