Abstract
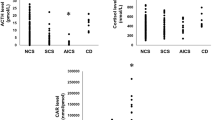
The purpose of this study is to verify whether acute pre-treatment with alprazolam (ALP), a benzodiazepine that inhibits HPA secretion in normal subjects, could better characterize patients with subclinical Cushing’s syndrome (SCS) than the 1-mg dexamethasone test (DST). In 22 patients with SCS, 10 with overt Cushing’s syndrome (CS), 11 with non-functioning adrenal incidentalomas (NF) and 14 normal subjects (NS) we studied the effect of ALP (1 mg, p.o. at 2300 hours) on cortisol levels after 1-mg DST. Cortisol levels (mean ± SEM) after DST were lower (P = 0.012) in SCS (3.9 ± 0.3 μg/dl) than in overt CS (10.4 ± 1.9 μg/dl), while they were higher (P = 0.0005) than in NF (1.1 ± 0.1 μg/dl) and NS (1.5 ± 0.1 μg/dl). After ALP pre-treatment, cortisol levels further decreased (P = 0.004) in SCS (3.0 ± 0.3 μg/dl), but neither in CS (9.3 ± 1.3 μg/dl) nor in NF (1.3 ± 0.1 μg/dl) and in NS (1.3 ± 0.1 μg/dl). In SCS, cortisol levels after ALP + 1-mg DST persisted lower (P = 0.0005) than those in CS, but higher (P = 0.0005) than those in NF and NS. Considering individual cases, ALP pre-treatment reduced cortisol levels <3 and <1.8 μg/dl in 50 and 23 % of SCS patients, respectively. ALP amplifies the cortisol inhibition exerted by 1-mg DST in patients with SCS but not in those with CS. The clinical usefulness of ALP to increase the sensitivity of 1-mg DST to identify true autonomous cortisol release in patients with adrenal incidentalomas as well as to predict different clinical outcomes remains to be clarified.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reincke M (2000) Subclinical Cushing’s syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 29:43–56
Terzolo M, Reimondo G, Bovio S, Angeli A (2004) Subclinical Cushing’s syndrome. Pituitary 7:217–223
Tsagarakis S, Vassiliadi D, Thalassinos N (2006) Endogenous subclinical hypercortisolism: diagnostic uncertainties and clinical implications. J Endocrinol Invest 29:471–482
Chiodini I (2011) Diagnosis and treatment of subclinical hypercortisolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:1223–1236
Terzolo M, Pia A, Reimondo G (2012) Subclinical Cushing’s syndrome: definition and management. Clin Endocrinol 76:12–18
Beierwaltes WH, Sturman MF, Ryo U, Ice RD (1973) Imaging functional nodules of adrenal gland with 131-I-9iodocholesterol. J Nucl Med 15:246–251
Charbonnel B, Chatal JF, Ozanne P (1981) Does the corticoadrenal adenoma with “pre-Cushing’s syndrome” exist? J Nucl Med 22:1059–1061
Terzolo M, Stigliano A, Chiodini I, Loli P, Furlani L, Arnaldi G, Reimondo G, Pia A, Toscano V, Zini M, Borretta G, Papini E, Garofalo P, Allolio B, Dupas B, Mantero F, Tabarin A (2011) Italian association of clinical endocrinologists. AME position statement on adrenal incidentaloma. Eur J Endocrinol 164:851–870
Cole MA, Kim PJ, Kalman BA, Spencer RL (2000) Dexamethasone suppression of corticosteroid secretion: evaluation of the site of action by receptor measures and functional studies. Psychoneuroendocr 25:151–167
Feldman S, Weidenfeld J (2002) Further evidence for the central effect of dexamethasone at the hypothalamic level in the negative feedback mechanism. Brain Res 958:291–296
Nieman LK, Biller BM, Findling JW, Newell-Price J, Savage MO, Stewart PM, Montori VM (2008) The diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:1526–1540
Grumbach MM, Biller BM, Braunstein GD, Campbell KK, Carney JA, Godley PA, Harris EL, Lee JK, Oertel YC, Posner MC, Schlechte JA, Wieand HS (2003) Management of the clinically inapparent adrenal mass (‘incidentaloma’). Ann Int Med 138:424–429
Tabarin A, Bardet S, Bertherat J, Dupas B, Chabre O, Hamoir E, Laurent F, Tenenbaum F, Cazalda M, Lefebvre H, Valli N, Rohmer V (2008) Exploration and management of adrenal incidentalomas. French Society of Endocrinology Consensus. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 69:487–500
Zeiger MA, Thompson GB, Duh QY, Hamrahian AH, Angelos P, Elaraj D, Fishman E, Kharlip J (2009) American association of clinical endocrinologists; American association of endocrine surgeons: The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American Association of Endocrine Surgeons medical guidelines for the management of adrenal incidentalomas. Endocr Pract 15(Suppl. 1):1–20
Kalogeras KT, Calogero AE, Kuribayashi T, Khan I, Gallucci WT, Kling MA, Chrousos GP, Gold PW (1990) In vitro and in vivo effects of the triazolobenzodiazepine alprazolam on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function: pharmacological and clinical implications. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 70:1462–1471
Arvat E, Giordano R, Grottoli S, Ghigo E (2002) Benzodiazepine and anterior pituitary function. J Endocrinol Invest 25:735–747
Breier A, Davis O, Buchanan R, Listwak SJ, Holmes C, Pickar D, Goldstein DS (1992) Effects of alprazolam on pituitary-adrenal and catecholaminergic responses to metabolic stress in humans. Biol Psychiatry 32:880–890
Torpy DJ, Grice JE, Hockings GI, Walters MW, Crosbie GV, Jackson RV (1993) Alprazolam blocks the naloxone-stimulated hyphotalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 76:388–391
Roher T, von Richthofen V, Schulz C, Beyer J, Lehnert H (1994) The stress, but not corticotropin-releasing hormone-induced activation of the pituitary-adrenal axis in man is blocked by alprazolam. Horm Metab Res 26:200–206
Torpy DJ, Grice JE, Hockings GI, Walters MW, Crosbie GV, Jackson RV (1994) Alprazolam attenuates vasopressin-stimulated adrenocorticotropin and cortisol release: evidence for sinergy between vasopressin and corticotropin-releasing hormone in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 79:140–144
Arvat E, Maccagno B, Ramunni J, Di Vito L, Gianotti L, Broglio F, Benso A, Deghenghi R, Camanni F, Ghigo E (1998) Effects of dexametasone and alprazolam, a benzodiazepine, on the stimulatory effect of Hexarelin, a synthetic GHRP, on ACTH, cortisol and GH secretion in humans. Neuroendocrinology 67:310–316
Grottoli S, Arvat E, Gauna C, Maccagno B, Ramunni J, Giordano R, Maccario M, Deghenghi R, Ghigo E (1999) Effects of alprazolam, a benzodiazepine, on the ACTH, GH- and PRL-releasing activity of Hexarelin, a synthetic peptidyl GH secretagogue (GHS), in patients with simple obesity and in patients with Cushing’s disease. Pituitary 2:197–204
Grottoli S, Maccagno B, Ramunni J, Di Vito L, Giordano R, Gianotti L, Destefanis S, Camanni F, Arvat E (2002) Alprazolam, a benzodiazepine, does not modify the ACTH and cortisol response to CRH and AVP, but blunts the cortisol response to ACTH in humans. J Endocrinol Invest 25:420–425
Arvat E, Maccagno B, Ramunni J, Di Vito L, Giordano R, Gianotti L, Broglio F, Camanni F, Ghigo E (1999) The inhibitory effect of alprazolam, a benzodiazepine, overrides the stimulated effect of metyrapone-induced lack of negative cortisol feedback on corticotroph secretion in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:2611–2615
Giordano R, Grottoli S, Brossa PC, Pellegrino M, Destefanis S, Lanfranco F, Gianotti L, Ghigo E, Arvat E (2003) Alprazolam (a benzodiazepine activating GABA receptor) reduces the neuroendocrine responses to insulin induced hypoglycaemia in humans. Clin Endocrinol 53:314–320
Grottoli S, Giordano R, Maccagno B, Pellegrino M, Ghigo E, Arvat E (2002) The stimulatory effect of canrenoate, a mineralocorticoid antagonist, on the activity of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis is abolished by alprazolam, a benzodiazepine, in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:4616–4620
Korbonits M, Trainer PJ, Edwards R, Besser GM, Grossman AB (1995) Benzodiazepines attenuate the pituitary-adrenal responses to corticotrophin-releasing hormone in healthy volunteers, but not in patients with Cushing’s syndrome. Clin Endocrinol 43:29–35
Papadopoulos V (1993) Peripheral-type benzodiazepine/diazepam binding inhibitor receptor: biological role in steroidogenic cell function. Endocr Rev 14:222–240
Whitehouse BJ (1992) Benzodiazepines and steroidogenesis. J Endocrinol 134:1–3
Nelder JA (1974) A user’s guide to the evaluation of statistical packages and systems. Int Stat Rev 42:291–298
Lopez AL, Kathol RG, Noyes R Jr (1990) Reduction in urinary free cortisol during benzodiazepine treatment of panic disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 15:23–28
Huizenga NA, Koper JW, de Lange P, Pols HA, Stolk RP, Grobbee DE, de Jong FH, Lamberts SW (1998) Interperson variability but intraperson stability of baseline plasma cortisol concentrations, and its relation to feedback sensitivity of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis to a low dose of dexamethasone in elderly individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:47–54
Calogero AE, Kamilaris TC, Bernardini R, Johnson EO, Chrousos GP, Gold PW (1990) Effects of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligands on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis function in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:729–737
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by University of Turin and the Foundation for the Study of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giordano, R., Berardelli, R., Karamouzis, I. et al. Acute administration of alprazolam, a benzodiazepine activating GABA receptors, inhibits cortisol secretion in patients with subclinical but not overt Cushing’s syndrome. Pituitary 16, 363–369 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-012-0433-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-012-0433-5