Abstract
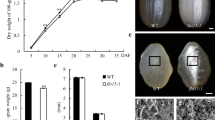
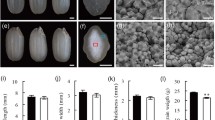
Starch is the major component of cereal grains. In rice, starch properties determine the eating and cooking quality. The dull endosperm of rice grains is a classical morphological and agronomical trait that has long been exploited for breeding and genetics study. To understand the molecular mechanism that regulates the starch biosynthesis in rice grains, we characterized a classic rice mutant dull endosperm1 (du1) and isolated Du1 through a map-based cloning approach. Du1, encoding a member of pre-mRNA processing (Prp1) family, is expressed mainly in panicles. Du1 specifically affects the splicing efficiency of Wx b and regulates starch biosynthesis by mediating the expression of starch biosynthesis genes. Analysis of du1wx shows that Du1 acts upstream of Wx b. These results strongly suggest that Du1 may function as a regulator of the starch biosynthesis by affecting the splicing of Wx b and the expression of other genes involved in the rice starch biosynthetic pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Amylose content
- AGPase:
-
ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
- ASV:
-
Alkali spreading values
- BAC:
-
Bacterial artificial chromosome
- CAPS:
-
Cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences
- DAP:
-
Days after pollinating
- DBE:
-
Starch debraching enzyme
- du1 :
-
Dull endosperm1
- Du1L:
-
Du1-like
- GBSS:
-
Granule-bound starch synthase
- GC:
-
Gel consistency
- Prp:
-
Pre-mRNA processing
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- SBE:
-
Starch branching enzyme
- SR:
-
Serine–arginine-rich
- SSS:
-
Soluble starch synthase
- STS:
-
Sequence tagged site
- TPR:
-
Tetratric peptide repeats
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
References
Aluko G, Martinez C, Tohme J, Castano C, Bergman C, Oard JH (2004) QTL mapping of grain quality traits from the interspecific cross Oryza sativa x O. glaberrima. Theor Appl Genet 109:630–639
Bao JS, Sun M, Corke H (2002) Analysis of the genetic behavior of some starch properties in indica rice (Oryza sativa L.): thermal properties, gel texture, swelling volume. Theor Appl Genet 104:408–413
Bao J, Kong X, Xie J, Xu L (2004) Analysis of genotypic and environmental effects on rice starch. 1. Apparent amylose content, pasting viscosity, and gel texture. J Agric Food Chem 52:6010–6016
Cai XL, Wang ZY, Xing YY, Zhang JL, Hong MM (1998) Aberrant splicing of intron 1 leads to the heterogeneous 5’ UTR and decreased expression of waxy gene in rice cultivars of intermediate amylose content. Plant J 14:459–465
Chung S, McLean MR, Rymond BC (1999) Yeast ortholog of the Drosophila crooked neck protein promotes spliceosome assembly through stable U4/U6.U5 snRNP addition. RNA 5:1042–1054
Eguchi T, Ashikari M, Yoshimura A, Iwata N (1998) Loci of physiological and morphological characters on RFLP linkage map in rice. Breeding Sci 48:80
Fan CC, Yu XQ, Xing YZ, Xu CG, Luo LJ, Zhang Q (2005) The main effects, epistatic effects and environmental interactions of QTLs on the cooking and eating quality of rice in a doubled-haploid line population. Theor Appl Genet 110:1445–1452
Felsenstein J (2000) PHYLIP: Phylogeny Inference Package, v3.6. Seattle, WA
Frances H, Bligh J, Larkin PD, Roach PS, Jones CA, Fu H, Park WD (1998) Use of alternate splice sites in granule-bound starch synthase mRNA from low-amylose rice varieties. Plant Mol Biol 38:407–415
Fujita N, Kubo A, Suh DS, Wong KS, Jane JL, Ozawa K, Takaiwa F, Inaba Y, Nakamura Y (2003) Antisense inhibition of isoamylase alters the structure of amylopectin and the physicochemical properties of starch in rice endosperm. Plant Cell Physiol 44:607–618
Gao Z, Zeng D, Cui X, Zhou Y, Yan M, Huang D, Li J, Qian Q (2003) Map-based cloning of the ALK gene, which controls the gelatinization temperature of rice. Sci China Ser C 46:661–668
Hirano HY, Sano Y (2000) Comparison of Waxy gene regulation in the endosperm and pollen in Oryza sativa L. Genes Genet Syst 75:245–249
Hirano HY, Eiguchi M, Sano Y (1998) A single base change altered the regulation of the Waxy gene at the posttranscriptional level during the domestication of rice. Mol Biol Evol 15:978–987
Isshiki M, Morino K, Nakajima M, Okagaki RJ, Wessler SR, Izawa T, Shimamoto K (1998) A naturally occurring functional allele of the rice waxy locus has a GT to TT mutation at the 5’ splice site of the first intron. Plant J 15:133–138
Itoh K, Ozaki H, Okada K, Hori H, Takeda Y, Mitsui T (2003) Introduction of Wx transgene into rice wx mutants leads to both high- and low-amylose rice. Plant Cell Physiol 44:473–480
Juliano BO (1971) A simplified assay for milled rice amylose. Cereal Sci Today 16:334–360
Kinoshita T (1987) Report of the committee on gene symbolization, nomenclature and linkage groups. II. Registration of new gene symbols. Rice Genet Newslett 4:3–7
Koh HJ, Cha KW, Heu MH (1997) Inheritance and some physicochemical properties of newly induced “low-amylose endosperm” mutants in rice. Korean J Breed 29:368–375
Kubo A, Fujita N, Harada K, Matsuda T, Satoh H, Nakamura Y (1999) The starch-debranching enzymes isoamylase and pullulanase are both involved in amylopectin biosynthesis in rice endosperm. Plant Physiol 121:399–410
Lamb JR, Tugendreich S, Hieter P (1995) Tetratrico peptide repeat interactions: to TPR or not to TPR? Trends Biochem Sci 20:257–259
Lan L, Chen W, Lai Y, Suo J, Kong Z, Li C, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Zhang X, Han B, Cheng J, Xue Y (2004) Monitoring of gene expression profiles and isolation of candidate genes involved in pollination and fertilization in rice (Oryza sativa L.) with a 10K cDNA microarray. Plant Mol Biol 54:471–487
Lanceras JC, Huang ZL, Naivikul O, Vanavichit A, Ruanjaichon V, Tragoonrung S (2000) Mapping of genes for cooking and eating qualities in Thai jasmine rice (KDML105). DNA Res 7:93–101
Li X, Qian Q, Fu Z, Wang Y, Xiong G, Zeng D, Wang X, Liu X, Teng S, Hiroshi F, Yuan M, Luo D, Han B, Li J (2003a) Control of tillering in rice. Nature 422:618–621
Li Y, Qian Q, Zhou Y, Yan M, Sun L, Zhang M, Fu Z, Wang Y, Han B, Pang X, Chen M, Li J (2003b) BRITTLE CULM1, which encodes a COBRA-like protein, affects the mechanical properties of rice plants. Plant Cell 15:2020–2031
Liu Q, Wang Z, Chen X, Cai X, Tang S, Yu H, Zhang J, Hong M, Gu M (2003) Stable inheritance of the antisense Waxy gene in transgenic rice with reduced amylose level and improved quality. Transgenic Res 12:71–82
Lockhart SR, Rymond BC (1994) Commitment of yeast pre-mRNA to the splicing pathway requires a novel U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide, Prp39p. Mol Cell Biol 14:3623–3633
Makarov EM, Makarova OV, Achsel T, Luhrmann R (2000) The human homologue of the yeast splicing factor prp6p contains multiple TPR elements and is stably associated with the U5 snRNP via protein-protein interactions. J Mol Biol 298:567–575
Mou Z, He Y, Dai Y, Liu X, Li J (2000) Deficiency in fatty acid synthase leads to premature cell death and dramatic alterations in plant morphology. Plant Cell 12:405–418
Nakamura Y (2002) Towards a better understanding of the metabolic system for amylopectin biosynthesis in plants: rice endosperm as a model tissue. Plant Cell Physiol 43:718–725
Okuno K, Fuwa H., Yano M (1983) A new mutant gene lowering amylose content in endosperm starch of rice, Oryza Sativa L. Jpn J Breed 33:387–394
Page RD (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Qian Q, Lin J, Song J, Yang C (1991) Genetic analysis of dull and its effect on kernal traits. Annual Report China National Rice Research Institute, p 3
Qian Q, Zhu X, Zeng D, Xiong Z, Min S (1996) The improvement of three new-type rice with special embryo and endosperm (in Chinese). Zhejiang Agricult Sci 4:155–156
Sano Y, Maekawa M, Kikuchi H (1985) Temperature effects on the Wx protein level an amylose content in the endosperm of rice. J Hered 76:221–223
Satoh H, Omura T (1981) New endosperm mutations induced by chemical mutagen in rice, Oryza sativa L. Japan J Breed 31:316–326
Satoh H, Omura T (1986) Mutagenesis in rice by treating fertilized egg cells with nitroso compounds. Rice Genet, p 707–717
Septiningsih EM, Trijatmiko KR, Moeljopawiro S, McCouch SR (2003) Identification of quantitative trait loci for grain quality in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O. rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 107:1433–1441
Simpson GG, Filipowicz W (1996) Splicing of precursors to mRNA in higher plants: mechanism, regulation and sub-nuclear organisation of the spliceosomal machinery. Plant Mol Biol 32:1–41
Tan YF, Li JX, Yu SB, Xing YZ, Xu CG, Zhang Q (1999) The three important traits for cooking and eating quality of rice grains are controlled by a single locus in an elite rice hybrid, Shanyou 63. Theor Appl Genet 99:642–648
Terada R, Nakajima M, Isshiki M, Okagaki RJ, Wessler SR, Shimamoto K (2000) Antisense waxy genes with highly active promoters effectively suppress waxy gene expression in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Physiol 41:881–888
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Urushiyama S, Tani T, Ohshima Y (1997) The prp1 gene required for pre-mRNA splicing in Schizosaccharomyces pombe encodes a protein that contains TPR motifs and is similar to Prp6p of budding yeast. Genetics 147:101–115
Wang ZY, Zheng FQ, Shen GZ, Gao JP, Snustad DP, Li MG, Zhang JL, Hong MM (1995) The amylose content in rice endosperm is related to the post-transcriptional regulation of the waxy gene. Plant J 7:613–622
Yano M, Okuno K, Satoh H, Omura T (1988) Chromosomal location of genes conditioning low amylose content of endosperm starches in rice, Oryza sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 76:183–189
Acknowledgements
We thank Zhixi Tian for the assistance in the analyses of starch properties and his critical comments on the manuscript, Kyushu University for providing the original du1 seeds, Bin Han (National Center for Gene Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for providing BAC and cDNA clones. This work was supported by grants from the State Key Basic Research Program (2005CB1208), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30530470, 30425034), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Y304442).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below are the electronic supplementary materials
11103_2007_9186_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Structural features of the Du1 gene. Numbers at left refer to the position of nucleotides. Red stands for the mutation in du1, blue for polymorphic bases between indica and japonica subspecies, pink for the N terminal domain, and green or orange for the TPR motifs (TIF 2,497 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, D., Yan, M., Wang, Y. et al. Du1, encoding a novel Prp1 protein, regulates starch biosynthesis through affecting the splicing of Wx b pre-mRNAs in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 65, 501–509 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9186-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9186-3