Abstract
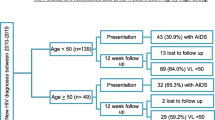
Background The number of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) patients aged 50 years or over is growing year on year, due to both late diagnoses and the chronicity of the illness. This increase is a new phenomenon. Objective To describe the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of the older HIV infected population and determine if there are differences in antiretroviral treatment between younger and older patients. Setting This study was conducted in the outpatient hospital pharmacy service of a University Hospital in Spain. Method A descriptive study involving HIV infected patients aged 50 years or older who received ambulatory antiretroviral therapy between January and December 2011. Variables related to HIV and to antiretroviral therapy were collected. A comparison of antiretroviral drugs used was made with the populations older and younger than 50 years. Main outcome measure Antiretroviral therapy differences between older and younger HIV-patients. Results 130 patients (20 % of the antiretroviral treated patients) were 50 or over and 77 % of these was aged between 50 and 59. At the time of diagnosis, 50 % suffered an advanced state of disease. At the end of the study period, 58 % had CD4 lymphocyte levels of over 500 cells/mm3 and 90 % had an undetectable viral load. The antiretroviral therapy of the older group that was based on protease inhibitors was used in the 51.5 % of the patients compared with 54.4 % in the younger group. The figures for nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors based therapy were 43.8 and 39.8 %, respectively. The older population used treatments that included tenofovir (56.9 vs. 64.8 %, p = 0.105) less frequently and used more treatments that included abacavir (26.9 vs. 19.1 %, p = 0.054) than the under 50′s. Conclusion Half the older HIV-infected patients were diagnosed with an advanced disease and the majority showed a positive response to antiretroviral therapy. There are no statistically significant differences between the frequency of antiretroviral therapy use in older and younger HIV-patients, although older HIV-patients has less often used treatments with tenofovir and more often used treatments with abacavir.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanco JR, Caro AM, Pérez-Cachafeiro S, Gutierrez F, Iribarren JA, Gonzalez- Garcia J, et al. HIV infection and aging. AIDS Rev. 2010;12:218–30.
Montaner JSG, Hogg R, Wood E, Kerr T, Tyndal M, Levy A, et al. The case for expanding access to highly active antiretroviral therapy to curb the growth of HIV epidemic. Lancet. 2006;368:531–6.
Deeks SG, Lewin SR, Havlir DV. The end of AIDS: HIV infection as a chronic disease. Lancet. 2013;2(382):1525–33.
The Antiretroviral Therapy Cohort Collaboration. Causes of death in HIV-1-Infected patients treated with antiretroviral therapy, 1996–2006: Collaborative analysis of 13 HIV cohort studies. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50:1387–96.
The Antiretroviral Therapy Cohort Collaboration. Life expectancy of individual son combination antiretroviral therapy in high-income countries: A collaborative analysis of 14 cohort studies. Lancet. 2008;372:293–9.
Work Group for the HIV and Aging Consensus Project. Summary report from the human immunodeficiency virus and aging consensus project: Treatment strategies for clinicians managing older individuals with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60:974–9.
Hasse B, Ledergerber B, Furrer H, Battegay M, Hirschel B, Cavassini M, et al. Morbidity and aging in HIV-infected persons: The Swiss HIV cohort study. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:1130–9.
Blanco JR, Jarrín I, Vallejo M, Berenguer J, Solera C, Rubio R, et al. Definition of advance age in HIV infection: Looking for an age cut-off. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2012;28:1000–6.
Panel de expertos de GeSIDA y Plan Nacional del Sida. [Consensus Statement by GeSIDA/National AIDS Plan Secretariat on antiretroviral treatment in adults infected by the human immunodeficiency virus (Updated January 2013)]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2013;31:602–613.
Guaraldi G, Orlando G, Zona S, Menozzi M, Carli F, Garlassi E, et al. Premature age-related comorbidities among HIV-infected persons compared with the general population. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:1120–6.
Önen NF, Overton ET, Seyfried W, Stumm ER, Snell M, Mondy K, et al. Aging and HIV infection: A comparison between older HIV-infected persons and the general population. HIV Clin Trials. 2010;11:100–9.
Panel de expertos de Secretaría del Plan Nacional sobre el Sida (SPNS), Sociedad Española de Farmacia Hospitalaria (SEFH), Grupo Estudio del SIDA (GESIDA). [Improving adhesion to antiretroviral treatment]. Farm Hosp. 2008;32:349–357.
Plan Nacional Sobre el Sida, Centro Nacional de Epidemiología, Instituto de Salud Carlos III. Encuesta Hospitalaria de pacientes con VIH/SIDA [internet]. Madrid: Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad; [updated 2011, cited 2012 April]. http://www.msssi.gob.es/ciudadanos/enfLesiones/enfTransmisibles/sida/vigilancia/InformeEncuestaHospitalaria2011.pdf. Spanish.
Marzolini C, Back D, Weber R, Furrer H, Cavassini M, Calmy A, et al. Ageing with HIV: Medication use and risk for potential drug-drug interactions. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:2107–11.
Navarro G, Nogueras MM, Segura F, Casabona J, Miro JM, Murillas J, et al. HIV-1 infected patients older than 50 years. PISCIS cohort study. J Infect. 2008;57:64–71.
Oliva J, Galindo S, Vives N, Arrillaga A, Izquierdo A, Nicolau A, et al. Delayed diagnosis of HIV infection in Spain. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2010;28:583–9.
Díez M, Oliva J, Sánchez J, Vives N, Cevallos C. Izquierdo A [Incidence of new HIV diagnoses in Spain, 2004–2009]. Gac Sanit. 2012;26:107–15.
Lima VD, Harrigan R, Bangsberg DR, Hogg RS, Gross R, Yip B, et al. The combined effect of modern highly active antiretroviral therapy regimens and adherence on mortality over time. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009;50:529–36.
Ortego C, Huedo-Medina TB, Vejo J, Llorca FJ. Adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy in Spain. A meta-analysis. Gac Sanit. 2011;25:282–9.
Ibarra O, Ortega L. Survey of the pharmaceutical care situation of the HIV patient in Spain. Farm Hosp. 2008;32:170–7.
Hinkin CH, Hardy DJ, Mason KI, Castellon SA, Durvasula RS, Lam MN, et al. Medication adherence in HIV- infected adults: Effect of patient age, cognitive status, and substance abuse. AIDS. 2004;18:S19–25.
Acknowledgments
We thank Elena Rivero for the final manuscript.
Funding
There has not been any funding for this study.
Conflicts of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gimeno-Gracia, M., Crusells-Canales, M.J. & Rabanaque-Hernández, M.J. Clinical characteristics and antiretroviral treatment of older HIV-infected patients. Int J Clin Pharm 36, 1190–1195 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-014-0015-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-014-0015-x