Abstract
Aims
The aims of this work were to characterize the soil bacterial communities in an arenized area in southern Brazil subjected to different management regimes through cultivation-dependent and cultivation-independent methods and to evaluate the potential of selected plant growth-promoting (PGP) bacteria to improve the growth of native Lupinus albescens plants.
Methods
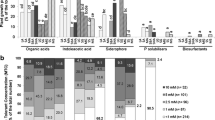
Bulk soil samples from an arenized site and rhizospheric soil and roots of L. albescens grown in this arenized site as well as samples from soils of the same region outside of the arenized area and rhizospheric soil and roots of L. albescens grown in non-arenized sites were evaluated. Phosphate solubilization, indolic compound and siderophore production abilities of the isolates were screened and compared. Some isolates were selected for in vivo plant growth promotion in greenhouse experiment.
Results
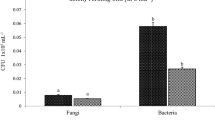
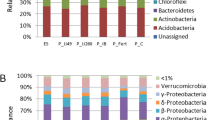
The samples from the arenized area presented less microbial biomass and less diverse bacterial communities compared with those from non-arenized areas. The PGP characteristics produced by the bacterial isolates showed differences among arenized and non arenized areas. A growth chamber experiment with L. albescens showed that phosphate-insoluble conditions coupled with bacterial inoculation resulted in the best PGP effect.
Conclusions
Culture-dependent and culture-independent methods showed converging results regarding diversity indices and the rhizospheric environments increased bacterial diversity and biomass when compared to bulk soils. The PGP traits analyzed in this work were affected by environmental conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MA, Pate JS, Pate A (1992) Availability of organic and inorganic forms of phosphorus to iupins. Plant Soil 145:107–113
Ajai A, Arya AS, Dhinwa PS, Pathan SK (2009) Desertification/land degradation status mapping of India. Curr Sci India 97(10):1478–1483
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaeffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Ambrosini A, Beneduzi A, Stefanski T, Pinheiro FG, Vargas LK, Passaglia LMP (2012) Screening of plant growth promoting Rhizobacteria isolated from sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Plant Soil 356(1):245–264
Andam CP, Parker MA (2007) Novel alphaproteobacterial root nodule symbiont associated with Lupinus texensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(17):5687–5691
Arruda L, Beneduzi A, Martins A, Lisboa B, Lopes C, Bertolo F, Passaglia LMP, Vargas LK (2012) Screening of rhizobacteria isolated from maize (Zea mays L.) in Rio Grande do Sul State (South Brazil) and analysis of their potential to improve plant growth. Appl Soil Ecol. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2012.09.001
Assih E, Ouattara AS, Thierry S, Cayol J-L, Labat M, Macarie H (2002) Stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila sp. nov., a strictly aerobic bacterium isolated from an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:559–568
Balachandar D, Raja P, Kumar K, Sundaram SP (2007) Non-rhizobial nodulation in legumes. Biotechnol Mol Rev 2(2):49–57
Barea JM, Requena N, Jimenez I (1996) A revegetation strategy based on the management of arbuscular mycorrhizae, Rhizobium and rhizobacterias for the reclamation of desertified Mediterranean shrubland ecosystems. Desertif Mediterr Ecosyst 75–86
Bashan Y (1999) Interactions of Azospirillum spp. in soils: a review. Biol Fertil Soils 29:246–256
Batool R, Hasnain S (2005) Growth stimulatory effects of Enterobacter and Serratia isolated from biofilms on plant growth and soil aggregation. Biotech 4(4):347–353
Belimov AA, Kojemiakov AP, Chuvarliyeva (1995) Interaction between barley and mixed cultures of nitrogen fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Plant Soil 173:29–37
Beneduzi A, Peres D, Vargas LK, Bodanese-Zanettini MH, Passaglia LMP (2008) Evaluation of genetic diversity and plant growth promoting activities of nitrogen-fixing bacilli isolated from rice fields in South Brazil. Appl Soil Ecol 39:311–320
Bissett A, Richardsona AE, Bakerb G, Thrall PH (2011) Long-term land use effects on soil microbial community structure and function. App Soil Ecol 51:66–78
Brosius J, Palmer ML, Kennedy PJ, Noller HF (1978) Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75(10):4801–4805
Chun J, Lee JH, Jung Y, Kim M, Kim S, Kim BK, Lim YW (2007) EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2259–2261
Cobley JG, Cox JC (1983) Energy conservation in acidophilic bacteria. Microbiol Rev 48:344
Coenye T, Vandamme P (2003) Diversity and significance of Burkholderia species occupying diverse ecological niches. Environ Microbiol 5:719–729
Cole CV, Elliott ET, Hunt HW, Coleman DC (1978) Trophic interactions in soils as they affect energy and nutrient dynamics. V. phosphorus transformations. Microb Ecol 4:381–387
Costa PB, Beneduzi A, Souza R, Schoenfeld R, Vargas LK, Passaglia LMP (2013) The effects of different fertilization conditions on bacterial plant growth promoting traits: guidelines for directed bacterial prospection and testing. Plant Soil. doi:10.1007/s11104-012-1513-z
Crabtree WL (1999) Deep placement of Mn fertiliser on a sandy soil increased grain yield and reduced split seed in Lupinus angustifolius. Plant Soil 214:9–14
Dai M, Rogers JB, Warner JR, Copley SD (2003) A previously unrecognized step in pentachlorophenol degradation in Sphingobium chlorophenolicum is catalyzed by tetrachlorobenzoquinone. J Bacteriol 185(1):302–310
Dessureault-Rompré J, Nowack B, Schulin R, Luster J (2007) Spatial and temporal variation in organic acid anion exudation and nutrient anion uptake in the rhizosphere of Lupinus albus L. Plant Soil 301:123–134
Dregne HE (1986) Desertification of arid lands. In: El-Baz F, Hassan MHA (eds) Physics of desertification. Martinus, Nijhoff, Dordrecht
Emmert EA, Handelsman J (1999) Biocontrol of plant disease: a (gram-) positive perspective. FEMS Microbiol Lett 171:1–9
Esitken A, Pirlak L, Turan M, Sahin F (2006) Effects of floral and foliar application of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on yield, growth and nutrition of sweet cherry. Sci Hortic Amst 110:324–327
Exley C, Birchall JD (1992) The cellular toxicity of aluminium. J Theor Biol 159:83–98
Fang Y, Lu Z, Lv F, Bie X, Liu S, Ding Z, Xu W (2006) A newly isolated organic solvent tolerant Staphylococcus saprophyticus M36 produced organic solvent-stable lipase. Curr Microbiol 53:510–515
Farina R, Beneduzi A, Ambrosini A, de Campos SB, Lisboa BB, Wendisch V, Vargas LK, Passaglia LMP (2012) Diversity of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria communities associated with the stages of canola growth. Appl Soil Ecol 55:44–52
Felske A, Rheims H, Wokerink A, Stackebrandt E, Akkermans DL (1997) Ribosome analysis reveals prominent activity of an uncultured member of the class Actinobacteria in grasslands soils. Microbiology 143:2983–2989
Freitas JR, Banerjee MR, Germida JJ (1997) Phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria enhance the growth and yield but not phosphorus uptake of canola (Brassica napus L.). Biol Fertil Soils 24:358–364
Garcia C, Hemandez T, Costa F (1994) Microbial activity in soil under Mediterranean environmental conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1185–1191
Giongo A, Meneduzi A, Ambrosini A, Vargas LK, Stroschein MR, Eltz FL, Bodanese-Zanettini MH, Passaglia LMP (2010) Isolation and characterization of two plant growth-promoting bacteria from the rhizoplane of a legume (Lupinus albescens). Rev Bras Cienc Solo 34:361–369
Glick BR (2005) Modulation of plant ethylene levels by the bacterial enzyme ACC deaminase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 251:1–7
Glickmann E, Dessaux Y (1995) A critical examination of the specificity of the Salkowski Reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:793–796
Gomez-Alvarez V, King GM, Nüsslein K (2007) Comparative bacterial diversity in recent Hawaiian volcanic deposits of different ages. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:60–73
Griffiths BS, Kuan HL, Ritz K, Glover LA, McCaig AE, Fenwick C (2004) The relationship between microbial community structure and functional stability, tested experimentally in an upland pasture soil. Microbial Ecol 47:104–113
Gulati A, Sood S, Rahi P, Thakur R, Chauhan S, Chawla I (2011) Diversity analysis of diazotrophic bacteria associated with the roots of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:545–555
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hammer O, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis Version 2.09. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):9
Hashidoko Y (2005) Ecochemical studies of interrelationships between epiphytic bacteria and host plants via secondary metabolites. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69(8):1427–1441
Hayat R, Ali S, Amara U, Khalid R, Ahmed I (2010) Soil beneficial bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion: a review. Ann Microbiol 60:579–598
Hi H, Srinivasan S, Kim MK (2010) Stenotrophomonas panacihumi sp. nov., isolated from soil of a ginseng field. J Microbiol 48:30–35
Hoagland DR, Snyder WC (1933) Nutrition of strawberry plants under controlled conditions. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci 30:288–294
Horwath WR, Paul EA, Harris D, Norton J, Jagger L, Horton KA (1996) Defining a realistic control for the chloroform fumigation incubation method using microscopic counting and 14C substrates. Can J Soil Sci 76:459–467
Hu X-J, Lin X, Wang J, Chu H, Yin R, Zhang J (2009) Population size and specific potential of P-mineralizing and -solubilizing bacteria under long-term P-deficiency fertilization in a sandy loam soil. Pedobiologia 53:49–58
Hu X-J, Li Z-J, Cao Y-C, Zhang J, Gong Y-X, Yang Y-F (2010) Isolation and identification of a phosphate-solubilizing bacterium Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii g6, and effects of temperature, salinity, and pH on its growth under indoor culture conditions. Aquacult Int 18:1079–1091
Husník F, Chrudimský T, Hypša V (2011) Multiple origins of endosymbiosis within the Enterobacteriaceae (γ-Proteobacteria): convergence of complex phylogenetic approaches. BMC Biol 9:87
Ibekwe AM, Kennedy AC (1998) Phospholipid fatty acid profiles and carbon utilization patterns for analysis of microbial community structure under field and greenhouse conditions. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 26:151–163
Jarabo-Lorenzo A, Pérez-Galdona R, Donate-Correa J et al (2003) Genetic diversity of bradyrhizobial populations from diverse geographic origins that nodulate Lupinus spp. and Ornithopus spp. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:611–623
Jha B, Thakur MC, Gontia I, Albrecht V, Stoffels M, Schmid M, Hartmann A (2009) Isolation, partial identification and application of diazotrophic rhizobacteria from traditional Indian rice cultivars. Eur J Soil Biol 45:62–72
Kim H, Nishiyama M, Kunito T, Senoo K, Kawahara K, Murakami K, Oyaizu H (1998) High population of Sphingomonas species on plant surface. J Appl Microbiol 85:731–736
Kim H-B, Srinivasan S, Sathiyaraj G, Quan L-H, Kim S-H, Bui TPN, Liang Z-Q, Kim Y-J, Yang D-C (2010) Stenotrophomonas ginsengisoli sp. nov., isolated from a ginseng field. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1522–1526
Krsek M, Wellington EMH (1999) Comparison of different methods for the isolation and purification of total community DNA from soil. J Microbiol Methods 39:1–16
Kuhlman KRW, Fusco WG, La Duc MT et al (2006) Diversity of Microorganisms within Rock Varnish in the Whipple Mountains, California. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(2):1708–1715
Kunito T, Owaki M, Ihyo Y, Sumi H, Toda H, Fukuda D, Park H-D (2012) Genera Burkholderia and Lipomyces are predominant aluminum-resistant microorganisms isolated from acidic forest soils using cycloheximide-amended growth media. Ann Microbiol 62:1339–1344
Laheurte J, Berthelin (1988) Effect of a phosphate solubilizing bacteria on maize growth and root exudation over four levels of labile phosphorus. Plant Soil 105:11–17
Liu X, Lindemann WC, Whitford WG, Steiner RL (2000) Microbial diversity and activity of disturbed soil in the northern Chihuahuan Desert. Biol Fertil Soils 32:243–249
Lynch JM, Whipps JM (1990) Substrate flow in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 129(1):11–10
Manucharova NA, Vlasenko NA, Tourova TP, Panteleeva NA, Stepanov LA, Zenova GM (2008) Thermophilic chitinolytic microorganisms of brown semidesert soil. Microbiology 77:610–614
Martini JEJ (1979) Karst in Black Reef Quartzite near Kaapsehoop, Eastern Transvaal. Ann South Afr Geol Surv 13:115–128
Minkwitz A, Berg G (2001) Comparison of antifungal activities and 16S ribisomal DNA sequences of clinical and environmental isolates of Stenotrophomonas altophilia. J Clin Microbiol 39:139–145
Morales-García YE, Juárez-Hernández D, Aragón-Hernández C, Mascarua-Esparza M, Bustillos-Cristales MR, Fuentes-Ramírez LE, Martinez-Contreras RD, Munoz-Rojas J (2011) Growth response of maize plantlets inoculated with Enterobacter spp., as a model for alternative agriculture. Rev Argent Microbiol 43:287–293
Nacke H, Thürmer A, Wollherr A, Will C, Hodac L, Herold N, Schöning I, Schrumpf M, Daniel R (2011) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of bacterial community structure along different management types in German forest and grassland soils. PLoS One 6(2):1–12
Nakayama T, Homma Y, Hashidoko Y, Mizutani J, Tahara S (1999) Possible role of xanthobaccins produced by Stenotrophomonas sp. strain sb-k88 in suppression of sugar beet damping-off disease. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(10):4334–4339
Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini MT, Landi L, Pietramellara G, Renella G (2003) Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur J Soil Sci 54:655–670
Neilson JW, Quade J, Ortiz M et al (2012) Life at the hyperarid margin: novel bacterial diversity in arid soils of the Atacama Desert, Chile. Extremophiles 16(3):553–566
Nweke CO, Okpokwasili GC (2003) Drilling fluid base oil biodegradation potential of a soil Staphylococcus species. Afr J Biotechnol 2:293–295
Okayasu T, Okuro T, Jamsran U, Takeuchi K (2010) Desertification emerges through cross-scale interaction. Global Environ Res 14:71–77
Ordookhani K, Khavazi K, Moezzi A, Rejali F (2010) Influence of PGPR and AMF on antioxidant activity, lycopene and potassium contents in tomato. Afr J Agric Res 5(10):1108–1116
Ovreås L, Forney L, Daae FL, Torsvik V (1997) Distribution of bacterioplankton in meromictic lake Saelenvannet, as determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of PCR-amplified gene fragments coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3367–3373
Puranik PR, Paknikar KM (1999) Biosorption of lead, cadmium, and zinc by Citrobacter strain MCM B-181: characterization studies. Biotechnol Prog 15:228–237
Rico A, Ortiz-Barredo A, Ritter E, Murillo J (2004) Genetic characterization of Erwinia amylovora strains by amplified fragment length polymorphism. J Appl Microbiol 96:302–310
Rodríguez H, Fraga R (1999) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnol Adv 17:319–339
Roesch LFW, Vieira FCB, Pereira VA, Schünemann AL, Teixeira IF, Senna AJT, Stefenon VM (2009) The Brazilian Pampa: a fragile biome. Diversity 1:182–198
Rovedder APM, Eltz FLF (2008) Revegetation with cover crops for soils under arenization and wind erosion in Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil. Rev Bras Cienc Solo 32:315–321
Sambrook J, Russel DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NewYork
Sarkar A, Islam T, Biswas GC, Alam S, Hossain M, Talukder NM (2012) Screening for phosphate solubilizing bacteria inhabiting the rhizoplane of rice grown in acidic soil in Bangladesh. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 59(2):199–213
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Ann Biochem 160:47–56
Sequeira Braga MS, Paquet H, Begonha A (2002) Weathering of granites in a temperate climate (NW Portugal): granitic saprolites and arenization. Catena 49:41–56
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Sheikh BA, Soomro GH (2006) Desertification: causes, consequences and remedies. Pak J Agric 22(1):44–51
Sheng XF (2005) Growth promotion and increased potassium uptake of cotton and rape by a potassium releasing strain of Bacillus edaphicus. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1918–1922
Singh JS, Pandey VC, Singh DP (2011) Efficient soil microorganisms: a new dimension for sustainable agriculture and environmental development. Agric Ecosyst Environ 140:339–353
Smith JJ, Tow LA, Stafford W, Cary C, Cowan DA (2006) Bacterial diversity in three different Antarctic Cold Desert mineral soils. Microb Ecol 51:413–421
Soares RA, Roesch LFW, Zanatta G, Camargo FO, Passaglia LMP (2006) Occurrence and distribution of nitrogen fixing bacterial community associated with oat (Avena sativa) assessed by molecular and microbiological techniques. Appl Soil Ecol 33:221–234
Souza R, Beneduzi A, Ambrosini A, Costa PB, Meyer J, Vargas LK, Schoenfeld R, Passaglia LMP (2012) The effect of plant grow th-promoting rhizobacteria on the grow of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cropped in southern Brazilian fields. Plant Soil. doi:10.1007/s11104-012-1430-1
Sposito G (1996) The environmental chemistry of aluminum, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Stroschein MBD, Eltz FLF, Antoniolli ZI, Lupatini M, Vargas LK, Giongo A, Pontelli MP (2010) Symbiotic efficiency and genetic characteristics of Bradyrhizobium sp. strain UFSM LA 1. 3 isolated from Lupinus albescens (H. et Arn). Sci Agric 67(6):702–706
Suertegaray DMA (1987) A trajetória da natureza: um estudo geomorfológico sobre as areias de Quaraí. Phd Thesis, RS. São Paulo, Universidade de São Paulo, 243p.
Suertegaray DMA (1998) Deserto grande do sul: controvérsia, 2nd edn. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, 130p
Sundara B, Natarajan V, Hari K (2002) In fluence of phosphorus solubilizing bacteria on the changes in soil available phosphorus and sugarcane and sugar yields. Field Crop Res 77:43–49
Sylvester-Bradley R, Asakawa N, La Torraca S, Magalhães FMM, Oliveira L, Pereira RM (1982) Levantamento quantitativo de microrganismos solubilizadores de fosfatos na rizosfera de gramíneas e leguminosas forrageiras na Amazônia. Acta Amazon 12:15–22
Tantawy STA, Atef NM (2010) Growth responses of Lupinus termis to some plant growth promoting cyanobacteria and bacteria as biofertilizers. J food Agric Environ 8(3):1178–1183
Tedesco JM, Gianelo C, Bissani CA, Bohnen H, Volkweiss SJ (1995) Análises de solo, plantas e outros materiais. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre
Trujillo ME, Willems A, Abril A, Planchuelo AM, Rivas R, Ludena D, Mateos PF, Martinez-Molina E, Velázquez E (2005) Nodulation of Lupinus albus by Strains of Ochrobactrum lupini sp. nov. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(3):1318–1327
Unno Y, Okubo K, Wasaki J, Shinano T, Osaki M (2005) Plant growth promotion abilities and microscale bacterial dynamics in the rhizosphere of Lupin analysed by phytate utilization ability. Environ Microbiol 7:396–404
Verhoeven JTA, Schmitz MB (1991) Control of plant growth by nitrogen and phosphorus in mesotrophic fens. Biogeochemistry 12:135–148
Viallard V, Poirier I, Cournoyer B, Haurat J, Wiebkin S, Ophel-keller K, Balandreaul J (1998) Burkholderia graminis sp. nov., a rhizospheric Burkholderia species, and reassessment of [Pseudomonas] phenazinium, [Pseudomonas] pyrrocinia and [Pseudomonas] glathei as Burkholderia. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:549–563
Videira SS, de Araujo JLS, Rodrigues LDS, Baldani VLD, Baldani JI (2009) Occurrence and diversity of nitrogen-fixing Sphingomonas bacteria associated with rice plants grown in Brazil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 293:11–19
Wang X-P, Li X-R, Xiao H-L, Pan Y-X (2006) Evolutionary characteristics of the artificially revegetated shrub ecosystem in the Tengger Desert, northern China. Ecol Res 21:415–424
Weisskopf L, Heller S, Eberl L (2011) Burkholderia species are major inhabitants of white lupin cluster roots. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:7715–7720
Whipps JM (1990) Carbon economy. In: Lynch JM (ed) The rhizosphere. Wiley, Chichester, pp 59–97
Whipps JM (2001) Microbial interactions and biocontrol in the rhizosphere. J Exp Bot 52:487–511
Wittebolle L, Marzorati M, Clement L, Balloi A, Daffonchio D, Heylen K, De Vos P, Verstraete W, Boon N (2009) Initial community evenness favours functionality under selective stress. Nature 458:623–626
Wolf A, Fritze A, Hagemann M, Berg G (2002) Stenotrophomonas rhizophila sp. nov., a novel plant-associated bacterium with antifungal properties. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1937–1944
Yrjälä K, Mancano G, Fortelius C, Akerman ML, Sipila TP (2010) The incidence of Burkholderia in epiphytic and endophytic bacterial cenoses in hybrid aspen grown on sandy peat. Boreal Environ Res 15:81–96
Zhang W, Wang H, Zhang R, Yu X-Z, Qian P-Y, Wong MH (2010) Bacterial communities in PAH contaminated soils at an electronic-waste processing center in China. Ecotoxicology 19:96–104
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Drs. Flávio Eltz and Sandro Giacomini from the Universidade Federal de Santa Maria, RS, for the Lupinus samples. This work was financed by a grant and fellowships from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq/Brazil), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES/Brazil) and Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia (INCT) da Fixação Biológica do Nitrogênio (Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Peter A.H. Bakker.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Granada, C., da Costa, P.B., Lisboa, B.B. et al. Comparison among bacterial communities present in arenized and adjacent areas subjected to different soil management regimes. Plant Soil 373, 339–358 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1796-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1796-8