Abstract
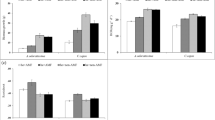
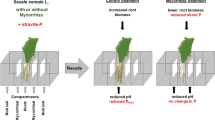
Seedlings of Lotus glaberMill., were grown in a native saline-sodic soil in a greenhouse for 50 days and then subjected to waterlogging for an additional period of 40 days. The effect of soil waterlogging was evaluated by measuring plant growth allocation, mineral nutrition and soil chemical properties. Rhizobiumnodules and mycorrhizal colonisation in L. glaberroots were measured before and after waterlogging. Compared to control plants, waterlogged plants had decreased root/shoot ratio, lower number of stems per plant, lower specific root length and less allocation of P and N to roots. Waterlogged plants showed increased N and P concentrations in plant tissues, larger root crown diameter and longer internodes. Available N and P and organic P, pH and amorphous iron increased in waterlogged soil, but total N, EC and exchangeable sodium were not changed. Soil waterlogging decreased root length colonised by arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi, arbuscular colonisation and number of entry points per unit of root length colonised. Waterlogging also increased vesicle colonisation and Rhizobium nodules on roots. AM fungal spore density was lower at the end of the experiment in non-waterlogged soil but was not reduced under waterlogging. The results indicate that L. glaber can grow, become nodulated by Rhizobium and colonised by mycorrhizas under waterlogged condition. The responses of L. glaber may be related its ability to form aerenchyma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F Amijee PB Tinker DP Stribley (1989) ArticleTitleThe development of endomycorrhizal systems VII A detailed study of the effects of soil phosphorus on colonisation New Phytologist. 111 435–446 Occurrence HandleA1989U175100010
C Arrese-Igor C RoyuelaMde Lorenzo MR Felipe Particlede PM Aparicio-Tejo (1993) ArticleTitleEffect of low rhizosphere oxygen on growth, nitrogen fixation and nodule morphology Physiol. Plantarum. 89 55–63 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXltVek
T Aziz D Sylvia R Doren (1995) ArticleTitleActivity and species composition of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi following soil removal Ecol. Appl. 5 776–784
Blumenthal M J, McGraw R L(1999). Lotus adaptation, use, and management. In: Beuselinck P R(ed), Trefoil The Science and Technology of Lotus. American Society of Agronomy Inc Crop Science Society of America Inc, Madison Wisconsin USA, pp: 97-119
P G Braunberger M H Miller R L Peterson (1991) ArticleTitleEffect of phosphorus nutrition on morphological characteristics of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal colonisation of maize New Phytol. 119 107–113 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XlvVWg
R H Bray L T Kurtz (1945) ArticleTitleDetermination of total organic and available forms of phosphorus in soils Soil Sci. 59 39–45 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaH2MXht1GjtA%3D%3D
Brenner J M, Mulvaney C S(1982). Nitrogen total. In: Methods in Soil Analysis: Agronomy. Ed. C A Black. pp 595-624. Am. Soc. Agron. Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA
A Brown C Bledsoe (1996) ArticleTitleSpatial and temporal dynamics of mycorrhizas in Jaumea carnosa, a tidal saltmarsh halophyte J Ecol. 84 703–715
L M Carvalho I Caçador M A Martins-Louçâo (2001) ArticleTitleTemporal and spatial variation of arbuscular mycorrhizas in salt marsh plants of the Tagus estuary (Portugal) Mycorrhiza. 11 303–309 Occurrence Handle000173195900007 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00572-001-0137-6
P M Chalk S A Waring (1970) ArticleTitleEvaluation of rapid test for assesing N availability in wheat soils I: Correlation with plant indices of availability obtained in pot culture Aust. J. Exp. Agric. Anim. Husb. 10 298–305 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3cXkvFOrtbg%3D
E Chaneton J Facelli R León (1988) ArticleTitleFloristic changes induced by flooding on grazed lowland grasslands in Argentina J. Range Manage. 41 495–499
M Collantes M Kade C Myacszynski O Santanatoglia (1988) ArticleTitleDistribución de especies en función de factores edáficos en un pastizal natural de la Depresión del Río Salado (Provincia de Buenos Aires) Stud. Oecologica 5 77–93
J C Cooke R H Butler G Madole (1993) ArticleTitleSome observations on the vertical distribution of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae in roots of salt marsh grasses growing in saturated soils Mycologia. 85 547–550 Occurrence HandleA1993LW37900003
BA Daniels HA Skipper (1982) Methods for the recovery and quantitative estimation of propagules from soil NC Schenck (Eds) Methods and Principles of Mycorrhizal Research American Phytopathological Society St Paul, MI, USA 29–35
MC Drew JM Lynch (1980) ArticleTitleSoil anaerobiosis, microorganisms, and root function Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 18 37–66 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXlsVKht7g%3D Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.py.18.090180.000345
J A Entry PT Rygiewicz LS Watrud PK Donnelly (2002) ArticleTitleInfluence of adverse soil conditions on the formation and function of Arbuscular mycorrhizas Adv. Envion. Res. 7 123–138 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xns1Cgsrw%3D
Escudero V G and Mendoza R E (2004). Seasonal variation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in temperate grasslands along a wide hydrologic gradient. Mycorrhiza. in press.
M Giovannetti B Mosse (1980) ArticleTitleAn evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots New Phytol. 84 489–500
JH Graham RT Leonard JA Menge (1981) ArticleTitleMembrane-mediated decrease in root exudation responsible for phosphorus inhibition of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza formation Plant Physiol. 68 548–552 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXlsVOgt7Y%3D Occurrence Handle16661955
IR Hall (1977) ArticleTitleSpecies and mycorrhizal infections of New Zealand Endogonaceae Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 68 341–356
IR Hall BJ Fish (1979) ArticleTitleA key to the Endogonaceae Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 73 261–270
EA Hiler CHM Bavel Particlevan MM Hossain WR Jordan (1972) ArticleTitleSensitivity of southern peas to plant water deficit at three growth stages Agron. J. 64 60–64 Occurrence Handle10.2134/agronj1972.00021962006400010020x
ML Jackson (1958) Soil chemical analysis CA Black DD Evans JR White GE Ensminger FE Clarck (Eds) Method of Soil Analysis Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties Prentice Hall Inc Englewood Cliffs 801
MB Jackson MC Drew (1984) Effect of flooding on growth and metabolism of herbaceous plant TT Kozlowski (Eds) Flooding and Plant Growth Academic Press Orlando 47–128
EK James RMM Crawford (1998) ArticleTitleEffect of oxygen availability on nitrogen fixation by two Lotus species under flooded conditions J. Exp. Bot. 49 599–609 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXit1ekt7k%3D Occurrence Handle10.1093/jexbot/49.320.599
S Juniper Abbot (1993) ArticleTitleVesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas and soil salinity Mycorrhiza 4 45–57 Occurrence HandleA1993MP53800001 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00204058
ID Kleiman DH Cogliatti GE Santa María (1992) ArticleTitleEfecto de la Hipoxia sobre el crecimiento y Adquisición de Nutrimentos en Lolium multiflorum Turrialba 42 IssueID2 210–219 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXlslylurw%3D
A Mazzanti L Montes D Minon H Sarlangue C Chepi (1988) ArticleTitleUtilización de Lotus tenuis en la Pampa Deprimida: resultado de una encuesta Rev. Agr. Prod. Anim. 8 301–305
T P McGonigle M H Miller DG Evans GL Fairchaild JA Swan (1990) ArticleTitleA new method which gives an objective measure of colonisation of roots by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi New Phytol. 115 495–501
RE Mendoza E Pagani (1997) ArticleTitleInfluence of phosphorous nutrition on mycorrhizal growth response and morphology of mycorrhizae in Lotus tenuis J. Plant Nutr. 20 IssueID6 625–639 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjsFeit7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10.1080/01904169709365282
R Mendoza E Pagani MC Pomar (2000) ArticleTitleVariabilidad poblacional de Lotus glaber en relación con la absorción de fósforo en suelo Ecología Austral. 10 3–14
SP Miller (2000) ArticleTitleArbuscular mycorrhizal colonisation of semi-aquatic grasses along a wide hydrologic gradient New Phytol. 145 145–155 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00566.x
JB Morton (1988) ArticleTitleTaxonomy of VA mycorrhizal fungi: Classification, nomenclature, and identification Mycotaxon. 32 267–324 Occurrence HandleA1988P253000018
JB Morton (1990) ArticleTitleEvolutionary relationships among arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the Endogonaceae Mycologia 82 192–207 Occurrence HandleA1990CZ89000007
B Mosse D Stribley F Le Tacon (1981) Ecology of mycorrhizas and mycorrhizal fungi M. Alexander (Eds) Advances in Microbial Ecology Plenun Press New York 137–210
T Muthukumar K Udaiyan A Karthikeyan S Manian (1997) ArticleTitleInfluence of native endomycorrhiza, soil flooding and nurse plant on mycorrhizal status and growth of puple nutsedge (Cyperus rotundus L.). Agricult Ecosyst. Environ. 61 51–58 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0167-8809(96)01073-0
R V Olson (1965) Chapter iron CA Black (Eds) Methods of Soil Analysis ASA Inc Publisher Madison, Wisconsin, USA 963–973
JM Phillips DS Hayman (1970) ArticleTitleImprove procedure for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 55 158–161 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0007-1536(70)80110-3
F N Ponnamperuma (1984) Effects of flooding on soils TT Kozlowski (Eds) Flooding and Plant Growth Academic Press NY 10–45
CL Powell (1974) ArticleTitleEffect of P fertilizer on root morphology and P uptake of Carex coriacea Plant Soil 41 661–667 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02185824
M Richter E Wistinghausen ParticleVon (1981) ArticleTitleUntersheridbarkeit von Humusfraktione in Boden bei Unterschiedlicher Bewirtschaftung Z. Pflanzenernaehr Bodenk. 144 395–406 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXls1Oltro%3D
DH Rickerl FO Sancho S Ananth (1994) ArticleTitleVesicular arbuscular endomycorrhizal colonisation of wetland plants J. Environ. Qual. 23 913–916 Occurrence Handle10.2134/jeq1994.00472425002300050010x
G Rubio G Casasola R S Lavado (1995) ArticleTitleAdaptations and biomass production of two grasses in response to waterlogging and soil nutrient enrichment Oecologia 102 102–105 Occurrence HandleA1995QY04600014
G Rubio M Oesterheld CR Alvarez RS Lavado (1997) ArticleTitleMechanisms for the increase in phosphorus uptake of waterlogged plants: Soil phosphorus availability, root morphology and uptake kinetics Oecologia 112 150–155 Occurrence HandleA1997YA69300002 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420050294
MH Ryan ME McCully CX Huang (2003) ArticleTitleLocation and quantification of phosphorus and other elements in fully hydrated, soil-grown arbuscular mycorrhizas: a cryo-analytical scanning electron microscopy study New Phytol. 160 429–441 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpt1Ogtr0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00884.x
RN Sah DS Mikkelsen AA Hafez (1989) ArticleTitlePhosphorus behavior in flooded-drained soils. II. iron transformation and phosphorus sorption Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 53 1723–1729 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXnsFyiug%3D%3D
SE Smith (1993) ArticleTitleTransport at the mycorrhizal interface Mycorrhiza News 5 1–4
Szaboles I (1991). Desertification and salinization. In Plant Salinity Research. Ed. R Choukr-Allah.
Vignolio O, Fernández O and Maceira N (1996). Respuestas de Lotus tenuis y Lotus corniculatus (Leguminosae) al anegamiento en plantas de distintas edades. Rev. de la Fac. de Agronomía, La Plata 101: 57-66
O Vignolio O Fernández N Maceira (1999) ArticleTitleFlooding tolerance in five populations of Lotus glaber Mill. (Syn. Lotus tenuis Waldst. Et. Kit.) Aust. J. Agric. Res. 50 555–559
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendoza, R., Escudero, V. & García, I. Plant growth, nutrient acquisition and mycorrhizal symbioses of a waterlogging tolerant legume (Lotus glaber Mill.) in a saline-sodic soil. Plant Soil 275, 305–315 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-2501-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-2501-3