Abstract
Aims
Uncovering the importance of soil and plant characteristics in driving the legacy effects of nitrogen (N) deposition on plant community nutrient stoichiometry would improve our understanding of plant-soil interaction during restoration of historically N-enriched ecosystems.
Methods
Based on a field experiment with the cessation of six-year N addition in a temperate steppe of northern China, we measured concentrations and stoichiometry of N and phosphorus (P) in soils and different plant functional groups, under both mown and unmown conditions.
Results
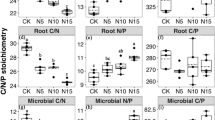
Historical N addition did not affect soil total and available N and P concentrations and stoichiometry, but significantly altered plant community composition. Plant nutrient concentrations and N:P ratios significantly differed among four plant functional groups. The concentrations and stoichiometric ratios of N and P between soils and plants were generally not correlated. The positive legacy effects of N addition on community N:P stoichiometry were caused by the biomass enhancement of tall bunchgrass, the functional group with the highest N:P ratios.
Conclusions
Changes in plant community composition instead of soil nutrient status were the main driver for the positive legacy effects of N enrichment on plant community stoichiometry. Given that the recovery of community composition after the cessation of N deposition is generally slow, our findings indicate that the legacy effects of N deposition on soil nutrient cycling would persist in long-term due to the importance of plant-mediated pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R, Chapin FS (1999) The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: a re-evaluation of processes and patterns. Adv Ecol Res 30:1–67
Austin AT, Zanne AE (2015) Whether in life or in death: fresh perspectives on how plants affect biogeochemical cycling. J Ecol 103:1367–1371
Bai YF, Wu JG, Clark CM, Naeem S, Pan QM, Huang JH, Zhang LX, Han XG (2010) Tradeoffs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: evidence from inner Mongolia grasslands. Glob Chang Biol 16:358–372
Bowman WD, Ayyad A, de Mesquita CPB, Fierer N, Potter TS, Sternagel S (2018) Limited ecosystem recovery from simulated chronic nitrogen deposition. Ecol Appl 28:1762–1772
Bridgham SD, Updegraff K, Pastor J (1998) Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus mineralization in northern wetlands. Ecology 79:1545–1561
Bruelheide H, Dengler J, Purschke O, Lenoir J, Jiménez-Alfaro B, Hennekens SM, Botta-Dukát Z, Chytrý M, Field R, Jansen F, Kattge J, Pillar VD, Schrodt F, Mahecha MD, Peet RK, Sandel B, van Bodegom P, Altman J, Alvarez-Dávila E, Arfin Khan MAS, Attorre F, Aubin I, Baraloto C, Barroso JG, Bauters M, Bergmeier E, Biurrun I, Bjorkman AD, Blonder B, Čarni A, Cayuela L, Černý T, Cornelissen JHC, Craven D, Dainese M, Derroire G, de Sanctis M, Díaz S, Doležal J, Farfan-Rios W, Feldpausch TR, Fenton NJ, Garnier E, Guerin GR, Gutiérrez AG, Haider S, Hattab T, Henry G, Hérault B, Higuchi P, Hölzel N, Homeier J, Jentsch A, Jürgens N, Kącki Z, Karger DN, Kessler M, Kleyer M, Knollová I, Korolyuk AY, Kühn I, Laughlin DC, Lens F, Loos J, Louault F, Lyubenova MI, Malhi Y, Marcenò C, Mencuccini M, Müller JV, Munzinger J, Myers-Smith IH, Neill DA, Niinemets Ü, Orwin KH, Ozinga WA, Penuelas J, Pérez-Haase A, Petřík P, Phillips OL, Pärtel M, Reich PB, Römermann C, Rodrigues AV, Sabatini FM, Sardans J, Schmidt M, Seidler G, Silva Espejo JE, Silveira M, Smyth A, Sporbert M, Svenning JC, Tang Z, Thomas R, Tsiripidis I, Vassilev K, Violle C, Virtanen R, Weiher E, Welk E, Wesche K, Winter M, Wirth C, Jandt U (2018) Global trait–environment relationships of plant communities. Nat Ecol Evol 2:1906–1917
Carnicer J, Sardans J, Stefanescu C, Ubach A, Bartrons M, Asensio D, Peñuelas J (2015) Global biodiversity, stoichiometry and ecosystem function responses to human-induced C-N-P imbalances. J Plant Physiol 172:82–91
Clark CM, Hobbie SE, Venterea R, Tilman D (2009) Long-lasting effects on nitrogen cycling 12 years after treatments cease despite minimal long-term nitrogen retention. Glob Chang Biol 15:1755–1766
Collins SL, Knapp AK, Briggs JM, Blair JM, Steinauer EM (1998) Modulation of diversity by grazing and mowing in native tallgrass prairie. Science 280:745–747
Dahlin KM, Asner GP, Field CB (2013) Environmental and community controls on plant canopy chemistry in a Mediterranean-type ecosystem. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:6895–6900
Danger M, Daufresne T, Lucas F, Pissard S, Lacroix G (2008) Does Liebig's law of the minimum scale up from species to communities? Oikos 117:1741–1751
Davidson EA, David MB, Galloway JN, Goodale CL, Haeuber R, Harrison JA, Howarth RW, Jaynes DB, Lowrance RR, Nolan BT, Peel JL, Pinder RW, Porter E, Snyder CS, Townsend AR, Ward MH (2012) Excess nitrogen in the U.S. environment: trends, risks, and solutions. Issu Ecol 15:1–16
Edmondson J, Terribile E, Carroll JA, Price EAC, Caporn SJM (2013) The legacy of nitrogen pollution in heather moorlands: ecosystem response to simulated decline in nitrogen deposition over seven years. Sci Total Environ 444:138–144
Elser JJ, Fagan WF, Kerkhoff AJ, Swenson NG, Enquist BJ (2010) Biological stoichiometry of plant production: metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol 186:593–608
Giese M, Brueck H, Gao YZ, Lin S, Steffens M, Kögel-Knabner I, Glindemann T, Susenbeth A, Taube F, Butterbach-Bahl K, Zheng XH, Hoffmann C, Bai YF, Han XG (2013) N balance and cycling of Inner Mongolia typical steppe: a comprehensive case study of grazing effects. Ecol Monogr 83:195–219
Green RA, Detling JK (2000) Defoliation-induced enhancement of total aboveground nitrogen yield of grasses. Oikos 91:280–284
Grime JP (1998) Benefits of plant diversity to ecosystems: immediate, filter and founder effects. J Ecol 86:902–910
Hall SR (2009) Stoichiometrically explicit food webs: feedbacks between resource supply, elemental constraints, and species diversity. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 40:503–528
Hamilton EW, Frank DA (2001) Can plants stimulate soil microbes and their own nutrient supply? Evidence from a grazing tolerant grass. Ecology 82:2397–2402
Han X, Sistla SA, Zhang YH, Lü XT, Han XG (2014) Hierarchical responses of plant stoichiometry to nitrogen deposition and mowing in a temperate steppe. Plant Soil 382:175–187
Härdtle W, Niemeyer M, Niemeyer T, Assmann T, Fottner S (2006) Can management compensate for atmospheric nutrient deposition in heathland ecosystems? J Appl Ecol 43:759–769
Harpole WS, Ngai JT, Cleland EE, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Bracken MES, Elser JJ, Gruner DS, Hillebrand H, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2011) Nutrient co-limitation of primary producer communities. Ecol Lett 14:852–862
Hautier Y, Niklaus PA, Hector A (2009) Competition for light causes plant biodiversity loss after eutrophication. Science 324:636–638
Hou SL, Lü XT, Yin JX, Yang JJ, Hu YY, Wei HW, Zhang ZW, Yang GJ, Liu ZY, Han XG (2019) The relative contributions of intra- and inter-specific variation in driving community stoichiometric responses to nitrogen deposition and mowing in a grassland. Sci Total Environ 666:887–893
Humbert JY, Dwyer JM, Andrey A, Arlettaz R (2016) Impacts of nitrogen addition on plant biodiversity in mountain grasslands depend on dose, application duration and climate: a systematic review. Glob Chang Biol 22:110–120
Isbell F, Tilman D, Polasky S, Binder S, Hawthorne P (2013) Low biodiversity state persists two decades after cessation of nutrient enrichment. Ecol Lett 16:454–460
Jia YL, Yu GR, He NP, Zhan XY, Fang HJ, Sheng WP, Zuo Y, Zhang DY, Wang QF (2014) Spatial and decadal variations in inorganic nitrogen wet deposition in China induced by human activity. Sci Rep 4:3763
Lepš J (2014) Scale-and time-dependent effects of fertilization, mowing and dominant removal on a grassland community during a 15-year experiment. J Appl Ecol 51:978–987
Lu RK (2000) Analytical methods of soil agricultural chemistry. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing
Lu M, Yang YH, Luo YQ, Fang CM, Zhou XH, Chen JK, Yang X, Li B (2011) Responses of ecosystem nitrogen cycle to nitrogen addition: a meta-analysis. New Phytol 189:1040–1050
Lü XT, Reed S, Yu Q, He NP, Wang ZW, Han XG (2013) Convergent responses of nitrogen and phosphorus resorption to nitrogen inputs in a semiarid grassland. Glob Chang Biol 19:2775–2784
Lü XT, Liu ZY, Hu YY, Zhang HY (2018) Testing nitrogen and water co-limitation of primary productivity in a temperate steppe. Plant Soil 432:119–127
Manzoni S, Trofymow JA, Jackson RB, Porporato A (2010) Stoichiometric controls on carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus dynamics in decomposing litter. Ecol Monogr 80:89–106
Mao JH, Mao QG, Zheng MH, Mo JM (2020) Responses of foliar nutrient status and stoichiometry to nitrogen addition in different ecosystems: a meta-analysis. J Geophys Res 125. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019jg005347
Marklein AR, Houlton BZ (2012) Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytol 193:696–704
Matejko M, Dore AJ, Hall J, Dore CJ, Blaś M, Kryza M, Smith R, Fowler D (2009) The influence of long term trends in pollutant emissions on deposition of Sulphur and nitrogen and exceedance of critical loads in the United Kingdom. Environ Sci Pol 12:882–896
Melts I, Lanno K, Sammul M, Uchida K, Heinsoo K, Kull T, Laanisto L (2018) Fertilising semi-natural grasslands may cause long-term negative effects on both biodiversity and ecosystem stability. J Appl Ecol 55:1951–1955
Mikola J, Setala H, Virkajarvi P, Saarijarvi K, Ilmarinen K, Voigt W, Vestberg M (2009) Defoliation and patchy nutrient return drive grazing effects on plant and soil properties in a dairy cow pasture. Ecol Monogr 79:221–244
Mooshammer M, Wanek W, Schnecker J, Wild B, Leitner S, Hofhansl F, Blöchl A, Hämmerle I, Frank AH, Fuchslueger L, Keiblinger KM, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Richter A (2012) Stoichiometric controls of nitrogen and phosphorus cycling in decomposing beech leaf litter. Ecology 93:770–782
Murphy J, Riley JP (1964) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chem Acta 27:31–36
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicabomate, USDA circular 939. Gov. Printing Office, Washington, DC, pp 1–19
Peng YF, Li F, Zhou GY, Fang K, Zhang DY, Li CB, Yang GB, Wang GQ, Wang J, Yang YH (2017) Linkages of plant stoichiometry to ecosystem production and carbon fluxes with increasing nitrogen inputs in an alpine steppe. Glob Chang Biol 23:5249–5259
Peñuelas J, Sardans J, Rivas-Ubach A, Janssens IA (2012) The human-induced imbalance between C, N and P in Earth's life system. Glob Chang Biol 18:3–6
Peñuelas J, Poulter B, Sardans J, Ciais P, van der Velde M, Bopp L, Boucher O, Godderis Y, Hinsinger P, Llusia J, Nardin E, Vicca S, Obersteiner M, Janssens IA (2013) Human-induced nitrogen-phosphorus imbalances alter natural and managed ecosystems across the globe. Nat Commun 4:2934
Perring MP, Hedin LO, Levin SA, McGroddy M, de Mazancourt C (2008) Increased plant growth from nitrogen addition should conserve phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:1971–1976
Power SA, Green ER, Barker CG, Bell JNB, Ashmore MR (2006) Ecosystem recovery: heathland response to a reduction in nitrogen deposition. Glob Chang Biol 12:1241–1252
Reichmann LG, Sala OE, Peters DPC (2013) Water controls on nitrogen transformations and stocks in an arid ecosystem. Ecosphere 4:1–17
Sardans J, Grau O, Chen HYH, Janssens IA, Ciais P, Piao S, Peñuelas J (2017) Changes in nutrient concentrations of leaves and roots in response to global change factors. Glob Chang Biol 23:3849–3856
Shahzad T, Chenu C, Repinçay C, Mougin C, Ollier JL, Fontaine S (2012) Plant clipping decelerates the mineralization of recalcitrant soil organic matter under multiple grassland species. Soil Biol Biochem 51:73–80
Shi SN, Yu ZY, Zhao Q (2014) Responses of plant diversity and species composition to the cessation of fertilization in a sandy grassland. J For Res 25:337–342
Sistla SA, Schimel JP (2012) Stoichiometric flexibility as a regulator of carbon and nutrient cycling in terrestrial ecosystems under change. New Phytol 196:68–78
Sistla SA, Appling AP, Lewandowska AM, Taylor BN, Wolf AA (2015) Stoichiometric flexibility in response to fertilization along gradients of environmental and organismal nutrient richness. Oikos 124:949–959
Stevens CJ (2016) How long do ecosystems take to recover from atmospheric nitrogen deposition? Biol Conserv 200:160–167
Storkey J, Macdonald AJ, Poulton PR, Scott T, Köhler IH, Schnyder H, Goulding KWT, Crawley MJ (2015) Grassland biodiversity bounces back from long-term nitrogen addition. Nature 528:401–404
Street LE, Burns NR, Woodin SJ (2015) Slow recovery of high arctic heath communities from nitrogen enrichment. New Phytol 206:682–695
Tian DS, Reich PB, Chen HYH, Xiang YZ, Luo YQ, Shen Y, Meng C, Han WX, Niu SL (2019) Global changes alter plant multi-element stoichiometric coupling. New Phytol 221:807–817
Violle C, Navas ML, Vile D, Kazakou E, Fortunel C, Hummel I, Garnier E (2007) Let the concept of trait be functional! Oikos 116:882–892
Vitousek P (1982) Nutrient cycling and nutrient use efficiency. Am Nat 119:553–572
Vitousek PM, Porder S, Houlton BZ, Chadwick OA (2010) Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen-phosphorus interactions. Ecol Appl 20:5–15
Wedin DA, Tilman D (1996) Influence of nitrogen loading and species composition on the carbon balance of grasslands. Science 274:1720–1723
Wei CZ, Yu Q, Bai E, Lü XT, Li Q, Xia JY, Kardol P, Liang WJ, Wang ZW, Han XG (2013) Nitrogen deposition weakens plant-microbe interactions in grassland ecosystems. Glob Chang Biol 19:3688–3697
Yang GJ, Lü XT, Stevens CJ, Zhang GM, Wang HY, Wang ZW, Zhang ZJ, Liu ZY, Han XG (2019) Mowing mitigates the negative impacts of N addition on plant species diversity. Oecologia 189:769–779
Zhang YH, Lü XT, Isbell F, Stevens C, Han X, He NP, Zhang GM, Yu Q, Huang JH, Han XG (2014) Rapid plant species loss at high rates and at low frequency of N addition in temperate steppe. Glob Chang Biol 20:3520–3529
Zhang YH, Loreau M, He NP, Zhang GM, Han XG (2017) Mowing exacerbates the loss of ecosystem stability under nitrogen enrichment in a temperate grassland. Funct Ecol 31:1637–1646
Zhao NX, Gao YB, Wang JL, Ren AZ (2008) Population structure and genetic diversity of Stipa grandis P. Smirn, a dominant species in the typical steppe of northern China. Biochem Syst Ecol 36:1–10
Acknowledgements
We thank the Inner Mongolia Grassland Ecosystem Research Station for logistical support. Comments and suggestions from three anonymous reviewers help improve the quality of this manuscript. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770503 and 31822006), Liaoning Revitalizing Talents Program (XLYC1807061), Key Laboratory of Vegetation Ecology, Ministry of Education, K.C.Wong Education Foundation (GJTD-2019-10), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0500601), Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2014174), and Key Research Program from CAS (QYZDB-SSW-DQC006). Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Manuel Delgado-Baquerizo.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 183 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, YY., Wei, HW., Zhang, ZW. et al. Changes of plant community composition instead of soil nutrient status drive the legacy effects of historical nitrogen deposition on plant community N:P stoichiometry. Plant Soil 453, 503–513 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04631-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04631-z