Abstract
Background and aims
Crop species differ in phosphorus (P) acquisition in P-limiting environments. However, it is not fully understood how elevated atmospheric CO2 concentrations affects these P acquisition mechanisms and the plant's ability to acquire P from soil. This study aimed to investigate the effect of elevated CO2 on P acquisition in crop species with contrasting P acquisition mechanisms.
Methods
White lupin, faba bean, canola and near-isogenic wheat lines with and without citrate efflux were grown for 70 days in a P-deficient Chromosol soil under ambient (400 ppm) and elevated (800 ppm) CO2. Plant P uptake and P transformation in the rhizosphere were determined.
Results
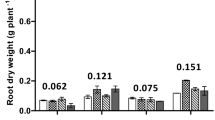
Elevated CO2 promoted total P uptake in white lupin and canola by 84% and 48%, respectively, and decreased the P uptake in the non-citrate-exuding wheat (by 24%) but not the exuding wheat. In white lupin, elevated CO2 enhanced phosphatase activity and depletion of organic P in the rhizosphere. Elevated CO2 increased P uptake by increasing root length which allowed canola to exploit a greater volume of soil for P. In the rhizosphere of faba bean, NaOH-extractable inorganic P was greater under elevated CO2.
Conclusion
Crops which rely on organic acid exudation and phosphatases appear to be better adapted to acquiring P under elevated CO2.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth EA, Long SP (2005) What have we learned from 15 years of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE)? A meta-analytic review of the responses of photosynthesis, canopy properties and plant production to rising CO2. New Phytol 165:351–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01224.x
Barrett DJ, Richardson AE, Gifford RM (1998) Elevated atmospheric CO2 concentrations increase wheat root phosphatase activity when growth is limited by phosphorus. Aust J Plant Physiol 25:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP97045
Barrow NJ, Debnath A, Sen A (2018) Mechanisms by which citric acid increases phosphate availability. Plant Soil 423:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3490-8
Bilyera N, Blagodatskaya E, Yevdokimov I, Kuzyakov Y (2018) Towards a conversion factor for soil microbial phosphorus. Eur J Soil Biol 87:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2018.03.002
Calvo OC, Franzaring J, Schmid I, Fangmeier A (2019) Root exudation of carbohydrates and cations from barley in response to drought and elevated CO2. Plant Soil 438:127–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-03998-y
Campbell CD, Sage RF (2002) Interactions between atmospheric CO2 concentration and phosphorus nutrition on the formation of proteoid roots in white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). plant. Cell Environ 25:1051–1059. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.2002.00883.x
Cotrufo MF, Gorissen A (1997) Elevated CO2 enhances below-ground C allocation in three perennial grass species at different levels of N availability. New Phytol 137:421–431. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.1997.00839.x
de Mendiburu F (2020) Agricolae: statistical procedures for agricultural research. R package version 1:3–2 https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=agricolae
Du C, Wang X, Zhang M, Jing J, Gao Y (2019) Effects of elevated CO2 on plant C-N-P stoichiometry in terrestrial ecosystems: a meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 650:697–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.051
Ellsworth DS, Anderson IC, Crous KY, Cooke J, Drake JE, Gherlenda AN, Gimeno TE, Macdonald CA, Medlyn BE, Powell JR, Tjoelker MG, Reich PB (2017) Elevated CO2 does not increase eucalypt forest productivity on a low-phosphorus soil. Nat Clim Chang 7:279–282. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3235
German DP, Weintraub MN, Grandy AS, Lauber CL, Rinkes ZL, Allison SD (2011) Optimization of hydrolytic and oxidative enzyme methods for ecosystem studies. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1387–1397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.03.017
Gilbert GA, Knight JD, Vance CP, Allan DL (1999) Acid phosphatase activity in phosphorus-deficient white lupin roots. Plant Cell Environ 22:801–810. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.1999.00441.x
Guppy CN, Menzies NW, Moody PW, Compton BL, Blamey FPC (2000) A simplified, sequential, phosphorus fractionation method. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 31:1981–1991. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620009370556
Guppy CN, Menzies NW, Moody PW, Blamey FPC (2005) Competitive sorption reactions between phosphorus and organic matter in soil: a review. Aust J Soil Res 43:189–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.03.017
Haase S, Neumann G, Kania A, Kuzyakov Y, Römheld V, Kandeler E (2007) Elevation of atmospheric CO2 and N-nutritional status modify nodulation, nodule-carbon supply, and root exudation of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2208–2221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.03.014
Han C, Zhang P, Ryan PR, Rathjen TM, Yan ZH, Delhaize E (2016) Introgression of genes from bread wheat enhances the aluminium tolerance of durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 129:729–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2661-3
Heuck C, Weig A, Spohn M (2015) Soil microbial biomass C:N:P stoichiometry and microbial use of organic phosphorus. Soil Biol Biochem 85:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.02.029
Huang W, Houlton BZ, Marklein AR, Liu J, Zhou G (2015) Plant stoichiometric responses to elevated CO2 vary with nitrogen and phosphorus inputs: evidence from a global-scale meta-analysis. Sci Rep 5:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18225
IPCC (2013). Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of the working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change
Isbell RF (2016) The Australian soil classification. CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood
Jin J, Tang C, Armstrong R, Sale P (2012) Phosphorus supply enhances the response of legumes to elevated CO2 (FACE) in a phosphorus-deficient vertisol. Plant Soil 358:91–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1270-z
Jin J, Tang C, Robertson A, Franks AE, Armstrong R, Sale P (2014) Increased microbial activity contributes to phosphorus immobilization in the rhizosphere of wheat under elevated CO2. Soil Biol Biochem 75:292–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.04.019
Jin J, Tang C, Sale P (2015) The impact of elevated carbon dioxide on the phosphorus nutrition of plants: a review. Ann Bot 116:987–999. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcv088
Joergensen RG (1996) The fumigation-extraction method to estimate soil microbial biomass: calibration of the kEC value. Soil Biol Biochem 28:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(95)00102-6
Khan FN, Lukac M, Turner G, Godbold DL (2008) Elevated atmospheric CO2 changes phosphorus fractions in soils under a short rotation poplar plantation (EuroFACE). Soil Biol Biochem 40:1716–1723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.02.008
Kouno K, Tuchiya Y, Ando T (1995) Measurement of soil microbial biomass phosphorus by an anion exchange membrane method. Soil Biol Biochem 27:1353–1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(95)00057-L
Lam SK, Chen D, Norton R, Armstrong R, Mosier AR (2012) Nitrogen dynamics in grain crop and legume pasture systems under elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration: a meta-analysis. Glob Chang Biol 18:2853–2859. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2012.02758.x
Lambers H, Shane MW, Cramer MD, Pearse SJ, Veneklaas EJ (2006) Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann Bot 98:693–713. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcl114
Lyu Y, Tang H, Li H, Zhang F, Rengel Z, Whalley WR, Shen J (2016) Major crop species show differential balance between root morphological and physiological responses to variable phosphorus supply. Front Plant Sci 7:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01939
Marx MC, Wood M, Jarvis SC (2001) A microplate fluorimetric assay for the study of enzyme diversity in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1633–1640. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00079-7
Motomizu S, Wakimoto T, Tôei K (1983) Spectrophotometric determination of phosphate in river waters with molybdate and malachite green. Analyst 108:361–367. https://doi.org/10.1039/an9830800361
Neumann G, Massonneau A, Langlade N, Dinkelaker B, Hengeler C, Römheld V, Martinoia E (2000) Physiological aspects of cluster root function and development in phosphorus-deficient white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Ann Bot 85:909–919. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.2000.1135
Nuruzzaman M, Lambers H, Bolland MDA, Veneklaas EJ (2005) Phosphorus benefits of different legume crops to subsequent wheat grown in different soils of Western Australia. Plant Soil 271:175–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-2386-6
Nuruzzaman M, Lambers H, Bolland MDA, Veneklaas EJ (2006) Distribution of carboxylates and acid phosphatase and depletion of different phosphorus fractions in the rhizosphere of a cereal and three grain legumes. Plant Soil 281:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-3936-2
Pearse SJ, Veneklaas EJ, Cawthray GR, Bolland MDA, Lambers H (2006). Carboxylate release of wheat, canola and 11 grain legume species as affected by phosphorus status plant soil 288:127-139 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9099-y
Pérez-López U, Miranda-Apodaca J, Muñoz-Rueda A, Mena-Petite A (2013) Lettuce production and antioxidant capacity are differentially modified by salt stress and light intensity under ambient and elevated CO2. J Plant Physiol 170:1517–1525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2013.06.004
Piñeiro J, Ochoa-Hueso R, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Dobrick S, Reich PB, Pendall E, Power SA (2017) Effects of elevated CO2 on fine root biomass are reduced by aridity but enhanced by soil nitrogen: a global assessment. Sci Rep 7:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15728-4
R Core Team (2020) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Reuter D, Robinson JB (1997) Plant analysis: an interpretation manual. CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne, Melbourne
Richardson AE, Hocking PJ, Simpson RJ (2009) George TS. Plant mechanisms to optimise access to soil phosphorus Crop Pasture Sci 60:124–143. https://doi.org/10.1071/Cp07125
Rogers GS, Payne L, Milham P, Conroy J (1993). Nitrogen and phosphorus requirements of cotton and wheat under changing atmospheric CO2 concentrations plant soil 155:231-234 https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00025026
Rose TJ, Rengel Z, Ma Q, Bowden JW (2009) Crop species differ in root plasticity response to localised P supply. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 172:360–368. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200800031
Rubio-Asensio JS, Bloom AJ (2017) Inorganic nitrogen form: a major player in wheat and Arabidopsis responses to elevated CO2. J Exp Bot 68:2611–2625. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw465
Shen J, Li H, Neumann G, Zhang F (2005) Nutrient uptake, cluster root formation and exudation of protons and citrate in Lupinus albus as affected by localized supply of phosphorus in a split-root system. Plant Sci 168:837–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.10.017
Six L, Smolders E, Merckx R (2013) The performance of DGT versus conventional soil phosphorus tests in tropical soils—maize and rice responses to P application. Plant Soil 366:49–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1375-4
Tadano T, Ozawa K, Sakai H, Osaki M, Matsui H (1993) Secretion of acid phosphatase by the roots of crop plants under phosphorus-deficient conditions and some properties of the enzyme secreted by lupin roots. Plant Soil 155:95–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00024992
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(87)90052-6
Vu DT, Armstrong RD, Sale PWG, Tang C (2010) Phosphorus availability for three crop species as a function of soil type and fertilizer history. Plant Soil 337:497–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9516-x
Wasaki J, Rothe A, Kania A, Neumann G, Römheld V, Shinano T, Osaki M, Kandeler E (2005) Root exudation, phosphorus acquisition, and microbial diversity in the rhizosphere of white lupine as affected by phosphorus supply and atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration. J Environ Qual 34:2157–2166. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2004.0423
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Mr. Mark Richards from New South Wales Department of Primary Industry for providing the white lupin and chickpea seeds and Professor Manny Delhaize from CSIRO for providing the wheat seeds. JBO was supported by an Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Honghua He.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Sullivan, J.B., Jin, J. & Tang, C. Elevated CO2 promotes the acquisition of phosphorus in crop species differing in physiological phosphorus-acquiring mechanisms. Plant Soil 455, 397–408 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04698-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04698-8