Abstract
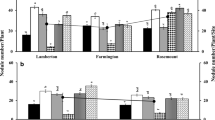
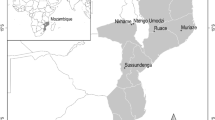
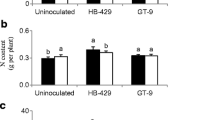
Azospirillum spp. have shown potential to enhance nodulation and plant growth of legumes when coinoculated with Rhizobium. The effect of Azospirillum on the Rhizobium-legume symbiosis is, however, dependent on the host genotype used. Previous greenhouse experiments identified two genotypes of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), BAT477 and DOR364, contrasting in nodulation response to Azospirillum when coinoculated with Rhizobium. Genetic analysis revealed a genetic basis (Quantitative Trait Loci) on the bean genome related to the differential responsiveness to Azospirillum between the two bean genotypes. In this study, on-station and on-farm field experiments in different regions in Cuba were conducted to evaluate the agronomic relevance of the differences in response to Azospirillum–Rhizobium coinoculation between the two genotypes BAT477 and DOR364. It was observed that Azospirillum–Rhizobium coinoculation as compared to single Rhizobium inoculation increased the amount of fixed nitrogen and the yield of DOR364 across all sites. For BAT477, on the contrary, a negative effect of Azospirillum–Rhizobium coinoculation on yield and nitrogen fixation was observed on most of the sites as compared to single Rhizobium inoculation. The modified stability regression equations resulting from this study may contribute to predict how a combination of genotype and inoculum will perform at a certain environmental setting. This study highlights the importance of genotype × inocula interactions in agricultural outputs and establishes a link between greenhouse phenotype, genetic background and performance in the field.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldani VLD, Alvarez MAB, Baldani JI, Döbereiner J (1986) Establishment of inoculated Azospirillum spp. in the rhizosphere and in roots of field grown wheat and sorghum. Plant Soil 90:35–46 DOI 10.1007/BF02277385
Bashan Y (1999) Interactions of Azospirillum spp. in soils: a review. Biol Fert Soils 29:246–256 DOI 10.1007/s003740050549
Boughton D, Crawford R, Krause M, de Frahan BH (1990) Economic analysis of on-farm trials: a review of approaches and implications for research program design. Staff paper No. 90-78. Dep. Agr. Econ., Michigan State University
Broughton WJ, Hernandez G, Blair MW, Beebe S, Gepts P, Vanderleyden J (2003) Beans (Phaseolus spp.)—model food legumes. Plant Soil 252:55–128 DOI 10.1023/A:1024146710611
Burdman S, Volpin H, Kigel J, Kapulnik Y, Okon Y (1996a) Promotion of nod gene inducers and nodulation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) roots inoculated with Azospirillum brasilense Cd. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3030–3033
Burdman S, Sarig S, Kigel J, Okon Y (1996b) Field inoculation of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L) and chick pea (Cicer arietinum L) with Azospirillum brasilense strain Cd. Symbiosis 21:41–48
Burdman S, Kigel J, Okon Y (1997) Effects of Azospirillum brasilense on nodulation and growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Soil Biol Biochem 29:923–929 DOI 10.1016/S0038-0717(96)00222-2
Christiansen I, Graham PH (2002) Variation in di-nitrogen fixation among Andean bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes at low and high levels of phosphorus supply. Field Crop Res 73:133–142
CIAT (1996) Centro internacional de agricultura tropical annual report 1996. CIAT, Cali, Colombia
Davis J, Giller K, Kipe-Nolt J, Awah M (1988) Non-nodulating mutants in common bean. Crop Sci 28:859–860
Dobbelaere S, Croonenborghs A, Thys A, Ptacek D, Vanderleyden J, Dutto P, Labandera-Gonzalez C, Caballero-Mellado J, Aguirre JF, Kapulnik Y, Brener S, Burdman S, Kadouri D, Sarig S, Okon Y (2001) Responses of agronomically important crops to inoculation with Azospirillum.. Aust J Plant Physiol 28:871–879
Garcia A (2006) Use of nuclear techniques to evaluate management practices for improving soil fertility and sustainable common bean production in Cuban soils. PhD thesis
Giller KE (2001) Nitrogen fixation in tropical cropping systems. CABI publishing. 423 pp
Hernandez G, Garcia A, Drevon J J, Beebe S, Mendez N, Toscano V, Mulling M, Galvez L (2000) Variation in di-nitrogen fixation among Phaseolus vulgaris L. RILs grown at low and high levels of phosphorus supply. PPR project report, MINAGRI, 2000
Hildebrand PE, Poey F (1985) On farm agronomic trials in farming systems research and extension. Lynne Rienner, Boulder, CO, USA
Itzigsohn R, Kapulnik Y, Okon Y, Dovrat A (1993) Physiological and morphological aspects of interaction between Rhizobium meliloti and alfalfa (Medicago sativa) in association with Azospirillum brasilense. Can J Microbiol 39:610–615
Jebara M, Aouania ME, Payreb H, Drevon JJ (2005) Nodule conductance varied among common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) genotypes under phosphorus deficiency. J Plant Physiol 162:309–315 DOI 10.1016/j.jplph.2004.06.015
Lynch J, White JW (1992) Shoot nitrogen dynamics in tropical common bean. Crop Sci 32:392–397
Maertens E, Thijs A, Smolders E, Degryse F, Cong PT, Merckx R (2004) An anion resin membrane technique to overcome detection limits of isotopically exchanged P in P-sorbing soils. Eur J Soil Sci 55:63–69 DOI 10.1046/j.1365-2389.2004.00588.x
McInnes A, Thies JE, Abbott LK, Howieson JG (2004) Structure and diversity among rhizobial strains, populations and communities—a review. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1295–1308 DOI 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.04.011
Michiels J, Moris M, Dombrecht B, Verreth C, Vanderleyden J (1998) Differential regulation of Rhizobium etli rpoN2 gene expression during symbiosis and free-living growth. J Bacteriol 180:3620–3628
Okon Y, Labandera-Gonzales CA (1994) Agronomic applications of Azospirillum—an evaluation of 20 years worldwide field inoculation. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1591–1601 DOI 10.1016/0038-0717(94)90311-5
Raverkar KP, Konde BK (1988) Effect of Rhizobium and Azospirillum lipoferum inoculation on nodulation, yield and nitrogen uptake of peanut cultivars. Plant Soil 106:249–252 DOI 10.1007/BF02371220
Remans R, Croonenborghs A, Torres Gutierrez R, Michiels J, Vanderleyden J (2007) Effects of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on nodulation of Phaseolus vulgaris L. are dependent on plant P nutrition. Eur J Plant Pathol 119:341–351 DOI 10.1007/s10658-007-9154-4
Remans R, Beebe S, Blair M, Manrique G, Tovar E, Rao I, Croonenborghs A, Torres-Gutierrez R, El-Howeity M, Michiels J, Vanderleyden J (2008) Physiological and genetic analysis of root responsiveness to auxin-producing plant growth-promoting bacteria in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Soil 302:149–161 DOI 10.1007/s11104-007-9462-7
Sarig S, Kapulnik Y, Okon Y (1986) Effect of Azospirillum inoculation on nitrogen fixation and growth of several winter legumes. Plant Soil 90:335–342 DOI 10.1007/BF02277406
Singh SP, Gepts P, Debouck DG (1991) Races of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris, Fabaceae). Econ Bot 45:379–396
Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J, Remans R (2007) Indole-3-acetic acid in microbial and microorganism-plant signaling. FEMS Microbiol Rev 31:425–448
Tang C, Hinsinger P, Jaillard B, Rengel Z, Drevon JJ (2001) Effect of phosphorus deficiency on the growth, symbiotic N2 fixation and proton release. Agronomie 21:683–689 DOI 10.1051/agro:2001161
Tang C, Drevon JJ, Jaillard B, Souche G, Hinsinger P (2004) Proton release of two genotypes of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as affected by N nutrition and P deficiency. Plant Soil 260:59–68 DOI 10.1023/B:PLSO.0000030174.09138.76
Tilak KVBR, Ranganayaki N, Manoharachari C (2006) Synergistic effects of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and Rhizobium on nodulation and nitrogen fixation by pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan) Eur. J Soil Sci 57:67–71 DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2006.00771.x
Unkovich MJ, Pate JS (2000) An appraisal of recent field measurements of symbiotic N2 fixation by annual legumes. Field Crop Res 65:211–228 DOI 10.1016/S0378-4290(99)00088-X
Vanstockem M, Michiels K, Vanderleyden J, Van Gool A (1987) Transposon mutagenesis of Azospirillum brasilense and Azospirillum lipoferum, physical analysis of Tn5 and Tn5-mob insertion mutants. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:410–415
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for the practica1 study of root-nodule bacteria. Blackwell Scientific Publishers, Oxford
Yahalom E, Okon Y, Dovrat A (1987) Azospirillum effects on susceptibility to Rhizobium nodulation and on nitrogen fixation of several forage legumes. Can J Microbiol 33:510–514
Acknowledgement
R.R. is a recipient of a predoctoral fellowship from the ‘Vlaamse Interuniversitaire Raad (VLIR)’. We thank the Cuban Ministry of Agriculture (MINAG) for the infrastructure of the field trials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Petra Marschner.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Data of plant growth and symbiotic parameters measured between V2 and V3 and between R6 and R7. In Havana and Holguin, samples were taken at 21 and 42 DAP for V2–V3 and R6–R7, respectively. In Piñar del Rio, samples were taken at 29 and 47 DAP for V2–V3 and R6–R7, respectively. Values given represent averages of four plot repeats ± standard errors (ANOVA). Table of primers used for RT-PCR (DOC 26.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Remans, R., Ramaekers, L., Schelkens, S. et al. Effect of Rhizobium–Azospirillum coinoculation on nitrogen fixation and yield of two contrasting Phaseolus vulgaris L. genotypes cultivated across different environments in Cuba. Plant Soil 312, 25–37 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9606-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9606-4