Abstract
Background and aims
Biochar additions to tropical soils have been shown to reduce N leaching and increase N use efficiency. No studies exist verifying reduced N leaching in field experiments on temperate agricultural soils or identifying the mechanism for N retention.
Methods
Biochar derived from maize stover was applied to a maize cropping system in central New York State at rates of 0, 1, 3, 12, and 30 t ha-1 in 2007. Secondary N fertilizer was added at 100, 90, 70, and 50 % of the recommended rate (108 kg N ha-1). Nitrogen fertilizer enriched with 15 N was applied in 2009 to the 0 and 12 t ha-1 of biochar at 100 and 50 % secondary N application.
Results
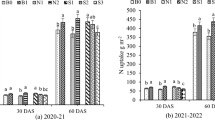
Maize yield and plant N uptake did not change with biochar additions (p > 0.05; n = 3). Less N (by 82 %; p < 0.05) was lost after biochar application through leaching only at 100 % N fertilization. The reason for an observed 140 % greater retention of applied 15 N in the topsoil may have been the incorporation of added 15 N into microbial biomass which increased approximately three-fold which warrants further research. The low leaching of applied fertilizer 15 N (0.42 % of applied N; p < 0.05) and comparatively high recovery of applied 15 N in the soil (39 %) after biochar additions after one cropping season may also indicate greater overall N retention through lower gaseous or erosion N losses with biochar.
Conclusions
Addition of biochar to fertile soil in a temperate climate did not improve crop growth or N use efficiency, but increased retention of fertilizer N in the topsoil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal GD, Lunkad SK, Malkhed T (1999) Diffuse agricultural nitrate pollution of groundwaters in India. Water Sci Technol 39:67–75
Bruulsema TW, Duxbury JM (1996) Simultaneous measurement of soil microbial nitrogen, carbon and carbon isotope ratio. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:1787–1791
Burkholder JM (1998) Implications of harmful microalgae and heterotrophic dinoflagellates in management of sustainable fisheries. Ecol Appl 8:S37–S62
Cahn MD, Bouldin DR, Cravo MS, Bowen WT (1993) Cation and nitrate leaching in an Oxisol of the Brazilian Amazon. Agron J 85:334–340
Campbell CA, Ellert BH, Jame YW (1993) Nitrogen mineralization potential in soils. In: Carter RM (ed) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp 341–349
Carpenter SR, Caraco NF, Correll DL, Howarth RW, Sharpley AN, Smith VH (1998) Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol Appl 8:559–568
Chan KY, Van Zwieten L, Meszaros I, Downie A, Joseph S (2007) Agronomic values of greenwaste biochar as a soil amendment. Austr J Soil Res 45:629–634
Chan KY, Van Zwieten L, Meszaros I, Downie A, Joseph S (2008) Using poultry litter biochars as soil amendments. Austr J Soil Res 46:437–444
Cheng CH, Lehmann J (2009) Ageing of black carbon along a temperature gradient. Chemosphere 75:1021–1027
Cheng CH, Lehmann J, Engelhard MH (2008) Natural oxidation of black carbon in soils: changes in molecular form and surface charge along a climosequence. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 72:1598–1610
Chun Y, Sheng G, Chiou CT, Xing B (2004) Compositions and sorptive properties of crop-residue derived char. Environ Sci Technol 38:4649–4655
DeLuca TH, MacKenxie MD, Gundale MJ, Holben WE (2006) Wildfire-produced charcoal directly influences nitrogen cycling in ponderosa pine forests. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:448–453
Dempster DN, Jones DL, Murphy DV (2012a) Clay and biochar amendments decreased inorganic but not dissolved organic nitrogen leaching in soil. Soil Res 50:216–221
Dempster DN, Jones DL, Murphy DV (2012b) Organic nitrogen mineralisation in two contrasting agro-ecosystems is unchanged by biochar addition. Soil Biol Biochem 48:47–50
Drinkwater LE, Wagoner P, Sarrantonio M (1998) Legume-based cropping systems have reduced carbon and nitrogen losses. Nature 396:262–265
Elad Y, Rav David D, Meller Harel Y, Borenshtein M, Ben Kalifa H, Silber A, Graber ER (2010) Induction of systemic resistance in plants by biochar, a soil-applied carbon sequestering agent. Phytopathology 100:913–921
Francis DD (1992) Control mechanisms to reduce fertilizer N movement into groundwater. J Soil Water Conserv 47:444–448
Gaskin JW, Speir RA, Harris K, Das KC, Lee RD, Morris LA, Fisher DS (2010) Effect of peanut hull and pine chip biochar on soil nutrients, corn nutrient status, and yield. Agron J 102:623–633
Grossman J, O’Neill BE, McPhillips L, Tsai SM, Liang B, Neves E, Lehmann J, Thies JE (2010) Amazonian anthrosols support similar microbial communities that differ distinctly from those extant in adjacent, unmodified soils of the same mineralogy. Microb Ecol 60:192–205
Haefele SM, Konboon Y, Wongboon W, Amarante S, Maarifat AA, Pfeiffer EM, Knoblauch C (2011) Effects and fate of biochar from rice residues in rice-based systems. Field Crop Res 121:430–440
Hidetoshi A, Benjamin SK, Haefele SM, Songyikhangsuthor K, Homma K, Kiyono Y, Inoue Y, Shiraiwa T, Horie T (2009) Biochar amendment techniques for upland rice production in Northern Laos 1. Soil physical properties, leaf SPAD and grain yield. Field Crops Res 111:81–84
Howarth RW, Billen G, Swaney D, Townsend A, Jaworski N, Lajtha K, Downing A, Elmgren R, Caraco N, Jordan T, Berendse F, Freney J, Kudeyarov V, Murdoch P, Zhao-Liang Z (1996) Nitrogen cycling in the North Atlantic Ocean and its watersheds. Biogeochemistry 35:75–139
Jin H (2010) Characterization of microbial life colonizing biochar and biochar-amended soils. Dissertation, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY
Jones DL, Rousk J, Edwards-Jones G, DeLuca TH, Murphy DV (2012) Biochar-mediated changes in soil quality and plant growth in a 3 year field trial. Soil Biol Biochem 45:113–124
Ketterings QM, Klausner SD, Czymmek KJ (2001) Nitrogen recommendations for field crops in New York. Department of Crop and Soil Sciences Extension Series EO1-04. Cornell University, Ithaca, NY
Kimetu J, Lehmann J, Ngoze S, Mugendi D, Kinyangi J, Riha S, Verchot L, Recha J, Pell A (2008) Reversibility of soil productivity decline with organic matter of differing quality along a degradation gradient. Ecosystems 11:726–739
Kolb SE, Fermanich KJ, Dornbush ME (2009) Effect of charcoal quantity on microbial biomass and activity in temperate soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:1173–1181
Kuzyakov Y, Subbotina I, Chen H, Bogomolova I, Xu X (2009) Black carbon decomposition and incorporation into soil microbial biomass estimated by 14 C labeling. Soil Biol Biochem 41:210–219
Laird DA, Fleming P, Davis DD, Horton R, Wang B, Karlen DL (2010a) Impact of biochar amendments on the quality of a typical Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 158:443–449
Laird DA, Fleming P, Wang B, Horton R, Karlen DL (2010b) Biochar impact on nutrient leaching from a Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 158:436–442
Lehmann J (2007) Bio-energy in the black. Front Ecol Environ 5:381–387
Lehmann J, da Silva P, Jr J, Steiner C, Nehls T, Zech W, Glaser B (2003) Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological Antrosol and Ferralsol of the Central Amazon basin: fertilizer, manure and charcoal amendments. Plant Soil 249:343–357
Lehmann J, Rillig M, Thies J, Masiello CA, Hockaday WC, Crowley D (2011) Biochar effects on soil biota—a review. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1812–1836
Liang B, Lehmann J, Solomon D, Kinyangi J, Grossman J, O’Neill B, Skjemstad J, Thies J, Luizão J, Petersen J, Neves E (2006) Black carbon increases cation exchange capacity in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:1719–1730
Liang B, Lehmann J, Sohi SP, Thies JE, O’Neill B, Trujillo L, Gaunt J, Solomon D, Grossman J, Neves EG, Luizão FJ (2010) Black carbon affects the cycling of non-black carbon in soil. Org Geochem 41:206–213
Major J, Steiner C, Downie A, Lehmann J (2009) Biochar effects on nutrient leaching. In: Lehmann J, Joseph S (eds) Biochar for environmental management: science and technology. Earthscan, London, pp 271–282
Major J, Rondon M, Molina D, Riha SJ, Lehmann J (2010) Maize yield and nutrition during 4 years after biochar application to a Colombian oxisol. Plant Soil 333:117–128
Major J, Rondon M, Molina D, Riha SJ, Lehmann J (2012) Nutrient leaching in a Colombian savanna Oxisol amended with biochar. J Environ Qual 41:1076–1086
Martin JH, Waldren RP, Stamp DL (2006) Principles of field crop production, 4th edn. Person Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Matson PA, Parton WJ, Power AG, Swift MJ (1997) Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties. Science 25:504–509
Matsubara Y-I, Hasegawa N, Fukui H (2002) Incidence of Fusarium root rot in asparagus seedlings infected with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus as affected by several soil amendments. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 71:370–374
Mitsch WJ, Day JW Jr, Gilliam JW, Groffman PM, Hey DL, Randall GW, Wang N (2001) Reducing nitrogen loading to the gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River Basin: strategies to counter a persistent ecological problem. BioScience 51:373–388
Mulvaney RL (1996) Nitrogen – Inorganic forms. In: Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH, Soltanpour PN, Tabatabai MA, Johnston CT, Summer ME (eds) Methods of soil analysis: Part 3—chemical methods, soil science society of America. Inc, Madison, WI, USA, pp 1129–1131
Novak JM, Busscher WJ, Laird DL, Ahmed M, Watts DW, Niandou MAS (2009) Impact of biochar amendment on fertility of southeastern costal plain soil. Soil Sci 174:105–112
O’Neill B, Grossman J, Tsai MT, Gomes JE, Lehmann J, Peterson J, Neves E, Thies JE (2009) Bacterial community composition in Brazilian Anthrosols and adjacent soils characterized using culturing and molecular identification. Microb Ecol 58:23–35
Oenema O, Boers PCM, van Erdt MM (1998) Leaching of nitrate from agriculture to groundwater: the effect of policies and measures in the Netherlands. Environ Pollut 102:471–478
Owens LB (1990) Nitrate-nitrogen concentrations in percolate from lysimeters planted to a legume-grass mixture. J Environ Qual 19:131–135
Pietikäinen J, Kiikkilä O, Fritze H (2000) Charcoal as a habitat for microbes and its effect on the microbial community of the underlying humus. Oikos 89:231–242
Rajkovich S, Enders A, Hanley K, Hyland C, Zimmerman AR, Lehmann J (2012) Corn growth and nitrogen nutrition after additions of biochars with varying properties to a temperate soil. Biol Fert Soils 48:271–284
Randall GW, Huggins DR, Russelle MP, Fuchs DJ, Nelson WW, Anderson JL (1997) Nitrate losses through subsurface tile drainage in conservation reserve program, alfalfa and row crop systems. J Environ Qual 26:1240–1247
Rondon MA, Lehmann J, Ramírez J, Hurtado M (2007) Biological nitrogen fixation by common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) increases with bio-char additions. Biol Fert Soils 43:699–708
SAS Institute Inc (2007) JMP version 7.0. Cary, NC
Scheer C, Grace PR, Rowlings DW, Kimber S, Van Zwieten L (2011) Effect of biochar amendment on the soil-atmosphere exchange of greenhouse gases from an intensive subtropical pasture in northern New South Wales, Australia. Plant Soil 345:47–58
Smernik RJ (2009) Biochar and sorption of organic compounds. In: Lehmann J, Joseph S (eds) Biochar for environmental management: science and technology. Earthscan, London, pp 289–300
Sogbedji JM, van Es HM, Yang CL, Geohring LD, Magdoff FR (2000) Nitrate leaching and nitrogen budget as affected by maize nitrogen rate and soil type. J Environ Qual 29:813–1820
Steiner C, Teixeira WG, Lehmann J, Zech W (2004) Microbial response to charcoal amendments of highly weathered soils and Amazonian Dark Earths in Central Amazonia—preliminary results. In: Glaser B, Woods WI (eds) Amazonian dark Earths: explorations in time and space. Springer, Berlin, pp 195–212
Steiner CB, Teixeira WG, Lehmann J, Nehls T, Macedo JLV, Blum WEH, Zech W (2007) Long term effects of manure, charcoal and mineralfertilization on crop production and fertility on a highly weathered Central Amazonian upland soil. Plant Soil 291:275–290
Steiner CB, Glaser B, Teixeira WG, Lehmann J, Blum WEH, Zech W (2008) Nitrogen retention and plant uptake on a highly weathered central Amazonian Ferralsol amended with compost and charcoal. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 171:893–899
Taghizadeh-Toosi A, Clough TJ, Condron LM, Sherlock RR, Anderson CR, Craigie RA (2011a) Biochar incorporation into pasture soil suppresses in situ nitrous oxide emissions from ruminant urine patches. J Environ Qual 40:468–476
Taghizadeh-Toosi A, Clough TJ, Sherlock RR, Condron LM (2011b) Biochar adsorbed ammonia is bioavailable. Plant Soil 350:57–69
Timlin DJ, Pachepsky Y, Snyder VA, Bryant RB (2001) Water budget approach to quantify corn grain yields under variable rooting depths. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:1219–1226
Townsend AR, Howarth RW, Bazzaz FA, Booth MS, Cleveland CC, Collinge SK, Dobson AP, Epstein PR, Holland EA, Keeney DR, Mallin MA, Rogers CA, Wayne P, Wolfe AH (2003) Human health effects of a changing global nitrogen cycle. Front Ecol Environ 1:240–246
Vaccari FP, Baronti S, Lugato E, Genesio L, Castaldi S, Fornasier F, Miglietta F (2011) Biochar as a strategy to sequester carbon and increase yield in durum wheat. Eur J Agron 34:231–238
van Es HM, Sogbedji JM, Shindelbeck RR (2006) Effect of manure application, timing, crop, and soil type on nitrate leaching. J Environ Qual 35:670–679
Van Zwieten L, Kimber S, Morris S, Chan KY, Downie A, Rust J, Joseph S, Cowie A (2010a) Effects of biochar from slow pyrolysis of papermill waste on agronomic performance and soil fertility. Plant Soil 327:235–246
Van Zwieten L, Kimber S, Morris S, Chan KY, Downie A, Rust J, Joseph S, Cowie A (2010b) A glasshouse study on the interaction of low mineral ash biochar with nitrogen in a sandy soil. Austr J Soil Res 48:569–576
Vitousek PM, Aber JD, Howarth RW, Likens GE, Matson PA, Schindler DW, Schlesinger WH, Tilman DG (1997) Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and consequences. Ecol Appl 7:737–750
Walters DT, Malzer GL (1990) Nitrogen management and nitrification inhibitor effects on nitrogen-15 N urea: II. Nitrogen leaching and balance. Soil Sci Soc Am J 54:122–130
Wardle DA, Nilsson M-C, Zackrisson O (2008) Fire-derived charcoal causes loss of forest humus. Science 320:629
Witt C, Gaunt JL, Galicia CC, Ottow JCG, Neue H (2000) A rapid chloroform-fumigation extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in flooded rice soils. Biol Fert Soils 30:510–519
Yamato M, Okimori Y, Wibowo IF, Anshori S, Ogawa M (2006) Effects of the application of charred bark of Acacia mangium on the yield of maize, cowpea, peanut and soil chemical properties in south Sumatra, Indonesia. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 52:489–495
Zhang A, Bian R, Pan G, Cui L, Hussain Q, Li L, Zheng J, Zheng J, Zhang X, Han X, Yu X (2012a) Effects of biochar amendment on soil quality, crop yield and greenhouse gas emission in a Chinese rice paddy: a field study of 2 consecutive rice growing cycles. Field Crop Research 127:153–160
Zhang A, Liu Y, Pan G, Hussain Q, Li L, Zheng J, Zhang X (2012b) Effect of biochar amendment on maize yield and greenhouse gas emissions from a soil organic carbon poor calcareous loamy soil from Central China Plain. Plant Soil 351:263–275
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the support by the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA Agreement 9891), a USDA Hatch grant, and a grant from the Cornell Graduate School to D.G. Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the donors. We thank Elena Miller-ter-Kuile and Shelby Rajkovich for help in conducting the experiment; we would also thank Bethany Guerena and several anonymous referees for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans Lambers.
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Esm 1
(PDF 31.8 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güereña, D., Lehmann, J., Hanley, K. et al. Nitrogen dynamics following field application of biochar in a temperate North American maize-based production system. Plant Soil 365, 239–254 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1383-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1383-4