Abstract
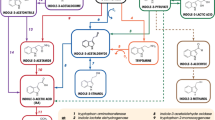
Diterpenoid phytoalexins such as momilactones and phytocassanes are produced via geranylgeranyl diphosphate in suspension-cultured rice cells after treatment with a chitin elicitor. We have previously shown that the production of diterpene hydrocarbons leading to phytoalexins and the expression of related biosynthetic genes are activated in suspension-cultured rice cells upon elicitor treatment. To better understand the elicitor-induced activation of phytoalexin biosynthesis, we conducted microarray analysis using suspension-cultured rice cells collected at various times after treatment with chitin elicitor. Hierarchical cluster analysis revealed two types of early-induced expression (EIE-1, EIE-2) nodes and a late-induced expression (LIE) node that includes genes involved in phytoalexins biosynthesis. The LIE node contains genes that may be responsible for the methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway, a plastidic biosynthetic pathway for isopentenyl diphosphate, an early precursor of phytoalexins. The elicitor-induced expression of these putative MEP pathway genes was confirmed by quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase (DXS), 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXR), and 4-(cytidine 5′-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-d-erythritol synthase (CMS), which catalyze the first three committed steps in the MEP pathway, were further shown to have enzymatic activities that complement the growth of E. coli mutants disrupted in the corresponding genes. Application of ketoclomazone and fosmidomycin, inhibitors of DXS and DXR, respectively, repressed the accumulation of diterpene-type phytoalexins in suspension cells treated with chitin elicitor. These results suggest that activation of the MEP pathway is required to supply sufficient terpenoid precursors for the production of phytoalexins in infected rice plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akatsuka T, Takahashi N, Kodama O, Sekido H, Kono Y, Takeuchi S (1985) Novel phytoalexins (Oryzalexins A, B and C) isolated from rice blast leaves infected with Pricularia oryzae. Part 1: isolation, characterization and biological activities of oryzalexins. Agric Biol Chem 49:1689–1694
Atawong A, Hasegawa M, Kodama O (2002) Biosynthesis of rice phytoalexin: enzymatic conversion of 3beta-hydroxy-9beta-pimara-7,15-dien-19,6beta-olide to momilactone A. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:566–570
Cartwright D, Langcake P, Pryce R, Leworthy D, Ride J (1981) Isolation and characterization of two phytoalexins from rice as momilactones A and B. Phytochemistry 20:535–537
Cho EM, Okada A, Kenmoku H, Otomo K, Toyomasu T, Mitsuhashi W, Sassa T, Yajima A, Yabuta G, Mori K, Oikawa H, Toshima H, Shibuya N, Nojiri H, Omori T, Nishiyama M, Yamane H (2004) Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding ent-cassa-12,15-diene synthase, a putative diterpenoid phytoalexin biosynthetic enzyme, from suspension-cultured rice cells treated with a chitin elicitor. Plant J 37:1–8
Duvold T, Bravo JM, Pale-Grosdemange C, Rohmer M (1997) Biosynthesis of 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol, a putative C 5 intermediate in the mevalonate independent pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis. Tetrahedron Lett 38:4769–4772
Guevara-García A, San Román C, Arroyo A, Cortés ME, de la Luz Gutiérrez-Nava M, León P (2005) Characterization of the Arabidopsis clb6 mutant illustrates the importance of posttranscriptional regulation of the methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway. Plant Cell 17:628–643
Heintz R, Benveniste P, Robinson WH, Coates RM (1972) Plant sterol metabolism. Demonstration and identification of a biosynthetic intermediate between farnesyl PP and squalene in a higher plant. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 49:1547–1553
Kato T, Kabuto C, Sasaki N, Tsunagawa M, Aizawa H, Fujita K, Kato Y, Kitahara Y, Takahashi N (1973) Momilactones, growth inhibitors from rice, Oryza sativa L. Tetrahedron Lett 14:3861–3864
Kato H, Kodama O, Akatsuka T (1993) Oryzalexin E, a diterpene phytoalexin from UV-irradiated rice leaves. Phytochemistry 33:79–81
Kato H, Kodama O, Akatsuka T (1994) Oryzalexin F, a diterpene phytoalexin from UV-irradiated rice leaves. Phytochemistry 36:299–301
Kato H, Kodama O, Akatsuka T (1995) Characterization of an inducible P450 hydroxylase involved in the rice diterpene phytoalexin biosynthetic pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 316:707–712
Kim BR, Kim SU, Chang YJ (2005) Differential expression of three 1-deoxy-D: -xylulose-5-phosphate synthase genes in rice. Biotechnol Lett 27:997–1001
Kim SM, Kuzuyama T, Chang YJ, Song KS, Kim SU (2006) Identification of class 2 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase and 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase genes from Ginkgo biloba and their transcription in embryo culture with respect to ginkgolide biosynthesis. Planta Med 72:234–240
Kodama O, Suzuki T, Miyakawa J, Akatsuka T (1988a) Ultraviolet-induced accumulation of phytoalexins in rice leaves. Agric Biol Chem 52:2469–2473
Kodama O, Yamada A, Yamamoto A, Takemoto T, Akatsuka T (1988b) Induction of phytoalexins with heavy metal ions in rice leaves. Nippon Noyaku Gakkaishi 13:615–617
Koga J, Shimura M, Oshima K, Ogawa N, Yamauchi T, Ogawasawara N (1995) Phytocassanes A, B, C and D, novel diterpene phytoalexins from rice, Oryza sativa L. Tetrahedron 51:7907–7918
Koga J, Ogawa N, Yamauchi T, Kikuchi M, Ogasawara N, Shimura M (1997) Functional moiety for the antifungal activity of phytocassane E, a diterpene phytoalexin from rice. Phytochemistry 44:249–253
Kuzuyama T, Shimizu T, Takahashi S, Seto H (1998a) Fosmidomycin, a specific inhibitor of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase in the nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis. Tetrahedron Lett 39:7913–7916
Kuzuyama T, Takahashi S, Watanabe H, Seto H (1998b) Direct formation of 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate from 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate by 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase, a new enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway to isopentenyl diphosphate. Tetrahedron Lett 39:4509–4512
Kuzuyama T, Takahashi S, Seto H (1999) Construction and characterization of Escherichia coli disruptants defective in the yaeM gene. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63:776–778
Kuzuyama T, Takagi M, Kaneda K, Dairi T, Seto H (2000) Formation of 4-(cytidine 5′-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-d-erythritol from 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate by 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase, a new enzyme in the nonmevalonate pathway. Tetrahedron Lett 41:703–706
Lange BM, Ghassemian M (2003) Genome organization in Arabidopsis thaliana: a survey for genes involved in isoprenoid and chlorophyll metabolism. Plant Mol Biol 51:925–948
Lichtenthaler HK (1999) The 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:47–65
Lichtenthaler HK, Schwender J, Disch A, Rohmer M (1997) Biosynthesis of isoprenoids in higher plant chloroplasts proceeds via a mevalonate-independent pathway. FEBS Lett 400:271–274
Nemoto T, Cho EM, Okada A, Okada K, Otomo K, Kanno Y, Toyomasu T, Mitsuhashi W, Sassa T, Minami E, Shibuya N, Nishiyama M, Nojiri H, Yamane H (2004) Stemar-13-ene synthase, a diterpene cyclase involved in the biosynthesis of the phytoalexin oryzalexin S in rice. FEBS Lett 571:182–186
Nes WD, Venkatramesh M (1999) Enzymology of phytosterol transformations. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 34:81–93
Okada K, Saito T, Nakagawa T, Kawamukai M, Kamiya Y (2000) Five geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthases expressed in different organs are localized into three subcellular compartments in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 122:1045–1056
Okada K, Kawaide H, Kuzuyama T, Seto H, Curtis IS, Kamiya Y (2002) Antisense and chemical suppression of the nonmevalonate pathway affects ent-kaurene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Planta 215:339–344
Otomo K, Kanno Y, Motegi A, Kenmoku H, Yamane H, Mitsuhashi W, Oikawa H, Toshima H, Itoh H, Matsuoka M, Sassa T, Toyomasu T (2004a) Diterpene cyclases responsible for the biosynthesis of phytoalexins, momilactones A, B, and oryzalexins A-F in rice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:2001–2006
Otomo K, Kenmoku H, Oikawa H, Konig WA, Toshima H, Mitsuhashi W, Yamane H, Sassa T, Toyomasu T (2004b) Biological functions of ent- and syn-copalyl diphosphate synthases in rice: key enzymes for the branch point of gibberellin and phytoalexin biosynthesis. Plant J 39:886–893
Peters RJ (2006) Uncovering the complex metabolic network underlying diterpenoid phytoalexin biosynthesis in rice and other cereal crop plants. Phytochemistry 67:2307–2317
Rohdich F, Wungsintaweekul J, Eisenreich W, Richter G, Schuhr CA, Hecht S, Zenk MH, Bacher A (2000) Biosynthesis of terpenoids: 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol synthase of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6451–6456
Rohmer M (1999) The discovery of a mevalonate-independent pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria, algae and higher plants. Nat Prod Rep 16:565–574
Sakakibara H, Kasahara H, Ueda N, Kojima M, Takei K, Hishiyama S, Asami T, Okada K, Kamiya Y, Yamaya T, Yamaguchi S (2005) Agrobacterium tumefaciens increases cytokinin production in plastids by modifying the biosynthetic pathway in the host plant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9972–9977
Sakata K, Nagamura Y, Numa H, Antonio BA, Nagasaki H, Idonuma A, Watanabe W, Shimizu Y, Horiuchi I, Matsumoto T, Sasaki T, Higo K (2002) RiceGAAS: an automated annotation system and database for rice genome sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 30:98–102
Sauret-Güeto S, Botella-Pavía P, Flores-Pérez U, Martínez-García JF, San Román C, León P, Boronat A, Rodríguez-Concepción M (2006) Plastid cues posttranscriptionally regulate the accumulation of key enzymes of the methylerythritol phosphate pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 141:75–84
Scolnik PA, Bartley GE (1994) Nucleotide sequence of an Arabidopsis cDNA for geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase. Plant Physiol 104:1469–1470
Stoessl A (1980) Phytoalexins: a biogenetic perspective. Phytopathol Z 99:251–272
Subba R, Strange RN (1994) Chemistry, biology, and role of groundnut phytoalexins in resistance to fungal attack. In: Daniel M, Purkayastha RP (eds) Handbook of phytoalexin metabolism and action. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 199–227
Takahashi S, Kuzuyama T, Watanabe H, Seto H (1998) A 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase catalyzing the formation of 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9879–9884
Tamogami S, Mitani M, Kodama O, Akatsuka T (1993) Oryzalexin S structure: a new stemarane-type rice plant phytoalexin and its biogenesis. Tetrahedron 49:2025–2032
Tamogami S, Rakwal R, Kodama O (1997) Phytoalexin production elicited by exogenously applied jasmonic acid in rice leaves (Oryza sativa L.) is under the control of cytokinins and ascorbic acid. FEBS Lett 412:61–64
VanEtten HD, Mansfield JW, Bailey JA, Farmer EE (1994) Two classes of plant antibiotics: phytoalexins versus “phytoanticipins”. Plant Cell 6:1191–1192
Walter MH, Hans J, Strack D (2002) Two distantly related genes encoding 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthases: differential regulation in shoots and apocarotenoid-accumulating mycorrhizal roots. Plant J 31:243–254
Yajima A, Mori K (2000) Diterpenoid total synthesis, XXXII synthesis and absolute configuration of (−)-phytocassane D, a diterpene phytoalexin isolated from the rice plant, Oryza sativa. Eur J Org Chem 2000:4079–4091
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Yoshiaki Nagamura and Ms Ritsuko Motoyama of the Rice Genome Resource Center for technical support with the microarray analysis, and also for providing the rice full-length cDNA clone that was developed in the Rice Genome Project of the National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, Japan, and Prof Tadao Asami in The University of Tokyo for distribution of 5-ketoclomazone. This work was supported by the Program for Promotion of Basic Research Activities for Innovative Biosciences (PROBRAIN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below are the electronic supplementary materials.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, A., Shimizu, T., Okada, K. et al. Elicitor induced activation of the methylerythritol phosphate pathway toward phytoalexins biosynthesis in rice. Plant Mol Biol 65, 177–187 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9207-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9207-2