Abstract
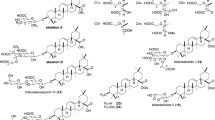
Chenopodium quinoa Willd. is a valuable food source which has gained importance in many countries of the world. The plant contains various bitter-tasting saponins which present an important antinutritional factor. Various triterpene saponins have been reported in C. quinoa including both monodesmosidic and bidesmosidic triterpene saponins of oleanolic acid, hederagenin, phytolaccagenic acid, and serjanic acid as the major aglycones and other aglycones as 3β-hydroxy-23-oxo-olean-12-en-28-oic acid, 3β-hydroxy-27-oxo-olean-12-en-28-oic acid, and 3β, 23α, 30β-trihydroxy-olean-12-en-28-oic acid. A tridesmosidic saponin of hederagenin has also been reported. Here we review the occurrence, analysis, chemical structures, and biological activity of triterpene saponins of C. quinoa. In particular, the mode of action of the mono- and bidesmosidic triterpene saponins and aglycones are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
Austria
- B:
-
Bolivia
- C:
-
Chile
- E:
-
Equador
- G:
-
Germany
- M:
-
Mexico
- P:
-
Peru
- SA:
-
South America
References
Ahamed NT, Singhal RS, Kulkarni PR, Pal M (1998) A lesser-known grain, Chenopodium quinoa: review of the chemical composition of its edible parts. Food Nutr Bull 19:61–70
Alvistur CE, White P, Chiriboga CC (1953) Biological value of quinoa. Bol Soc Quim Peru 19:197–209
Ando H, Chen YC, Tang HJ, Shimizu M, Watanabe K, Mitsunaga T (2002) Food components in fractions of quinoa seed. Food Sci Technol Res 8:80–84. doi:10.3136/fstr.8.80
Bhargava A, Shukla S, Ohri D (2006) Chenopodium quinoa—an Indian perspective. Ind Crops Prod 23:73–87. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2005.04.002
Bogacheva NG, Kogan LM, Libizov NI (1974) Triterpene glycosides of Chenopodium ambrosioides. Chem Nat Compd 8:392. doi:10.1007/BF00563766
Bonifacio A (2003) Chenopodium sp.: genetic resources, ethnobotany, and geographic distribution. Food Rev Int 19:1–7. doi:10.1081/FRI-120018863
Brady K, Ho CT, Rosen RT, Sang SM, Karwe MV (2007) Effects of processing on the nutraceutical profile of quinoa. Food Chem 100:1209–1216. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.12.001
Burnouf-Radosevich M, Delfel NE, England R (1985) Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry of oleanane- and ursane-type triterpenes-application to Chenopodium quinoa triterpenes. Phytochemistry 24:2063–2066. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)83122-2
Carlsson R, Hanczakowski P, Kaptur T (1984) The quality of the green fraction of leaf protein concentrate from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. grown at different levels of fertilizer nitrogen. Anim Feed Sci Technol 11:239–245. doi:10.1016/0377-8401(84)90039-7
Castello JD, Lakshman DK, Tavantzis SM, Rogers SO, Bachand GD, Jagels R, Carlisle J, Liu Y (1995) Detection of infectious tomato mosaic tobamovirus in fog and clouds. Phytopathology 85:1409–1412. doi:10.1094/Phyto-85-1409
Chirva VY, Cheban PL, Kintya PK, Bobeiko VA (1971) Structure of the triterpene glycosides from the roots of Chenopodium anthelminticum. Chem Nat Compd 7:23–25. doi:10.1007/BF01032019
Chwalek M, Lalun N, Bobichon H, Ple K, Voutquenne-Nazabadioko L (2006) Structure-activity relationships of some hederagenin diglycosides: haemolysis, cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1760:1418–1427. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2006.05.004
Coulter L, Lorenz K (1990) Quinoa-composition, nutritional value, food applications. LWT - Food Sci Technol 23:203–207
Cuadrado C, Ayet G, Burbano C, Muzquiz M, Camacho L, Cavieres E, Lovon M, Osagie A, Price KR (1995) Occurrence of saponins and sapogenols in Andean crops. J Sci Food Agric 67:169–172. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740670205
de Simone F, Dini A, Pizza C, Saturnino P, Schettino O (1990) Two flavonol glycosides from Chenopodium quinoa. Phytochemistry 29:3690–3692. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(90)85310-C
Dini I, Schettino O, Simioli T, Dini A (2001a) Studies on the constituents of Chenopodium quinoa seeds: Isolation and characterization of new triterpene saponins. J Agric Food Chem 49:741–746. doi:10.1021/jf000971y
Dini I, Tenore GC, Schettino O, Dini A (2001b) New oleanane saponins in Chenopodium quinoa. J Agric Food Chem 49:3976–3981. doi:10.1021/jf010361d
Dini I, Tenore GC, Dini A (2005) Nutritional and antinutritional composition of Kancolla seeds: an interesting and underexploited andine food plant. Food Chem 92:125–132. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.07.008
Dini I, Tenore GC, Trimarco E, Dini A (2006) Two novel betaine derivatives from Kancolla seeds (Chenopodiaceae). Food Chem 98:209–213. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.05.014
Dutcheshen JM (2003) Plant protection against bacterial diseases using saponins. U. S. Patent no. 2003162731
Escalante AM, Santecchia CB, Lopez SN, Gattuso MA, Gutierrez RA, Delle MF, Gonzalez SM, Zacchino SA (2002) Isolation of antifungal saponins from Phytolacca tetramera, an Argentinean species in critical risk. J Ethnopharmacol 82:29–34. doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(02)00145-9
Estrada A, Li B, Laarveld B (1998) Adjuvant action of Chenopodium quinoa saponins on the introduction of antibody responses to intragastric and intranasal administered antigens in mice. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 21:225–236. doi:10.1016/S0147-9571(97)00030-1
Facino RM, Carini M, Stefani R, Aldini G, Saibene L (1995) Anti-elastase and anti-hyaluronidase activities of saponins and sapogenins from Hedera helix, Aesculus hippocastanum, and Ruscus aculeatus: factors contributing to their efficacy in the treatment of venous insufficiency. Arch Pharm 328:720–724. doi:10.1002/ardp.19953281006
Gee JM, Price KR, Ridout CL, Johnson IT, Fenwick GR (1989) Effects of some purified saponins on transmural potential difference in mammalian small-intestine. Toxicol In Vitro 3:85–90. doi:10.1016/0887-2333(89)90049-0
Ghosh D, Thejomoorthy P, Veluchamy (1983) Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of oleanolic acid 3-/3-glucoside (RDG-1) from Randia dumetorum (Rubiaceae). Indian J Pharmacol 15:331–342
Gohar AA, Maatooq GT, Niwa M, Yoshiaki T (2002) A new triterpene saponin from Chenopodium ficifolium. Z Naturforsch C Biosci 57:597–602
Gross R, Koch F, Malaga I, de Miranda AF, Schoeneberger H, Trugo LC (1989) Chemical composition and protein quality of some local Andean food sources. Food Chem 34:25–34. doi:10.1016/0308-8146(89)90030-7
Gülçin I, Mshvildadze V, Gepdiremen A, Elias R (2006) The antioxidant activity of a triterpenoid glycoside isolated from the berries of Hedera colchica: 3-O-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-hederagenin. Phytother Res 20:130–134. doi:10.1002/ptr.1821
Hamburger M, Hostettmann K (1986) New saponins and a prosapogenin from Polygala chamaebuxus L. Helv Chim Acta 69:221–227. doi:10.1002/hlca.19860690126
Haralampidis K, Trojanowska M, Osbourn AE (2002) Biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins in plants. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 75:31–49
Holstein SA, Hohl RJ (2004) Isoprenoids: remarkable diversity of form and function. Lipids 39(4):293–309
Johnson IT, Gee JM, Price K, Curl C, Fenwick GR (1986) Influence of saponins on gut permeability and active nutrient transport in vitro. J Nutr 116:2270–2277
Khalik SMA, Miyase T, El-Ashaal HA, Melek FR (2000) Triterpenoid saponins from Fagonia cretica. Phytochemistry 54:853–859. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)00168-0
Kim YK, Kim RG, Park SJ, Ha JH, Choi JW, Park HJ, Lee KT (2002) In vitro antiinflammatory activity of kalopanaxsaponin A isolated from Kalopanax pictus in murine macrophage raw 264.7 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 25:472–476. doi:10.1248/bpb.25.472
Konishi Y, Hirano S, Tsuboi H, Wada M (2004) Distribution of minerals in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) seeds. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:231–234. doi:10.1271/bbb.68.231
Koziol MJ (1991) Afrosimetric estimation of threshold saponin concentration for bitterness in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). J Sci Food Agric 54:211–219. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740540206
Koziol MJ (1992) Chemical composition and nutritional evaluation of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). J Food Compost Anal 5:35–68. doi:10.1016/0889-1575(92)90006-6
Koziol MJ (1993) Quinoa: a potential new oil crop. In: Janick JE (ed) New crops. Wiley, New York, pp 328–336
Kuljanabhagavad T, Thongphasuk P, Chamulitrat W, Wink M (2008) Triterpene saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Phytochemistry 69:1919–1926. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.03.001
Lavaud C, Voutquenne L, Bal P, Pouny I (2000) Saponins from Chenopodium album. Fitoterapia 71:338–340. doi:10.1016/S0367-326X(99)00166-5
Liu J, Henkel T (2002) Traditional chinese medicine (TCM): are polyphenols and saponins the key ingredients triggering biological activities? Curr Med Chem 9:1483–1485
Ma WW, Heinstein PF, McLaughlin JL (1989) Additional toxic, bitter saponins from the seeds of Chenopodium quinoa. J Nat Prod 52:1132–1135. doi:10.1021/np50065a035
Madl T, Sterk H, Mittelbach M, Rechberger GN (2006) Tandem mass spectrometric analysis of a complex triterpene saponin mixture of Chenopodium quinoa. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 17:795–806. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2006.02.013
Mahato SB, Nandy AK (1991) Triterpenoid saponins discovered between 1987 and 1989. Phytochemistry 30:1357–1390. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(91)84170-W
Mahoney AW, Lopez JG, Hendricks DG (1975) An evaluation of the protein quality of quinoa. J Agric Food Chem 23:190–193. doi:10.1021/jf60198a035
Marston A, Gafner F, Dossaji SF, Hostettmann K (1988) Fungicidal and molluscicidal saponins from Dolichos kilimandscharicus. Phytochemistry 27:1325–1326. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(88)80186-9
Marston A, Wolfender JL, Hostettmann K (2000) Analysis and isolation of saponins from plant material. In: Oleszek WA, Marston A (eds) Saponins in food feedstuffs and medicinal plants. Annual Proceedings of the Phytochemical Society, Clarendon, pp 1–12
Mastebroek HD, Limburg H, Gilles T, Marvin HJP (2000) Occurrence of sapogenins in leaves and seeds of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). J Sci Food Agric 80:152–156. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0010(20000101)80:1<152::AID-JSFA503>3.0.CO;2-P
Meyer BN, Heinstein PF, Burnouf-Radosevich M, Delfel NE, McLaughlin JL (1990) Bioactivity-directed isolation and characterization of quinoside A: one of the toxic/bitter principles of quinoa seeds (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). J Nat Prod 38:205–208
Mizui F, Kasai R, Ohtani K, Tanaka O (1988) Saponins from the bran of quinoa, Chenopodium quinoa Willd. I. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 36:1415–1418
Mizui F, Kasai R, Ohtani K, Tanaka O (1990) Saponins from the bran of quinoa, Chenopodium quinoa Willd. II. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 38:375–377
Muir AD, Ballantyne KD, Hall TW (2000) LC-MS and LC-MS/MS analysis of saponins and sapogenins comparison of ionization techniques and their usefulness in compound identification. In: Oleszek WA, Marston A (eds) Saponins in food, feedstuffs and medicinal plants. Annual Proceedings of the Phytochemistry Society, Clarendon, pp 35–42
Mujica A (1994) Andean grains and legumes. In: Bermejo JEH, Leon J (eds) Neglected crops: 1492 from a different perspective. Plant production and protection. FAO, Rome, pp 131–148
Ng KG, Price KR, Fenwick GR (1994) A TLC method for the analysis of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) saponins. Food Chem 49:311–315. doi:10.1016/0308-8146(94)90177-5
Ng SC, Anderson A, Coker J, Ondrus M (2007) Characterization of lipid oxidation products in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). Food Chem 101:185–192. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.01.016
Nicholls FH (1996) New crops in the U.K.: from concept to bottom line profiles. In: Janick JE (ed) Progress in new crops. ASHS Press, Alexandria
Oakenfull D, Sidhu GS (1990) Could saponins be a useful treatment for hypercholesterolemia. Eur J Clin Nutr 44:79–88
Oda K, Matsuda H, Murakami T, Katayama S, Ohgitani T, Yoshikawa M (2000) Adjuvant and haemolytic activities of 47 saponins derived from medicinal and food plants. Biol Chem 381:67–74. doi:10.1515/BC.2000.009
Oleszek WA (2002) Chromatographic determination of plant saponins. J Chromatogr A 967:147–162. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01556-4
Popenoe H, King SR, Leon J, Kalinowski LS (1989) Lost crops of the Incas. In: Vietmeyer ND (ed) Little known plants of the Andes with promise for worldwide cultivation. National Academy Press, Washington
Price KR, Johnson IT, Fenwick GR (1987) The chemistry and biological significance of saponins in foods and feedingstuffs. CRC Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 26:27–135
Przybylski R, Chauhan GS, Eskin NAM (1994) Characterization of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) lipids. Food Chem 51:187–192. doi:10.1016/0308-8146(94)90255-0
Quetinleclercq J, Elias R, Balansard G, Bassleer R, Angenot L (1992) Cytotoxic activity of some triterpenoid saponins. Planta Med 58:279–281. doi:10.1055/s-2006-961456
Rastrelli L, de Simone F, Schettino O, Dini A (1996) Constituents of Chenopodium pallidicaule (Cañihua) seeds: isolation and characterization of new triterpene saponins. J Agric Food Chem 44:3528–3533. doi:10.1021/jf950253p
Renard CMGC, Wende G, Booth EJ (1999) Cell wall phenolics and polysaccharides in different tissues of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). J Sci Food Agric 79:2029–2034. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0010(199911)79:14<2029::AID-JSFA483>3.0.CO;2-B
Rhodes J (1989) Evidence for an intercellular covalent reaction essential in antigen-specific T cell activation. J Immunol 143:1482–1489
Risic J, Galwey NW (1984) The Chenopodium grains of the Andes: Inca crops for modern agriculture. In: Coaker TH (ed) Advances in applied biology. Academic Press, London, pp 145–216
Ruales J, Nair BM (1993a) Content of fat, vitamins and minerals in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) seeds. Food Chem 48:131–136. doi:10.1016/0308-8146(93)90047-J
Ruales J, Nair BM (1993b) Saponins, phytic acid, tannins and protease inhibitors in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa, Willd.) seeds. Food Chem 48:137–143. doi:10.1016/0308-8146(93)90048-K
San Martin R, Ndjoko K, Hostettmann K (2008) Novel molluscicide against Pomacea canaliculata based on quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) saponins. Crop Prot 27:310–319. doi:10.1016/j.cropro.2007.03.015
Schopke T (2000) Non-NMR methods for structure elucidation of saponins. In: Oleszek WA, Marston A (eds) Saponins in food, feedstuffs and medicinal plants. Annual Proceedings of the Phytochemical Society, Clarendon
Schwartzman RA, Cidlowski JA (1993) Apoptosis: the biochemistry and molecular biology of programmed cell death. Endocr Rev 14:133–151. doi:10.1210/er.14.2.133
Sosa S, Morelli CF, Tubaro A, Cairoli P, Speranza G, Manitto P (2007) Anti-inflammatory activity of Maytenus senegalensis root extracts and of maytenoic acid. Phytomedicine 14:109–114. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2005.11.002
Sparg SG, Light ME, van Staden J (2004) Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J Ethnopharmacol 94:219–243. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2004.05.016
Stuardo M, San Martín R (2008) Antifungal properties of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) alkali treated saponins against Botrytis cinerea. Ind Crops Prod 27:296–302. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2007.11.003
Tan N, Zhou J, Zhao S (1999) Advances in structural elucidation of glucuronide oleanane-type triterpene carboxylic acid 3, 28-O-bisdesmosides (1962–1997). Phytochemistry 52:153–192. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(98)00454-3
Tapia ME (1979) Historia y distribuición geográfica. In: Tapia ME (ed) Quinua y Kañihua. Cultivos Andinos. Serie Libros y Materiales Educativos. Instituto Interamericano de Ciencias Agrícolas, Bogotá, Colombia, pp 11–15
Thompson CB (1995) Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267:1456–1462. doi:10.1126/science.7878464
Treyvaud V, Marston A, Dyatmiko W, Hostettmann K (2000) Molluscicidal saponins from Phytolacca icosandra. Phytochemistry 55:603–609. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)00233-8
Vincken JP, Heng L, de Groot A, Gruppen H (2007) Saponins, classification and occurrence in the Plant Kingdom. Phytochemistry 68:275–297. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.10.008
Voutquenne L, Lavaud C, Massiot G, le Men-Olivier L (2002) Structure–activity relationships of haemolytic saponins. Pharm Biol 40:253–262. doi:10.1076/phbi.40.4.253.8470
Wiart C (2007) Anti-inflammatory plants. In: Hackworth J (ed) Ethnopharmacology of medicinal plants Asia and the Pacific. Humana Press, pp 1–55
Wink M (2004) Phytochemical diversity of secondary metabolites. Encyclopedia of plant & crop science. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 915–919
Wink M (2006) Importance of plant secondary metabolites for protection against insect and microbial infections. In: Rai M, Carpinella M (eds) Naturally occurring bioactive compounds. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 251–268
Woldemichael GM, Wink M (2001) Identification and biological activities of triterpenoid saponins from Chenopodium quinoa. J Agric Food Chem 49:2327–2332. doi:10.1021/jf0013499
Woldemichael GM, Montenegro G, Timmermann BN (2003) Triterpenoidal lupin saponins from the Chilean legume Lupinus oreophilus. Philos Phytochem 63:853–857. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00328-5
Wood SG, Lawson LD, Fairbanks DJ, Robison LR, Andersen WR (1993) Seed lipid content and fatty acid composition of three quinoa cultivars. J Food Compost Anal 6:41–44. doi:10.1006/jfca.1993.1005
Yawadio Nsimba R, Kikuzaki H, Konishi Y (2008) Antioxidant activity of various extracts and fractions of Chenopodium quinoa and Amaranthus spp. seeds. Food Chem 106:760–766. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.06.004
Zhu N, Kikuzaki H, Vastano BC, Nakatani N, Karwe MV, Rosen RT, Ho CT (2001a) Ecdysteroids of quinoa seeds (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). J Agric Food Chem 49:2576–2578. doi:10.1021/jf0014462
Zhu N, Sheng S, Li D, Lavoie EJ, Karwe MV, Rosen RT, Ho CT (2001b) Antioxidative flavonoid glycosides from quinoa seeds (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). J Food Lipids 8:37–44. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4522.2001.tb00182.x
Zhu NQ, Sheng SQ, Sang SM, Jhoo JW, Bai NS, Karwe MV, Rosen RT, Ho CT (2002) Triterpene saponins from debittered quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) seeds. J Agric Food Chem 50:865–867. doi:10.1021/jf011002l
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Commission on Higher Education (CHE) of the Ministry of Education, Bangkok, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuljanabhagavad, T., Wink, M. Biological activities and chemistry of saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd.. Phytochem Rev 8, 473–490 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-009-9121-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-009-9121-0