Abstract
Background and aims
Soil cadmium (Cd) contamination threatens food safety and human health. Increasing Cd phytoextraction efficiency by hyperaccumulators and growing safe products during remediation remain challenges.
Methods
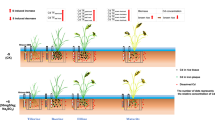
A pot experiment was conducted to explore the effects of different rates of sulfur (S) associated with alternating drying and wetting on a Sedum plumbizincicola-Oryza sativa rotation in Cd-contaminated neutral and calcareous soils.
Results
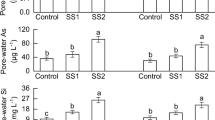
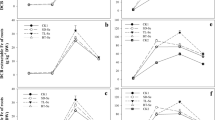
The oxidation of added S under aerobic conditions significantly decreased soil solution pH and increased soluble sulfate (SO42−), Cd and iron (Fe) concentrations in both soils. During the rice growing season the soil solution redox (Eh) decreased to < −200 mV and the solution pH increased to neutral during the first few days of flooding. Soluble SO42− and Cd in the S treatments decreased significantly with increasing duration of flooding. Sulfur addition promoted shoot Cd concentrations of S. plumbizincicola by 1.7–5.5 times on calcareous soil and 1.7–2.3 times on neutral soil compared to the controls. Rice yields increased but Cd concentrations decreased at suitable S addition rates.
Conclusions
Appropriate sulfur amendment combined with water management can be a feasible strategy to enhance the Cd remediation efficiency of the hyperaccumulator and reduce the accumulation of Cd in the rice grains in this rotation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anwar S, Khan S, Ashraf MY, Noman A, Zafar S, Liu LJ, Ullah S, Fahad S (2017) Impact of chelator-induced phytoextraction of cadmium on yield and ionic uptake of maize. Int J Phytoremediat 19:505–513
Attinti R, Barrett KR, Datta R, Sarkar D (2017) Ethylenediaminedisuccinic acid (EDDS) enhances phytoextraction of lead by vetiver grass from contaminated residential soils in a panel study in the field. Environ Pollut 225:524–533
Borch T, Kretzschmar R, Kappler A, Van Cappellen P, Ginder-Vogel M, Voegelin A, Campbell K (2010) Biogeochemical redox processes and their impact on contaminant dynamics. Environ Sci Technol 44:15–23
Burton ED, Johnston SG, Kraal P, Bush RT, Claff S (2013) Sulfate availability drives divergent evolution of arsenic speciation during microbially mediated reductive transformation of schwertmannite. Environ Sci Technol 47:2221–2229
Burton ED, Johnston SG, Kocar BD (2014) Arsenic mobility during flooding of contaminated soil: the effect of microbial sulfate reduction. Environ Sci Technol 48:13660–13667
Chen HY, Teng YG, Lu SJ, Wang YY, Wang JS (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512:143–153
Cui YS, Wang QR, Dong YT, Li HF, Christie P (2004) Enhanced uptake of soil Pb and Zn by Indian mustard and winter wheat following combined soil application of elemental sulphur and EDTA. Plant Soil 261:181–188
de Livera J, McLaughlin MJ, Hettiarachchi GM, Kirby JK, Beak DG (2011) Cadmium solubility in paddy soils: effects of soil oxidation, metal sulfides and competitive ions. Sci Total Environ 409:1489–1497
de Oliveira LM, Ma LQ, Santos JAG, Guilherme LRG, Lessl JT (2014) Effects of arsenate, chromate, and sulfate on arsenic and chromium uptake and translocation by arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. Environ Pollut 184:187–192
Deng L, Li Z, Wang J, Liu HY, Li N, Wu LH, Hu PJ, Luo YM, Christie P (2016) Long-term field phytoextraction of zinc/cadmium contaminated soil by Sedum plumbizincicola under different agronomic strategies. Int J Phytorem 18:134–140
Ding CP, Xu RK (2011) Oxidation-reduction processes of soils and their research methods. Science Press, Beijing, pp 197–220
Ditoro DM, Mahony JD, Hansen DJ, Scott KJ, Hicks MB, Mayr SM, Redmond MS (1990) Toxicity of cadmium in sediments: the role of acid volatile sulfide. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1487–1502
Dixit G, Singh AP, Kumar A, Singh PK, Kurnar S, Dwivedi S, Trivedi PK, Pandey V, Norton GJ, Dhankher OP, Tripathi RD (2015) Sulfur mediated reduction of arsenic toxicity involves efficient thiol metabolism and the antioxidant defense system in rice. J Hazard Mater 298:241–251
Fan JL, Hu ZY, Ziadi N, Xia X, Wu CYH (2010) Excessive sulfur supply reduces cadmium accumulation in brown rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Pollut 158:409–415
Freitas EV, Nascimento CW, Souza A, Silva FB (2013) Citric acid-assisted phytoextraction of lead: a field experiment. Chemosphere 92:213–217
Fulda B, Voegelin A, Kretzschmar R (2013) Redox-controlled changes in cadmium solubility and solid-phase speciation in a paddy soil as affected by reducible sulfate and copper. Environ Sci Technol 47:12775–12783
Furuya M, Hashimoto Y, Yamaguchi N (2016) Time-course changes in speciation and solubility of cadmium in reduced and oxidized paddy soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 80:870–877
Hashimoto Y, Furuya M, Yamaguchi N, Makino T (2016) Zerovalent iron with high sulfur content enhances the formation of cadmium sulfide in reduced paddy soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 80:55–63
Hell R (1997) Molecular physiology of plant sulfur metabolism. Planta 202:138–148
Hu ZY, Zhu YG, Li M, Zhang LG, Cao ZH, Smith EA (2007) Sulfur (S)-induced enhancement of iron plaque formation in the rhizosphere reduces arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Environ Pollut 147:387–393
Hu PJ, Li Z, Yuan C, Ouyang YN, Zhou LQ, Huang JX, Huang YJ, Luo YM, Christie P, Wu LH (2013) Effect of water management on cadmium and arsenic accumulation by rice (Oryza sativa L.) with different metal accumulation capacities. J Soils Sediments 13:916–924
Hu PJ, Wang YD, Przybylowicz WJ, Li Z, Barnabas A, Wu LH, Luo YM, Mesjasz-Przybylowicz J (2015) Elemental distribution by cryo-micro-PIXE in the zinc and cadmium hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola grown naturally. Plant Soil 388:267–282
Iqbal M, Puschenreiter M, Oburger E, Santner J, Wenzel WW (2012) Sulfur-aided phytoextraction of Cd and Zn by Salix smithiana combined with in situ metal immobilization by gravel sludge and red mud. Environ Pollut 170:222–231
Kayser A, Wenger K, Keller A, Attinger W, Felix HR, Gupta SK, Schulin R (2000) Enhancement of phytoextraction of Zn, Cd, and Cu from calcareous soil: the use of NTA and sulfur amendments. Environ Sci Technol 34:1778–1783
Kelly DP, Wood AP (2000) Reclassification of some species of Thiobacillus to the newly designated genera Acidithiobacillus gen. Nov., Halothiobacillus gen. Nov and Thermithiobacillus gen. Nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:511–516
Khaokaew S, Chaney RL, Landrot G, Ginder-Vogel M, Sparks DL (2011) Speciation and release kinetics of cadmium in an alkaline paddy soil under various flooding periods and draining conditions. Environ Sci Technol 45:4249–4255
Kocar BD, Borch T, Fendorf S (2010) Arsenic repartitioning during biogenic sulfidization and transformation of ferrihydrite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74:980–994
Li HH, Hu MH, Li TQ, Yang XE (2008) Effects of sulfur on growth, cadmium absorption and accumulation in hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance. J Soil Water Conserv 22(6):71–74 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Z, Wu LH, Hu PJ, Luo YM, Zhang H, Christie P (2014a) Repeated phytoextraction of four metal-contaminated soils using the cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola. Environ Pollut 189:176–183
Li Z, Wu LH, Luo YM, Christie P (2014b) Dynamics of plant metal uptake and metal changes in whole soil and soil particle fractions during repeated phytoextraction. Plant Soil 374:857–869
Li Z, Jia MY, Wu LH, Christie P, Luo YM (2016) Changes in metal availability, desorption kinetics and speciation in contaminated soils during repeated phytoextraction with the Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola. Environ Pollut 209:123–131
Li JT, Gurajala HK, Wu LH, Van der Ent A, Qiu RL, Baker AJM, Tang YT, Yang XE, Shu WS (2018) Hyperaccumulator plants from China: a synthesis of the current state of knowledge. Environ Sci Technol 52:11980–11994
Lu RK (2000) Analytical methods for soil and agrochemistry. Agricultural science and technology press. Beijing, China
Mann M, Kruger JE, Andari F, McErlean J, Gascooke JR, Smith JA, Worthington MJH, McKinley CCC, Campbell JA, Lewis DA, Hasell T, Perkins MV, Chalker JM (2019) Sulfur polymer composites as controlled-release fertilisers. Org Biomol Chem 17:1929–1936
Masood A, Iqbal N, Khan NA (2012) Role of ethylene in alleviation of cadmium-induced photosynthetic capacity inhibition by sulphur in mustard. Plant Cell Environ 35:524–533
Rao IM, Miles JW, Beebe SE, Horst WJ (2016) Root adaptations to soils with low fertility and aluminium toxicity. Ann Bot-London 118:593–605
Saito K (2000) Regulation of sulfate transport and synthesis of sulfur-containing amino acids. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:188–195
Sarwar N, Saifullah MSS, Zia MH, Naeem A, Bibi S, Farid G (2010) Role of mineral nutrition in minimizing cadmium accumulation by plants. J Sci Food Agric 90:925–937
Sebastian A, Prasad MNV (2014) Cadmium minimization in rice. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 34:155–173
Shen LB, Wu LH, Tan WN, Han XR, Luo YM, Ouyang YN, Jin QY, Jiang YG (2010) Effects of Sedum plumbizincicola-Oryza sativa rotation and phosphate amendment on Cd and Zn uptake by O. sativa. Chin J Appl Ecol 21:2952–2958 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Stroud JL, Norton GJ, Islam MR, Dasgupta T, White RP, Price AH, Meharg AA, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2011) The dynamics of arsenic in four paddy fields in the Bengal delta. Environ Pollut 159:947–953
Sun X, Li Z, Wu LH, Christie P, Luo YM, Fornara DA (2019) Root-induced soil acidification and cadmium mobilization in the rhizosphere of Sedum plumbizincicola: evidence from a high-resolution imaging study. Plant Soil 436:267–282
Teng YG, Wu J, Lu SJ, Wang YY, Jiao XD, Song LT (2014) Soil and soil environmental quality monitoring in China: a review. Environ Int 69:177–199
Van der Ent A, Baker AJM, Reeves RD, Pollard AJ, Schat H (2013) Hyperaccumulators of metal and metalloid trace elements: facts and fiction. Plant Soil 362:319–334
Wan XM, Lei M, Chen TB (2016) Cost-benefit calculation of phytoremediation technology for heavy metal-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 563:796–802
Wang AS, Angle JS, Chaney RL, Delorme TA, Reeves RD (2006) Soil pH effects on uptake of Cd and Zn by Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Soil 281:325–337
Wang GQ, Koopmans GF, Song J, Temminghoff EJM, Luo YM, Zhao QG, Japenga J (2007) Mobilization of heavy metals from contaminated paddy soil by EDDS, EDTA, and elemental sulfur. Environ Geochem Hlth 29:221–235
Wen G, Schoenau JJ, Yamamoto T, Inoue M (2001) A model of oxidation of an elemental sulfur fertilizer in soils. Soil Sci 166:607–613
Wu LH, Liu YJ, Zhou SB, Guo FG, Bi D, Guo XH, Baker AJM, Smith JAC, Luo YM (2013) Sedum plumbizincicola X.H. Guo et S.B. Zhou ex L.H. Wu (Crassulaceae): a new species from Zhejiang Province, China. Plant Syst Evol 299:487–498
Wu LH, Zhou JW, Zhou T, Li Z, Jiang JP, Zhu D, Hou JY, Wang ZY, Luo YM, Christie P (2018) Estimating cadmium availability to the hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola in a wide range of soil types using a piecewise function. Sci Total Environ 637:1342–1350
Wu C, Shi LZ, Xue SG, Li WC, Jiang XX, Rajendran M, Qian ZY (2019) Effect of sulfur-iron modified biochar on the available cadmium and bacterial community structure in contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 647:1158–1168
Xue SG, Shi LZ, Wu C, Wu H, Qin YY, Pan WS, Hartley W, Cui MQ (2017) Cadmium, lead, and arsenic contamination in paddy soils of a mining area and their exposure effects on human HEPG2 and keratinocyte cell-lines. Environ Res 156:23–30
Yang JX, Yang J, Huang J (2017) Role of co-planting and chitosan in phytoextraction of As and heavy metals by Pteris vittata and castor bean: a field case. Ecol Eng 109:35–40
Zhan FD, Qin L, Guo XH, Tan JB, Liu NN, Zu YQ, Li Y (2016) Cadmium and lead accumulation and low-molecular-weight organic acids secreted by roots in an intercropping of a cadmium accumulator Sonchus asper L. with Vicia faba L. RSC Adv 6:33240–33248
Zhao FJ, Ma YB, Zhu YG, Tang Z, McGrath SP (2015) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies. Environ Sci Technol 49:750–759
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2016YFE0106400 and 2016YFD0801104), the Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu Province (Nos. BE2017778 and BE2016812), and the Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. ISSASIP1613).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Antony Van der Ent.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, G., Hu, P., Zhou, J. et al. Sulfur application combined with water management enhances phytoextraction rate and decreases rice cadmium uptake in a Sedum plumbizincicola - Oryza sativa rotation. Plant Soil 440, 539–549 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04095-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04095-w