Abstract
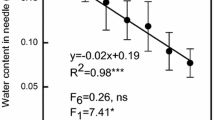
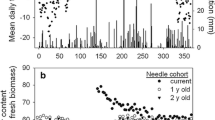
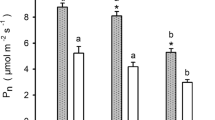
We studied the effects of applying 50 kg(N) ha−1 year−1 of nitrogen (N) on needle photosynthesis, N allocation and nutrient content in the sun- and shade crowns of the hybrid larch F1 (Larix gmelinii var. japonica × L. kaempferi). The light-saturated net photosynthetic rate (P Nmax) was not significantly affected by N application or crown position, although the contents of N, P, K, and chlorophyll (Chl), and the maximum rates of carboxylation and electron transport were lower in needles of the shade crown than of the sun crown. This difference was mainly due to an increase in the intercellular CO2 concentration (C i) in the needles of the shade crown. Analysis of N allocation in photosynthetic systems revealed that more N was allocated to functions related to electron transport and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration in needles of the shade crown. N allocation in needles of the hybrid larch F1 was regulated mainly by the light conditions, rather than by N application
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C a :
-
external CO2 concentration
- C i :
-
intercellular CO2 concentration
- Ca:
-
calcium
- Chl:
-
chlorophyll
- g s :
-
stomatal conductance of water vapor
- J max :
-
maximum rate of electron transport
- K:
-
potassium
- K c :
-
value of Rubisco Michaelis constants for CO2
- K o :
-
value of Rubisco Michaelis constants for O2
- LHCP:
-
light-harvesting chlorophyll complex protein
- LMA:
-
leaf mass per area
- Mg:
-
magnesium
- N:
-
nitrogen
- N 1 :
-
nitrogen allocated in light-harvesting chlorophyll complex protein and photosystems
- N 2 :
-
nitrogen allocated in bioenergetics (electron carriers except for photosystems, coupling factor and Calvin cycle enzymes except for Rubisco)
- N 3 :
-
nitrogen allocated in Rubisco
- N 4 :
-
nitrogen allocated in other components in needle
- N m :
-
N content per unit leaf mass
- P:
-
phosphorus
- P max :
-
net assimilation rate at 1,700 μmol mol−1 CO2
- P N :
-
net assimilation rate
- P Nmax :
-
light-saturated net photosynthetic rate
- PNUE:
-
photosynthetic nitrogen-use efficiency
- PPF:
-
photosynthetic photon flux
- V cmax :
-
maximum rate of carboxylation
- V cr :
-
the specific activity of Rubisco
- Γ*:
-
CO2 compensation point in the absence of dark respiration
References
Anten, N.P.R., During, H.J.: Is analyzing the nitrogen use at the plant canopy level a matter of choosing the right optimization criterion? & Oecologia 167: 293–303, 2011
Baker, N.R., Bowyer, J.R.: Photoinhibition of photosynthesis. & In: Baker, N.R., Bowyer, J.R.: Photoinhibition of Photosynthesis from Molecular Mechanisms to the Field. Pp. 1–19 BIOS Scientific Publishers, Oxford 1994
Barnes, J.D., Balaguer, L., Manrique, E., Elvira, S., Davison, A.W.: A reappraisal of the use of DMSO for the extraction and determination of chlorophylls a and b in lichens and higher plants. & Environ. Exp. Bot. 32: 85–100, 1992
Bernacchi, C.J., Singsaas, E.L., Pimentel, C., Portis, A.R., Long, S.P.: Improved temperature response functions for models of Rubisco-limited photosynthesis. & Plant Cell Environ. 24: 253–259, 2001
Braun, S., Thomas, V.F.D., Quiring, R., Flückiger, W.: Does nitrogen deposition increase forest production? The role of phosphorus. & Environ. Pollut. 158: 2043–2052, 2010
DeJong, T.M., Day, K.R., Johnson, R.S.: Partitioning of leaf nitrogen with respect to within canopy light exposure and nitrogen availability in peach (Prunus persica). & Trees 3: 89–95, 1989
Escudero, A., Mediavilla, S.: Decline in photosynthetic nitrogen use efficiency with leaf age and nitrogen resorption as determinants of leaf life span. & J. Ecol. 91: 880–889, 2003
Farquhar, G.D., von Caemmerer, S., Berry, J.A.: A biochemical model of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in leaves of C3 species. & Planta 149: 78–90, 1980
Field, C.: Allocating leaf nitrogen for the maximization of carbon gain: leaf age as a control on the allocation program. & Oecologia 56: 341–347, 1983
Fife, D.N., Nambiar, E.K.S.: Changes in the canopy and growth of Pinus radiata in response to nitrogen supply. & Forest Ecol. Manage. 93: 137–152, 1997
Galloway, J.N., Dentener, F.J., Capone, D.G. et al.: Nitrogen cycles: past, present and future. & Biogeochemistry 70: 153–226, 2004
Hirose, T., Werger, M.J.A.: Maximizing daily canopy photosynthesis with respect to the leaf nitrogen allocation pattern in the canopy. & Oecologia 72: 520–526, 1987
Hirose, T., Werger, M.J.A., Pons, T.L., Rheenen van, J.W.A.: Canopy structure and leaf nitrogen distribution in a stand of Lysimachia vulgaris L. as influenced by stand density. & Oecologia 77: 145–150, 1988 Japan Meteorological Agency: [Statistical Information of Meteorology.] http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/menu/report.html, 2012. [In Jap.]
Jordan, D.B., Ogren, W.L.: The CO2/O2 specificity of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Dependence on ribulose-bisphosphate concentration, pH and temperature. & Planta 161: 308–313, 1984
Johnson, I.R., Thornley, J.H.M., Frantz, J.M., Bugbee, B.: A model of canopy photosynthesis incorporating protein distribution through the canopy and its acclimation to light, temperature and CO2. & Ann. Bot. 106: 735–749, 2010
Kayama, M., Makoto, K., Nomura, M., Satoh, F., Koike, T.: Dynamics of elements in larch seedlings (Larix kaempferi) regenerated on serpentine soil in northern Japan. & Landscape Ecol. Eng. 5: 125–135, 2009
Kimura, S. D., Saito, M., Hara, H., Xu, Y.H., Okazaki, M.: Comparison of nitrogen dry deposition on cedar and oak leaves in the Tama Hills using foliar rinsing method. & Water Air Soil Pollut. 202: 369–377, 2009
Kitaoka, S., Mori, S., Matsuura, Y., Abaimov, A.P., Sugishita, Y., Satoh, F., Sasa, K. and Koike, T.: Comparison between the photosynthetic characteristics of larch species grown in northern Japan and central Siberia. & Proc. Joint Siberia Permafrost Studies 8: 49–54, 2000
Kitaoka, S., Koike, T.: Invasion of broadleaf tree species into a larch plantation: Seasonal light environment, photosynthesis, and nitrogen allocation. & Physiol. Plant. 121: 604–611, 2004
Kitaoka, S., Watanabe, Y., Koike, T.: The effects of cleared larch canopy and nitrogen supply on gas exchange and leaf traits in deciduous broad-leafed tree seedlings. & Tree Physiol. 29: 1503–1511, 2009
Koike, T.: A trial of revegetation practices with larch species under changing environment. & Landscape Ecol. Eng. 5: 97–98, 2009
Koike, T., Yazaki, K., Funada, R., Maruyama, Y., Mori, S., Sasa, K.: Forest health and vitality in northern Japan. A history of larch plantation. & Res. Notes Fac. Forestry, The Univ. Joensuu 92: 49–60, 2000
Kupper, P., Sellin, A., Tenhunen, J., Schmidt, M., Rahi, M.: Effects of branch position on water relations and gas exchange of European larch trees in an alpine community. & Trees. 20: 265–272, 2006
Kuuluvainen, T., Pukkala, T.: Simulation of within-tree and between-tree shading of direct radiation in a forest canopy: effect of crown shape and sun elevation. & Ecol. Model. 49: 89–100, 1989
Lambers, H., Chapin, F.S., III, Pons, T.L.: Plant Physiological Ecology. & Springer Science + Bussiness Media LIC, New York 2008
Long, S.P., Bernacchi, C.J.: Gas exchange measurements, what can they tell us about the underlying limitations to photosynthesis? Procedures and sources of error. & J. Exp. Bot. 54: 2393–2401, 2003
Magnani, F., Mencuccini, M., Borghetti, M., et al.: The human footprint in the carbon cycle of temperate and boreal forests. & Nature 447: 848–850, 2007
Marek, M.V., Urban, O., Šprtová, M., Pokorný, R., Rosová, Z., Kulhavý, J.: Photosynthetic assimilation of sun versus shade Norway spruce [Picea abies (L.) Karst] needles under the long-term impact of elevated CO2 concentration. & Photosynthetica 40: 259–267, 2002
Matyssek, R., Fromm, H., Roloff, A.: [Biologie der Bäume.] & Eugen Ulmer Kg, Stuttgart 2008. [In Germ.]
Nakaji, T., Takenaga, S., Kuroh, M., Izuta, T.: Photosynthetic response of Pinus densiflora seedlings to high nitrogen load. & Environ. Sci. 9: 269–282, 2002
Niinemets, Ü.: Distribution patterns of foliar carbon and nitrogen as affected by tree dimensions and relative light conditions in the canopy of Picea abies. & Trees 11: 144–154, 1997
Niinemets, Ü., Tenhunen, J.D.: A model separating leaf structural and physiological effects on carbon gain along light gradients for the shade tolerant species Acer saccharum. & Plant Cell Environ. 20: 545–566, 1997
Niinemets, Ü., Tenhunen, J.D., Canta, N.R., Chavis, M.M., Faria, T., Pereira, J.S., Reynolds, J.F.: Interactive effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on the acclimation potential of foliage photosynthetic properties of cork oak, Quercus suber, to elevated atmospheric CO2 concentrations. & Global Change Biol. 5: 455–470, 1999
Posch, S., Warren, C.R., Kruse, J., Guttenberger, H., Adams, M.A.: Nitrogen allocation and the fate of absorbed light in 21-year-old Pinus radiata. & Tree Physiol. 28: 375–384, 2008
Qu, L.Y., Shinano, T., Quoreshi, A.M., Tamai, Y., Osaki, M., Koike, T.: Allocation of 14C-Carbon in two species of larch seedlings infected with ectomycorrhizal fungi. & Tree Physiol. 24: 1369–1376, 2004
Rosati, A., Day, K.R., DeJong, T. M.: Distribution of leaf mass per unit area and leaf nitrogen concentration determine partitioning of leaf nitrogen within tree canopies. & Tree Physiol. 20: 271–276, 2000
Ryu, K., Watanabe, M., Shibata, H., Takagi, K., Nomura, M., Koike, T.: Ecophysiological responses of the larch species in northern Japan to environmental changes as a base of afforestation. & Landscape Ecol. Eng. 5: 99–106, 2009
Schulze, E.-D., Beck, E., Müller-Hohenstein, E.: Plant Ecology. & Springer, Berlin — Heidelberg 2005
Šesták, Z.(ed.): Photosynthesis during Leaf Development. & Academia Praha, Dr. W. Junk Publ., Dordrecht — Boston — Lancaster 1985
Shinano, T., Lei, T.T., Kawamukai, T., Inoue, M.T., Koike, T., Tadano, T.: Dimethylsulfoxide method for the extraction of chlorophylls a and b from the leaves of wheat, field bean, dwarf bamboo, and oak. & Photosynthetica 32: 409–415, 1996
Takashima, T., Hikosaka, K., Hirose, T.: Photosynthesis or persistence: nitrogen allocation in leaves of evergreen and deciduous Quercus species. & Plant Cell Environ. 27: 1047–1054, 2004
Tissue, D.T., Lewis, J.D.: Photosynthetic responses of cottonwood seedlings grown in glacial through future atmospheric [CO2] vary with phosphorus supply. & Tree Physiol. 30: 1361–1372, 2010
Warren, C.R., Adams, M.A.: Evergreen trees do not maximize instantaneous photosynthesis. & Trend Plant Sci. 9: 270–274, 2004
Warren, C.R., Ethier, G.J., Livingston, N.J. et al.: Transfer conductance in second growth Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco) canopies. & Plant Cell Environ. 26: 1215–1227, 2003
Wilson, K.B., Baldocchi, D.D., Hanson, P.J.: Spatial and seasonal variability of photosynthetic parameters and their relationship to leaf nitrogen in a deciduous forest. & Tree Physiol. 20: 565–575, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: We thank Dr. N.P.R. Anten and Prof. Ü. Niinemets for their encouragment in this study. Thanks are also due to Dr. Anthony Garrett of Scitext Cambridge, U.K. for linguistic comments. We acknowledge financial support in part via a Grant-in-Aid from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science through Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (to T. Koike). Research Fellowships for Young Scientists program (to M. Watanabe and Y.S. Kim), and Young Scientists B (to M. Watanabe), and also a project study grant from Development of Mitigation and Adaptation Techniques to Global Warming in the Sectors of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries (to K. Kita)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Q.Z., Watanabe, M., Imori, M. et al. Photosynthesis and nitrogen allocation in needles in the sun and shade crowns of hybrid larch saplings: effect of nitrogen application. Photosynthetica 50, 422–428 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-012-0049-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-012-0049-z