Abstract
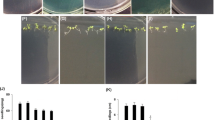
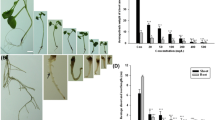
The physiological and biochemical behaviour of rice (Oryza sativa, var. Jyoti) treated with copper (II) oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) was studied. Germination rate, root and shoot length, and biomass decreased, while uptake of Cu in the roots and shoots increased at high concentrations of CuO NPs. The accumulation of CuO NPs was observed in the cells, especially, in the chloroplasts, and was accompanied by a lower number of thylakoids per granum. Photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance, maximal quantum yield of PSII photochemistry, and photosynthetic pigment contents declined, with a complete loss of PSII photochemical quenching at 1,000 mg(CuO NP) L−1. Oxidative and osmotic stress was evidenced by increased malondialdehyde and proline contents. Elevated expression of ascorbate peroxidase and superoxide dismutase were also observed. Our work clearly demonstrated the toxic effect of Cu accumulation in roots and shoots that resulted in loss of photosynthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAS:
-
atomic absorption spectrophotometer
- APX:
-
ascorbate peroxidase
- DM:
-
dry mass
- E :
-
transpiration rate
- FM:
-
fresh mass
- Fm :
-
maximum fluorescence
- Fo :
-
initial fluorescence
- Fs :
-
steady-state fluorescence
- Fv/Fm :
-
maximal quantum yield of PSII photochemistry
- GR:
-
glutathione reductase
- gs :
-
stomatal conductance
- IRGA:
-
infra red gas analyser
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- NP(s):
-
nanoparticle(s)
- P N :
-
photosynthetic rate
- qP :
-
photochemical quenching
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SEM:
-
scanning electron microscope
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- TBA:
-
thiobarbituric acid
- TEM:
-
transmission electron microscope
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
Abdelkader A.F., Aronsson H., Solymosi K. et al.: High salt stress induces swollen prothylakoids in dark-grown wheat and alters both prolamellar body transformation and reformation after irradiation. — J. Exp. Bot. 58: 2553–2564, 2007.
Alia, Pardha Saradhi, P.: Proline accumulation under heavy metal stress. — J. Plant Physiol. 138: 554–558, 1991.
Bassi R., Sharma S.S.: Changes in proline content accompanying the uptake of zinc and copper by Lemna minor. — Ann. Bot.-London 72: 151–154, 1993.
Bates L.S., Waldren R.P., Teare I.D.: Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. — Plant Soil 39: 205–207, 1973.
Bohnert H.J., Nelson D.E., Jensen R.G.: Adaptations to environmental stresses. — Plant Cell 7: 1099–1111, 1995.
Campbell R., Greaves M.P.: Anatomy and community structure of the rhizosphere. — In: Lynch J.M. (ed.): The Rhizosphere. Pp. 11–34. John Wiley and Sons Ltd. Publ., London 1990.
Caverzan A., Passaia G., Rosa S.B. et al.: Plant responses to stresses: Role of ascorbate peroxidase in the antioxidant protection. — Genet. Mol. Biol. 35: 1011–1019, 2012.
Corredor E., Testillano P.S., Coronado M.-J. et al.: Nanoparticle penetration and transport in living pumpkin plants: in situ subcellular identification. — BMC Plant Biol. 9: 45–45, 2009.
Harrison P.: Emerging challenges: nanotechnology and the environment. — In: GEO Year Book 2007. Pp. 61–68. United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), Nairobi 2007.
Haverkamp R.G., Marshall A.T.: The mechanism of metal nanoparticle formation in plants: Limits on accumulation. — J. Nanoparticle Res. 11: 1453–1463, 2009.
Inzé D., Van Montagu M.: Oxidative stress in plants. — Curr. Opin. Biotech. 6: 153–158, 1995.
Kampfenkel K., Van Montagu M., Inzé D.: Extraction and determination of ascorbate and dehydroascorbate from plant tissue. — Anal. Biochem. 225: 165–167, 1995.
Kennedy C.D., Gonsalves F.A.N.: The action of divalent zinc, cadmium, mercury, copper and lead on the trans-root potential and H+ efflux of excised roots. — J. Exp. Bot. 38: 800–817, 1987.
Kirchhoff H., Horstmann S., Weis E.: Control of the photosynthetic electron transport by PQ diffusion microdomains in thylakoids of higher plants. — BBA-Bioenergetics 1459: 148–168, 2000.
Klaine S.J., Alvarez P.J.J., Batley G.E. et al.: Nanomaterials in the environment: behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. — Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 27: 1825–1851, 2008.
Lee C.W., Mahendra S., Zodrow K. et al.: Developmental phytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles to Arabidopsis thaliana. — Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 29: 669–675, 2010.
Lee S., Kim S., Kim S. et al.: Assessment of phytotoxicity of ZnO NPs on a medicinal plant, Fagopyrum esculentum. — Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 20: 848–854, 2013.
Lee W.M., An Y.J., Yoon H. et al.: Toxicity and bioavailability of copper nanoparticles to the terrestrial plants mung bean (Phaseolus radiatus) and wheat (Triticum aestivum): plant agar test for water-insoluble nanoparticles. — Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 27: 1915–1921, 2008.
Lidon F.C., Henriques F.S.: Role of rice shoot vacuoles in copper toxicity regulation. — Environ. Exp. Bot. 39: 197–202, 1998.
Lin D., Xing B.: Root uptake and phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. — Environ. Sci. Technol. 42: 5580–5585, 2008.
Manceau A., Nagy K.L., Marcus M.A. et al.: Formation of metallic copper nanoparticles at the soil-root interface. — Environ. Sci. Technol. 42: 1766–1772, 2008.
Marschner H.: Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Pp. 889. Academic Press, London 1995.
Maynard A.D., Aitken R.J., Butz T. et al.: Safe handling of nanotechnology. — Nature 444: 267–269, 2006.
Mehta S.K., Gaur J.P.: Heavy metal-induced proline accumulation and its role in ameliorating metal toxicity in Chlorella vulgaris. — New Phytol. 143: 253–259, 1999.
Musante C., White J.C.: Toxicity of silver and copper to Cucurbita pepo: Differential effects of nano and bulk-size particles. — Environ. Toxicol. 27: 510–517, 2012.
Nagajyoti P.C., Lee K.D., Sreekanth T.V.M. et al.: Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. — Environ. Chem. Lett. 8: 199–216, 2010.
Navarro E., Baun A., Behra R. et al.: Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. — Ecotoxicology 5: 372–386, 2008.
Nekrasova G.F., Ushakova O.S., Ermakov A.E. et al.: Effects of copper (II) ions and copper oxide nanoparticles on Elodea densa Planch. — Russian J. Ecol. 42: 458–463, 2011.
Noctor G., Foyer C.H.: Ascorbate and glutathione: Keeping active oxygen under control. — Annu. Rev. Plant Phys. 49: 249–279, 1998.
Ojamäe L., Aulin C., Pedersen H. et al.: IR and quantumchemical studies of carboxylic acid and glycine adsorption on rutile TiO2 nanoparticles. — J. Colloid Interface Sci. 296: 71–78, 2006.
Perreault F., Oukarroum A., Pirastru L. et al.: Evaluation of copper oxide nanoparticles toxicity using chlorophyll a fluorescence imaging in Lemna gibba. — J. Bot. 2010, 1–9, 2010.
Raven J.A., Evans M.C., Korb R.E.: The role of trace metals in photosynthetic electron transport in O2 - evolving organisms. — Photosynth. Res. 60: 111–150, 1999.
Rico C.M., Majumdar S., Duarte-Gardea M. et al.: Interaction of nanoparticles with edible plants and their possible implications in the food chain. — J. Agric. Food Chem. 59: 3485–3498, 2011.
Saison C., Perreault F., Daigle J.C. et al.: Effect of core-shell copper oxide nanoparticles on cell culture morphology and photosynthesis (photosystem II energy distribution) in the green alga, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. — Aquat. Toxicol. 96: 109–114, 2010.
Sankhalkar S., Sharma P.K.: Protection against photooxidative damage provided by enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant system in sorghum seedlings. — Indian J. Exp. Biol. 40: 1260–1268, 2002.
Sharma P.K., Hall D.O.: Effect of photoinhibition and temperature on carotenoids in sorghum leaves. — Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 33: 471–477, 1996.
Sharma P.K., Shetye R., Bhonsle S.: Effect of supplementary ultraviolet-B radiation on young wheat seedlings. — Curr. Sci. 72: 400–405, 1997.
Shaw A.K., Hossain Z.: Impact of nano-CuO stress on rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. — Chemosphere 93: 906–915, 2013.
Shi J., Abid A.D., Kennedy I.M. et al.: To duckweeds (Landoltia punctata), nanoparticulate copper oxide is more inhibitory than the soluble copper in the bulk solution. — Environ. Pollut. 159: 1277–1282, 2011.
Smirnoff N.: Tansley Review 52. The role of active oxygen in the response of plants to water-deficit and desiccation. — New Phytol. 125: 27–58, 1993.
Solymosi K., Bertrand M.: Soil metals, chloroplasts, and secure crop production: a review. — Agron. Sustain. Dev. 32: 245–272, 2012.
Song, L., Vijver, M. G., Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M.: Comparative toxicity of copper nanoparticles across three Lemnaceae species. — Sci. Total Environ. 518–519: 217–224, 2015.
Stampoulis D., Sinha S.K., White J.C.: Assay-dependent phytotoxicity of nanoparticles to plants. — Environ. Sci. Technol. 43: 9473–9479, 2009.
Ünnep R., Zsiros O., Solymosi K. et al.: The ultrastructure and flexibility of thylakoid membranes in leaves and isolated chloroplasts as revealed by small-angle neutron scattering. — BBA-Bioenergetics 1837: 1572–1580, 2014.
Wang S.-H., Yang Z.-M., Yang H. et al.: Copper-induced stress and antioxidative responses in roots of Brassica juncea L. — Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin. 45: 203–212, 2004.
Wierzbicka M.S., Obidzińska J.: The effect of lead on seed imbibition and germination in different plant species. — Plant Sci. 137: 155–171, 1998.
Wiesner M.R., Lowry G.V., Alvarez P. et al.: Assessing the risks of manufactured nanomaterials. — Environ. Sci. Technol. 40: 4336–4345, 2006.
Yoshimura K., Yabuta Y., Ishikawa T. et al.: Expression of spinach ascorbate peroxidase isoenzymes in response to oxidative stresses. — Plant Physiol. 123: 223–233, 2000.
Yruela I.: Copper in plants. — Brazilian J. Plant Physiol. 17: 145–156, 2005.
Zhang W., Elliott D.W.: Applications of iron nanoparticles for groundwater remediation. — Remediat. J. 16: 7–21, 2006.
Zhang Z., He X., Zhang H. et al.: Uptake and distribution of ceria nanoparticles in cucumber plants. — Metallomics 3: 816–822, 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: We thank the Department of Science & Technology (DST), New Delhi (SR/SO/PS-63/2009) and UGC-SAP (F. 3-50/2009 (SAP-II) for funding this work. We would like to thank All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi for TEM imaging; NIO, Goa for SEM imaging and atomic absorption spectrophotometry; Physics Department, Goa University for NP size determination using X-ray diffractometer. We are grateful to Andrew Willis, Centre for Agroecology, Water and Resilience (CAWR), Coventry University, Coventry, United Kingdom for correcting the English of the manuscript.
Both authors made equal contribution to the work presented in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Da Costa, M.V.J., Sharma, P.K. Effect of copper oxide nanoparticles on growth, morphology, photosynthesis, and antioxidant response in Oryza sativa . Photosynthetica 54, 110–119 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-015-0167-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-015-0167-5