Abstract
Aims
The objective of this study was to investigate changes in soil total organic C (TOC), total nitrogen (TN), phosphorus (P) fractions, and microbial community structure during secondary succession after abandonment of vineyards on calcareous soils.
Methods
Two chronosequences covering 200 years and differing in aspect and slope were established in Hungary, and the upper 10 cm of the mineral soils were studied.
Results
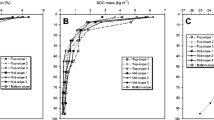
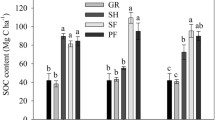
We found strong increases in TOC concentrations after land-use abandonment, especially at the south-exposed sites. The TOC/TN ratio increased by a factor of 1.3 in the south-west exposed chronosequence and by a factor of 1.6 in south exposed chronosequence. The concentration of labile P (NaHCO3-extractable P) diminished during the first 50 years after land-use abandonment, leading to low P availability at the later stages of the succession. The total organic P (TOP) concentration increased during the first 40 years after abandonment. At the later stages of succession, TOP concentrations decreased again, while the ratio of TOC/TOP increased continuously over 200 years. The ratio of arbuscular-mycorrhizal-fungi-to-bacteria (AMF/bacteria) increased strongly during the first decade after abandonment of the vineyards.
Conclusions
Our study indicates that impacts of former cultivation on secondary ecosystems persisted for more than a century, and that especially P concentrations showed long lasting legacy effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison VJ, Miller RM, Jastrow JD, Matamala R, Zak DR (2005) Changes in soil microbial community structure in a tallgrass prairie chronosequence. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:1412–1421
Allison VJ, Yermakov Z, Miller RM, Jastrow JD, Matamala R (2007) Using landscape and depth gradients to decouple the impact of correlated environmental variables on soil microbial community composition. Soil Biol Biochem 39:505–516
Alt F, Oelmann Y, Herold N, Schrumpf M, Wilcke W (2011) Phosphorus partitioning in grassland and forest soils of Germany as related to land‐use type, management intensity, and land use–related pH. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174:195–209
Baer SG, Kitchen DJ, Blair JM, Rice CW (2002) Changes in ecosystem structure and function along a chronosequence of restored grasslands. Ecol Appl 12:1688–1701
Bardgett RD, Bowman WD, Kaufmann R, Schmidt KS (2005) A temporal approach to linking aboveground and belowground ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 20:634–641
Brandtberg PO, Davis MR, Clinton PW, Condron LM, Allen RB (2010) Forms of soil phosphorus affected by stand development of mountain beech Nothofagus forests in New Zealand. Geoderma 157:228–234
R Core Team (2013) R: A language and environment for statistical computing R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria URL http://www.R-projectorg/
Crews TE, Kitayama K, Fownes JH, Riley RH, Herbert DA, Mueller-Dombois D, Vitousek PM (1995) Changes in soil phosphorus fractions and ecosystem dynamics across a long chronosequence in Hawaii. Ecology 76:1407–1424
De Schrijver A, Vesterdal L, Hansen K, De Frenne P, Augusto L, Achat DL, Verheyen K (2012) Four decades of post-agricultural forest development have caused major redistributions of soil phosphorus fractions. Oecologia 169:221–234
Demoling F, Figueroa D, Bååth E (2007) Comparison of factors limiting bacterial growth in different soils. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2485–2495
Dickie IA, Yeates GW, St John MG, Stevenson BA, Scott JT, Rillig MC, Aislabie J (2011) Ecosystem service and biodiversity trade‐offs in two woody successions. J Appl Ecol 48:926–934
Dunjó G, Pardini G, Gispert M (2003) Land use change effects on abandoned terraced soils in a Mediterranean catchment, NE Spain. Catena 52:23–37
Dupouey JL, Dambrine E, Laffite JD, Moares C (2002) Irreversible impact of past land use on forest soils and biodiversity. Ecology 83:2978–2984
Falkengren-Grerup U, Brink DJT, Brunet J (2006) Land use effects on soil N, P, C and pH persist over 40–80 years of forest growth on agricultural soils. For Ecol Manag 225:74–81
Fierer N, Strickland MS, Liptzin D, Bradford MA, Cleveland CC (2009) Global patterns in belowground communities. Ecol Lett 12:1238–1249
Foster D, Swanson F, Aber J, Burke I, Brokaw N, Tilman D, Knapp A (2003) The importance of land-use legacies to ecology and conservation. Bioscience 53:77–88
Frostegård Å, Tunlid A, Bååth E (1991) Microbial biomass measured as total lipid phosphate in soils of different organic content. J Microbiol Methods 14:151–163
Gough MW, Marrs RH (1990) A comparison of soil fertility between semi-natural and agricultural plant communities: implications for the creations of species-rich grassland on abandoned agricultural land. Biol Conserv 51:83–96
Gunina A, Dippold MA, Glaser B, Kuzyakov Y (2014) Fate of low molecular weight organic substances in an arable soil: from microbial uptake to utilisation and stabilisation. Soil Biol Biochem 77:304–313
Guo LB, Gifford RM (2002) Soil carbon stocks and land use change: a metaanalysis. Glob Chang Biol 8:345–360
Harris J (2009) Soil microbial communities and restoration ecology: facilitators or followers? Science 329:573–574
Heinrichs H, Brumsack HJ, Loftfield N, König N (1986) Verbessertes Druckaufschlußsystem für biologische und anorganische Materialien. Z Pflanzenernaehr Bodenkd 149:350–353
Heuck C, Weig A, Spohn M (2015) Soil microbial biomass C: N: P stoichiometry and microbial use of organic phosphorus. Soil Biol Biochem 85:119–129
Hinsinger P (2001) Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review. Plant Soil 237:173–195
Hooker TD, Compton JE (2003) Forest ecosystem carbon and nitrogen accumulation during the first century after agricultural abandonment. Ecol Appl 13:299–313
Joergensen RG, Scheu S (1999) Response of soil microorganisms to the addition of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in a forest Rendzina. Soil Biol Biochem 31:859–866
Johnson NC, Zak DR, Tilman D, Pfleger FL (1991) Dynamics of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae during old field succession. Oecologia 86:349–358
Kalinina O, Goryachkin SV, Karavaeva NA, Lyuri DI, Najdenko L, Giani L (2009) Self-restoration of post-agrogenic sandy soils in the southern taiga of Russia: soil development, nutrient status, and carbon dynamics. Geoderma 152:35–42
Kalinina O, Krause SE, Goryachkin SV, Karavaeva NA, Lyuri DI, Giani L (2011) Self-restoration of post-agrogenic Chernozems of Russia: soil development, carbon stocks and dynamics of carbon pools. Geoderma 162:196–206
Knops JM, Tilman D (2000) Dynamics of soil nitrogen and carbon accumulation for 61 years after agricultural abandonment. Ecology 81:88–98
Koulouri M, Giourga C (2007) Land abandonment and slope gradient as key factors of soil erosion in Mediterranean terraced lands. Catena 69:274–281
Kurganova IN, Kudeyarov VN, Lopes de Gerenyu VO (2010) Updated estimate of carbon balance on Russian territory. Tellus B 62:497–505
Kurganova I, Lopes de Gerenyu V, Six J, Kuzyakov Y (2014) Carbon cost of collective farming collapse in Russia. Glob Chang Biol 20:938–947
MacDonald GK, Bennett EM, Taranu ZE (2012) The influence of time, soil characteristics, and land‐use history on soil phosphorus legacies: a global meta‐analysis. Glob Chang Biol 18:1904–1917
Matamala R, Jastrow JD, Miller RM, Garten CT (2008) Temporal changes in C and N stocks of restored prairie: implications for C sequestration strategies. Ecol Appl 18:1470–1488
Matar A, Torrent J, Ryan J (1992) Soil and fertilizer phosphorus and crop responses in the dryland Mediterranean zone. In: Advances in Soil Science (pp 81–146) Springer, New York
McLauchlan K (2006) The nature and longevity of agricultural impacts on soil carbon and nutrients: a review. Ecosystems 9:1364–1382
McMahon SM, Parker GG, Miller DR (2010) Evidence for a recent increase in forest growth. PNAS 107:3611–3615
Olander LP, Vitousek PM (2000) Regulation of soil phosphatase and chitinase activityby N and P availability. Biogeochem 49:175–191
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils using NaHCO3. United States Department of Agriculture Circular 939
Poeplau C, Don A, Vesterdal L, Leifeld J, Van Wesemael BAS, Schumacher J, Gensior A (2011) Temporal dynamics of soil organic carbon after land‐use change in the temperate zone–carbon response functions as a model approach. Glob Chang Biol 17:2415–2427
Poschlod P, WallisDeVries MF (2002) The historical and socioeconomic perspective of calcareous grasslands—lessons from the distant and recent past. Biol Conserv 104:361–376
Post WM, Kwon KC (2000) Soil carbon sequestration and land‐use change: processes and potential. Glob Chang Biol :317–327
Potthoff M, Steenwerth KL, Jackson LE, Drenovsky RE, Scow KM, Joergensen RG (2006) Soil microbial community composition as affected by restoration practices in California grassland. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1851–1860
Poulton PR, Pye E, Hargreaves PR, Jenkinson DS (2003) Accumulation of carbon and nitrogen by old arable land reverting to woodland. Glob Chang Biol 9:942–955
Ramankutty N (2006) Global land-cover change: recent progress, remaining challenges. In: Lambin EF, Geist HJ (eds) Land-Use and Land-Cover Change. Springer, Berlin, pp 9–41
Ramankutty N, Foley JA (1998) Characterizing patterns of global land use: an analysis of global croplands data. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 12:667–85
Richardson SJ, Peltzer DA, Allen RB, McGlone MS, Parfitt RL (2004) Rapid development of phosphorus limitation in temperate rainforest along the Franz Josef soil chronosequence. Oecologia 139:267–276
Saunders WMH, Williams EG (1955) Observations on the determination of total organic phosphorus in soils. Eru J Soil Sci 6:254–267
Sendtko A (1999) Succession of xerothermic vegetation in abandoned vineyards of the Tokaj region (northeastern Hungary): studies in phytosociology and population biology. Phytocoenologia 29:345–448
Spohn M, Kuzyakov Y (2013a) Distribution of microbial-and root-derived phosphatase activities in the rhizosphere depending on P availability and C allocation–coupling soil zymography with 14C imaging. Soil Biol Biochem 67:106–113
Spohn M, Kuzyakov Y (2013b) Phosphorus mineralization can be driven by microbial need for carbon. Soil Biol Biochem 61:69–75
Stevens CJ, Dise NB, Mountford JO, Gowing DJ (2004) Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands. Science 303:1876–1879
Tarolli P, Preti F, Romano N (2014) Terraced landscapes: from an old best practice to a potential hazard for soil degradation due to land abandonment. Anthropocene 6:10–25
van der Wal A, van Veen JA, Smant W, Boschker HT, Bloem J, Kardol P, de Boer W (2006) Fungal biomass development in a chronosequence of land abandonment. Soil Biol Biochem 38:51–60
van Veldhoven PP, Mannaerts GP (1987) Inorganic and organic phosphate measurements in the nanomolar range. Anal Biochem 161:45–48
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soils microbial biomass-C Soil. Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Walker LR, Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Clarkson BD (2010) The use of chronosequences in studies of ecological succession and soil development. J Ecol 98:725–736
Wassen MJ, Venterink HO, Lapshina ED, Tanneberger F (2005) Endangered plants persist under phosphorus limitation. Nature 437:547–550
Young IM, Ritz K (2000) Tillage, habitat space and function of soil microbes. Soil Till Res 53:201–213
Zak DR, Grigal DF, Gleeson S, Tilman D (1990) Carbon and nitrogen cycling during old-field succession: constraints on plant and microbial biomass. Biogeochemistry 11:111–129
Zeller V, Bardgett RD, Tappeiner U (2001) Site and management effects on soil microbial properties of subalpine meadows: a study of land abandonment along a north–south gradient in the European Alps. Soil Biol Biochem 33:639–649
Zornoza R, Guerrero C, Mataix-Solera J, Scow KM, Arcenegui V, Mataix-Beneyto J (2009) Changes in soil microbial community structure following the abandonment of agricultural terraces in mountainous areas of Eastern Spain. Appl Soil Ecol 42:315–323
Acknowledgments
Research was allowed by the Northern-Hungary Inspectorate for Environmental Protection Nature Conservation and Water Management, Miskolc, in accordance with decree No. 16496-3/2011. We would like to thank all students that helped with the field work. We are grateful to Carolin Apostel and Michaela Dippold for their help with the PLFA analysis, and to Carlos A. Sierra for his help with the software program R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Benjamin L. Turner.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix 1
(DOCX 15 kb)
Appendix 2
(DOCX 18.0 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spohn, M., Novák, T.J., Incze, J. et al. Dynamics of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in calcareous soils after land-use abandonment – A chronosequence study. Plant Soil 401, 185–196 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2513-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2513-6