Abstract
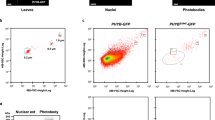
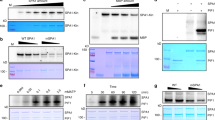
Phytochrome Interacting Factor 1 (PIF1), a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) protein, functions as a negative regulator of various facets of photomorphogenesis. To indentify PIF1-interacting proteins, we performed yeast two-hybrid screening using PIF1 as a bait and identified a group of proteins including PIF1 itself, PIF3 and long hypocotyl in far-red 1 (HFR1), an atypical HLH protein. Directed yeast two-hybrid interaction assays showed that PIF1 can form heterodimers with all other PIFs as well as with HFR1. PIF1 and PIF3 interacted with each other in both in vitro and in vivo co-immunoprecipitation assays. PIF1-PIF3 heterodimer also bound to a G-box DNA sequence element in vitro. To understand the biological significance of these interactions, a pif1pif3 double mutant was obtained and characterized. Analyses of the single and double mutants showed that PIF3 plays a prominent role in repressing photomorphogenesis under continuous blue light conditions. pif1 and pif3 showed additive phenotypes more prominently under discontinuous blue light conditions. Similar to PIF1, PIF3 was also rapidly phosphorylated, poly-ubiquitylated and degraded in response to blue light. PIF3 also interacted with phytochromes in response to blue light. A PIF3 mutant defective in interaction with both phyA and phyB displayed reduced degradation under blue light, suggesting that phy-interaction was necessary for the blue light-induced degradation of PIF3. Taken together, these data suggest a combinatorial control of photomorphogenesis by bHLH proteins in response to light in Arabidopsis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Sady B, Ni W, Kircher S, Schafer E, Quail PH (2006) Photoactivated phytochrome induces rapid PIF3 phosphorylation prior to proteasome-mediated degradation. Mol Cell 23:439–446
Al-Sady B, Kikis EA, Monte E, Quail PH (2008) Mechanistic duality of transcription factor function in phytochrome signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2232–2237
Bae G, Choi G (2008) Decoding of light signals by plant phytochromes and their interacting proteins. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:281–311
Bu Q, Zhu L, Dennis M, Yu L, Lu SX, Person MD, Tobin EM, Browning K, Huq E (2011) Phosphorylation by CK2 enhances the rapid light-induced degradation of PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 1 in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 286:12066–12074
Castillon A, Shen H, Huq E (2007) Phytochrome interacting factors: central players in phytochrome-mediated light signaling networks. Trends Plant Sci 12:514–521
Castillon A, Shen H, Huq E (2009) Blue light induces degradation of the negative regulator phytochrome interacting factor 1 to promote photomorphogenic development of Arabidopsis seedlings. Genetics 182:161–171
Chory J (2010) Light signal transduction: an infinite spectrum of possibilities. Plant J 61:982–991
Clack T, Shokry A, Moffet M, Liu P, Faul M, Sharrock RA (2009) Obligate heterodimerization of arabidopsis phytochromes C and E and interaction with the PIF3 basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor. Plant Cell 21:786–799
Duek PD, Fankhauser C (2003) HFR1, a putative bHLH-transcription factor, mediates both phytochrome A and cryptochrome signaling. Plant J 34:827–836
Duek PD, Fankhauser C (2005) bHLH class transcription factors take centre stage in phytochrome signalling. Trends Plant Sci 10:51–54
Durfee T, Becherer K, Chen PL, Yeh SH, Yang Y, Kilburn AE, Lee WH, Elledge SJ (1993) The retinoblastoma protein associates with the protein phosphatase type 1 catalytic subunit. Genes Dev 7:555–569
Fairchild CD, Schumaker MA, Quail PH (2000) HFR1 encodes an atypical bHLH protein that acts in phytochrome A signal transduction. Genes Dev 14:2377–2391
Fankhauser C, Chen M (2008) Transposing phytochrome into the nucleus. Trends Plant Sci 13:596–601
Hornitschek P, Lorrain S, Zoete V, Michielin O, Fankhauser C (2009) Inhibition of the shade avoidance response by formation of non-DNA binding bHLH heterodimers. EMBO J 28:3893–3902
Huq E, Quail PH (2002) PIF4, a phytochrome-interacting bHLH factor, functions as a negative regulator of phytochrome B signaling in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 21:2441–2450
Huq E, Al-Sady B, Hudson M, Kim C, Apel K, Quail PH (2004) Phytochrome-interacting factor 1 is a critical bHLH regulator of chlorophyll biosynthesis. Science 305:1937–1941
Kang X, Ni M (2006) Arabidopsis SHORT HYPOCOTYL UNDER BLUE1 contains SPX and EXS domains and acts in cryptochrome signaling. Plant Cell 18:921–934
Kim J, Yi H, Choi G, Shin B, Song PS, Choi G (2003) Functional characterization of phytochrome interacting factor 3 in phytochrome-mediated light signal transduction. Plant Cell 15:2399–2407
Kunihiro A, Yamashino T, Mizuno T (2010) PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTORS PIF4 and PIF5 are implicated in the regulation of hypocotyl elongation in response to blue light in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci Biotech Biochem 74:2538–2541
Leivar P, Quail PH (2011) PIFs: pivotal components in a cellular signaling hub. Trends Plant Sci 16:19–28
Leivar P, Monte E, Oka Y, Liu T, Carle C, Castillon A, Huq E, Quail PH (2008) Multiple phytochrome-interacting bHLH transcription factors repress premature seedling photomorphogenesis in darkness. Curr Biol 18:1815–1823
Leivar P, Tepperman JM, Monte E, Calderon RH, Liu TL, Quail PH (2009) Definition of early transcriptional circuitry involved in light-induced reversal of pif-imposed repression of photomorphogenesis in young Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 21:3535–3553
Littlewood T, Evans GI (1998) Helix-loop-helix transcription factors. Oxford University Press, New York
Martinez-Garcia JF, Huq E, Quail PH (2000) Direct targeting of light signals to a promoter element-bound transcription factor. Science 288:859–863
Mathews S, Sharrock RA (1997) Phytochrome gene diversity. Plant Cell Environ 20:666–671
Monte E, Tepperman JM, Al-Sady B, Kaczorowski KA, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Li X, Zhang Y, Quail PH (2004) The phytochrome-interacting transcription factor, PIF3, acts early, selectively, and positively in light-induced chloroplast development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:16091–16098
Moon J, Zhu L, Shen H, Huq E (2008) PIF1 directly and indirectly regulates chlorophyll biosynthesis to optimize the greening process in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9433–9438
Ni M, Tepperman JM, Quail PH (1998) PIF3, a phytochrome-interacting factor necessary for normal photoinduced signal transduction, is a novel basic helix-loop-helix protein. Cell 95:657–667
Oh E, Kim J, Park E, Kim JI, Kang C, Choi G (2004) PIL5, a phytochrome-interacting basic helix-loop-helix protein, is a key negative regulator of seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16:3045–3058
Oh E, Kang H, Yamaguchi S, Park J, Lee D, Kamiya Y, Choi G (2009) Genome-wide analysis of genes targeted by PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 3-LIKE5 during seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:403–419
Quail PH (2010) Phytochromes. Curr Biol 20:R504–R507
Rizzini L, Favory J–J, Cloix C, Faggionato D, O’Hara A, Kaiserli E, Baumeister R, Schäfer E, Nagy F, Jenkins GI, Ulm R (2011) Perception of UV-B by Arabidopsis UVR8 Protein. Science 332:103–106
Rockwell NC, Su Y-S, Lagarias JC (2006) Phytochrome structure and signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:837–858
Sato S, Huq E, Tepperman JM, Quail PH (2002) A light-switchable gene promoter system. Nat Biotech 20:1041–1044
Schaefer E, Nagy F (2006) Photomorphogenesis in plants and bacteria. Springer, Dordrecht
Shen H, Moon J, Huq E (2005) PIF1 is regulated by light-mediated degradation through the ubiquitin-26S proteasome pathway to optimize seedling photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 44:1023–1035
Shen H, Ling Z, Castillon A, Majee M, Downie B, Huq E (2008) Light-induced phosphorylation and degradation of the negative regulator PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 1 depends upon its direct physical interactions with photoactivated phytochromes. Plant Cell 20:1586–1602
Shimizu-Sato S, Huq E, Tepperman JM, Quail PH (2002) A light-switchable gene promoter system. Nat Biotechnol 20:1041–1044
Shin J, Kim K, Kang H, Zulfugarov IS, Bae G, Lee CH, Lee D, Choi G (2009) Phytochromes promote seedling light responses by inhibiting four negatively-acting phytochrome-interacting factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:7660–7665
Stephenson PG, Fankhauser C, Terry MJ (2009) PIF3 is a repressor of chloroplast development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:7654–7659
Toledo-Ortiz G, Huq E, Quail PH (2003) The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 15:1749–1770
Toledo-Ortíz G, Huq E, Rodríguez-Concepción M (2010) Direct regulation of phytoene synthase gene expression and carotenoid biosynthesis by phytochrome-interacting factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:11626–11631
Zimmermann P, Hirsch-Hoffmann M, Hennig L, Gruissem W (2004) GENEVESTIGATOR. Arabidopsis microarray database and analysis toolbox. Plant Physiol 136:2621–2632
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Guy Thompson for critical reading of the manuscript, Peter Quail for sharing YFP-PIF3 and His-PIF3-myc transgenic plants, and Rebecca Campos for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from NSF (IOS-0822811 and IOS-0849287) to E.H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bu, Q., Castillon, A., Chen, F. et al. Dimerization and blue light regulation of PIF1 interacting bHLH proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 77, 501 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9827-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9827-4