Abstract
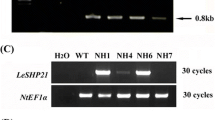
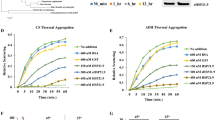
Heat stress is a major constraint to wheat production and negatively impacts grain quality, causing tremendous economic losses, and may become a more troublesome factor due to global warming. At the cellular level, heat stress causes denaturation and aggregation of proteins and injury to membranes leading to alterations in metabolic fluxes. Protein aggregation is irreversible, and protection of proteins from thermal aggregation is a strategy a cell uses to tolerate heat stress. Here we report on the development of transgenic wheat (Triticum aestivum) events, expressing a maize gene coding for plastidal protein synthesis elongation factor (EF-Tu), which, compared to non-transgenic plants, display reduced thermal aggregation of leaf proteins, reduced heat injury to photosynthetic membranes (thylakoids), and enhanced rate of CO2 fixation after exposure to heat stress. The results support the concept that EF-Tu ameliorates negative effects of heat stress by acting as a molecular chaperone. This is the first demonstration of the introduction of a plastidal EF-Tu in plants that leads to protection against heat injury and enhanced photosynthesis after heat stress. This is also the first demonstration that a gene other than HSP gene can be used for improvement of heat tolerance and that the improvement is possible in a species that has a complex genome, hexaploid wheat. The results strongly suggest that heat tolerance of wheat, and possibly other crop plants, can be improved by modulating expression of plastidal EF-Tu and/or by selection of genotypes with increased endogenous levels of this protein.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khatib K, Paulsen GM (1989) Enhancement of thermal injury to photosynthesis in wheat plants and thylakoids by high light intensity. Plant Physiol 90:1041–1048
Baldauf SL, Manhart JR, Palmer JD (1990) Different fates of the chloroplast tufA gene following its transfer to the nucleus in green algae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5317–5321. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.14.5317
Beck BD (1979) Polymerization of the bacterial elongation factor for protein synthesis, EF-Tu. Eur J Biochem 97:495–502. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13137.x
Berry JA, Björkman Ö (1980) Photosynthetic response and adaptation to temperature in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 31:491–543. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.31.060180.002423
Bhadula SK, Elthon TE, Habben JE, Helentjaris TG, Jiao S, Ristic Z (2001) Heat-stress induced synthesis of chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factor (EF-Tu) in a heat-tolerant maize line. Planta 212:359–366. doi:10.1007/s004250000416
Blumenthal T, Landers TA, Weber K (1972) Bacteriophage Qβ replicase contains the protein biosynthesis elongation factors EF-Tu and EF-Ts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69:1313–1317. doi:10.1073/pnas.69.5.1313
Boyer JS (1982) Plant productivity and the environment. Science 218:443–448. doi:10.1126/science.218.4571.443
Caldas TD, Yaagoubi AE, Richarme G (1998) Chaperone properties of bacterial elongation factor EF-Tu. J Biol Chem 273:11478–11482. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.19.11478
Cheng M, Fry JE, Pang S, Zhou H, Hironaka CM, Duncan DR et al (1997) Genetic transformation of wheat mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Physiol 115:971–980
Christensen AH, Sharrock RA, Quail PH (1992) Maize polyubiquitin genes: Structure, thermal perturbation of expression and transcript splicing, and promoter activity following transfer to protoplasts by electroporation. Plant Mol Biol 18:675–689. doi:10.1007/BF00020010
Dellaporta SI, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA mini-preparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21. doi:10.1007/BF02712670
Feder ME, Hofmann GE (1999) Heat-shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu Rev Physiol 61:243–282. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.61.1.243
Hajdukiewicz P, Svab Z, Maliga P (1994) The small, versatile pPZP family of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 25:989–994. doi:10.1007/BF00014672
Hendrick JP, Hartl FU (1993) Molecular chaperone functions of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 62:349–384. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002025
Katiyar-Agarwal S, Agarwal M, Grover A (2003) Heat-tolerant basmati rice engineered by over-expression of hsp101. Plant Mol Biol 51:677–686. doi:10.1023/A:1022561926676
Koncz C, Schell J (1986) The promoter of TL-DNA gene 5 controls the tissue specific expression of chimaeric genes carried by a novel type of Agrobacterium binary vector. Mol Gen Genet 204:383–396. doi:10.1007/BF00331014
Krause GH, Weis E (1984) Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool in plant physiology. II. Interpretation of fluorescence signals. Photosynth Res 5:139–157. doi:10.1007/BF00028527
Larkindale J, Mishkind M, Vierling E (2005) Plant responses to high temperature. In: Jenks MA, Hasegawa PM (eds) Plant abiotic stress. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, UK, pp 100–144
Levitt J (1980) Responses of plants to environmental stress. Chilling, freezing and high temperature stresses. Academic Press, New York, NY, pp 347–470
Lobell DB, Asner GP (2003) Climate and management contributions to recent trends in U.S. agricultural yields. Science 299:1032
Maestri E, Klueva N, Perrotta C, Gulli M, Nguyen HT, Marmiroli N (2002) Molecular genetics of heat tolerance and heat shock proteins in cereals. Plant Mol Biol 48:667–681
Malik MK, Slovin JP, Hwang CH, Zimmerman JL (1999) Modified expression of a carrot small heat shock protein gene, Hsp17.7, results in increased or decreased thermotolerance. Plant J 20:89–99
Matzke MA, Matzke AJM (1995) How and why do plants inactivate homologous (trans) genes? Plant Physiol 107:679–685
Maurer F, Maximilien M, Stutz E (1996) The tuf gene family of soybean: structure and differential transcription. Plant Sci 117:83–93
Momcilovic I, Ristic Z (2004) Localization and abundance of chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factor (EF-Tu) and heat stability of chloroplast stromal proteins in maize. Plant Sci 166:81–88
Momcilovic I, Ristic Z (2007) Expression of chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factor, EF-Tu, in two lines of maize with contrasting tolerance to heat stress during early stages of plant development. J Plant Physiol 164:90–99
Moriarty T, West R, Small G, Rao D, Ristic Z (2002) Heterologous expression of maize chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factor (EF-Tu) enhances Escherichia coli viability under heat stress. Plant Sci 163:1075–1082
Mullarkey M, Jones P (2000) Isolation and analysis of thermotolerant mutants of wheat. J Exp Bot 51:139–146
Nissen P, Kjeldgaard M, Thirup S, Polekhina G, Reshetnikova L, Clark BFC, Nyborg J (1995) Crystal structure of the ternary complex of Phe-tRNAPhe, EF-Tu, and a GTP analog. Science 270:1464–1472
Paulsen GM (1994) High temperature responses of crop plants. In: Boote KJ, Bennet IM, Sinclair TR, Paulsen GM (eds) Physiology and determination of crop yield. ASA, CSS, SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 365–389
Peng S, Huang J, Sheehy JE, Laza RC, Visperas RM, Zhong X, Centeno GS, Khush GS, Cassman KG (2004) Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9971–9975
Queitsch C, Hong SW, Vierling E, Lindquist S (2000) Heat shock protein 101 plays a crucial role in thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:479–492
Rao D, Momcilovic I, Kobayashi S, Callegari E, Ristic Z (2004) Chaperone activity of recombinant maize chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factor, EF-Tu. Eur J Biochem 271:3684–3692
Reddy P, Miller D, Peterkofsky A (1986) Simulation of Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase activity by elongation factor Tu, a GTP-binding protein essential for protein synthesis. J Biol Chem 261:11448–11451
Richarme G (1998) Protein-disulfide isomerase activity of elongation factor EF-Tu. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 252:156–161
Riis B, Rattan SIS, Clark BFC, Merrick WC (1990) Eukaryotic protein elongation factors. Trends Biol Sci 15:420–424
Ristic Z, Wilson K, Nelsen C, Momcilovic I, Kobayashi S, Meeley R, Muszynski M, Habben J (2004) A maize mutant with decreased capacity to accumulate chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factor (EF-Tu) displays reduced tolerance to heat stress. Plant Sci 167:1367–1374
Ristic Z, Momčilović I, Fu J, Callegari E, DeRidder BP (2007) Chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factor, EF-Tu, reduces thermal aggregation of rubisco activase. J Plant Physiol 164:1564–1571
Ristic Z, Bukovnik U, Momčilović I, Fu J, Prasad PVV (2008) Heat-induced accumulation of chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factor, EF-Tu, in winter wheat. J Plant Physiol 165:192–202
Salvucci ME, Osteryoung KW, Crafts-Brandner SJ, Vierling E (2001) Exceptional sensitivity of Rubisco activase to thermal denaturation in vitro and in vivo. Plant Physiol 127:1053–1064
Sambrook J, Fritrch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, NY
Sanmiya K, Suzuki K, Egawa Y, Shono M (2004) Mitochondrial small heat-shock protein enhances thermotolerance in tobacco plants. FEBS Lett 557:265–268
SAS (2003) User Manual for SAS for Windows Version 8. Cary, NC, USA: Statistical Analysis System (SAS) Institute Inc
Schöffl F, Prändl R, Reindl A (1998) Regulation of the heat-shock response. Plant Physiol 117:1135–1141
Stone PJ, Nicolas ME (1994) Wheat cultivars vary widely in their responses of grain yield and quality to short periods of post-anthesis heat stress. Aust J Plant Physiol 21:887–900
Stone PJ, Nicolas ME (1995) A survey of the effects of high temperature during grain filling on yield and quality of 75 wheat cultivars. Aust J Agric Res 46:475–492
Sugita M, Murayama Y, Sugiura M (1994) Structure and differential expression of two distinct genes encoding the chloroplast elongation factor Tu in tobacco. Curr Genet 25:164–168
Takai K, Nunoura T, Sako Y, Uchida A (1998) Acquired thermotolerance and temperature-induced protein accumulation in the extremely thermophilic bacterium Rhodothermus obamensis. J Bacteriol 180:2770–2774
Tanford C (1968) Protein denaturation. In: Anfinsen CB, Edsall JT, Anson ML, Richards FM (eds) Advances in protein chemistry, vol 23. Academic Press, New York, NY, pp 121–282
Vierling E (1991) The roles of heat shock proteins in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42:579–620
Willson KS, Noller HF (1998) Molecular movement inside the translational engine. Cell 92:337–349
Young CC, Bernlohr RW (1991) Elongation factor Tu is methylated in response to nutrient deprivation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 173:3096–3100
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support for this research from the United States Department of Agriculture grant (Agreement No. 2004-35100-14886) to Z. Ristic. This publication is approved as Kansas Agriculture Experiment Station No: 08-247-J. Mention of a trademark or proprietary product does not constitute a guarantee or warranty of the product by the United States Department of Agriculture, and does not imply its approval to the exclusion of other products that may also be suitable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, J., Momčilović, I., Clemente, T.E. et al. Heterologous expression of a plastid EF-Tu reduces protein thermal aggregation and enhances CO2 fixation in wheat (Triticum aestivum) following heat stress. Plant Mol Biol 68, 277–288 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9369-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9369-6