ABSTRACT
Purpose
The high prevalence of pure red cell aplasia in Thailand has been associated with the sharp increase in number of recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) copy products, based on a classical generic regulatory pathway, which have entered the market. This study aims to assess the quality of rhEPO copy products being used in Thailand.
Methods
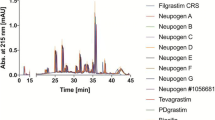
Twelve rhEPO copy products were purchased from pharmacies in Thailand, shipped under controlled cold chain conditions to the Netherlands and characterized using (1) high performance size-exclusion chromatography, (2) asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation, (3) sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in combination with (4) Western blotting and additionally tested for (5) host cell protein impurities as well as (6) endotoxin contamination.
Results
Some of the tested rhEPO copy products showed high aggregate levels and contained a substantial amount of protein fragments. Also, one of rhEPO copy products had a high endotoxin level, exceeding the FDA limit.
Conclusions
Our observations show that some of the tested copy products on the Thai market differ significantly from the originator rhEPO product, Epogen®. This comparison study supports a link between the quality attributes of copy rhEPO products and their immunogenicity.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AF4:
-
asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation
- CHO:
-
Chinese hamster ovary
- EPO-BRP:
-
erythropoietin—biological reference product
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- HMW:
-
high molecular weight
- HP-SEC:
-
high performance size exclusion chromatography
- HSA:
-
human serum albumin
- LAL:
-
limulus amebocyte lysate
- LMW:
-
low molecular weight
- PRCA:
-
pure red cell aplasia
- R-AUC:
-
relative-area under the curve
- RHEPO:
-
recombinant human erythropoietin
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
REFERENCES
Casadevall N, Nataf J, Viron B, Kolta A, Kiladjian J-J, Martin-Dupont P, et al. Pure red-cell aplasia and antierythropoietin antibodies in patients treated with recombinant erythropoietin. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(7):469–75.
Schellekens H, Jiskoot W. Erythropoietin-Associated PRCA: Still an unsolved mystery. J Immunotoxicol. 2006;3(3):123–30.
Schellekens H, Jiskoot W. Eprex-associated pure red cell aplasia and leachates. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24(6):613–4.
Hermeling S, Schellekens H, Crommelin DJA, Jiskoot W. Micelle-associated protein in epoetin formulations: A risk factor for immunogenicity? Pharm Res. 2003;20(12):1903–7.
Seidl A, Hainzl O, Richter M, Fischer R, Böhm S, Deutel B, et al. Tungsten-induced denaturation and aggregation of epoetin alfa during primary packaging as a cause of immunogenicity. Pharm Res. 2012;29(6):1454–67.
Schellekens H. Biosimilar epoetins: how similar are they? EAHP [Internet]. 2004 [cited 2012 Jul 30]; Available from: http://en.scientificcommons.org/59573968.
Brinks V, Hawe A, Basmeleh AHH, Joachin-Rodriguez L, Haselberg R, Somsen GW, et al. Quality of original and biosimilar epoetin products. Pharm Res. 2011;28(2):386–93.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Biosimilars [Internet]. [cited 2013 Jun 12]. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsareDevelopedandApproved/ApprovalApplications/TherapeuticBiologicApplications/Biosimilars/default.htm.
EMA. Guideline on non-clinical and clinical development of similar biological medicinal products containing recombinant erythropoietins (Revision) [Internet]. 2010. Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2010/04/WC500089474.pdf.
Praditpornsilpa K, Tiranathanagul K, Kupatawintu P, Jootar S, Intragumtornchai T, Tungsanga K, et al. Biosimilar recombinant human erythropoietin induces the production of neutralizing antibodies. Kidney Int. 2011;80(1):88–92.
Wish JB. Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and pure red-cell aplasia: you can’t fool Mother Nature. Kidney Int. 2011;80(1):11–3.
Praditpornsilpa K, Kupatawintu P, Mongkonsritagoon W, Supasyndh O, Jootar S, Intarakumthornchai T, et al. The association of anti-r-HuEpo-associated pure red cell aplasia with HLA-DRB1*09-DQB1*0309. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24(5):1545–9.
Park SS, Park J, Ko J, Chen L, Meriage D, Crouse-Zeineddini J, et al. Biochemical assessment of erythropoietin products from Asia versus US Epoetin alfa manufactured by Amgen. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98(5):1688–99.
Jelkmann W. Molecular biology of erythropoietin. Intern Med. 2004;43(8):649–59.
Romanowski RR, Sytkowski AJ. The molecular structure of human erythropoietin. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1994;8(5):885–94.
Miyake T, Kung CK, Goldwasser E. Purification of human erythropoietin. J Biol Chem. 1977;252(15):5558–64.
Egrie JC, Strickland TW, Lane J, Aoki K, Cohen AM, Smalling R, et al. Characterization and biological effects of recombinant human erythropoietin. Immunobiology. 1986;172(3–5):213–24.
Browne JK, Cohen AM, Egrie JC, Lai PH, Lin FK, Strickland T, et al. Erythropoietin: gene cloning, protein structure, and biological properties. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):693–702.
Sytkowski AJ, Feldman L, Zurbuch DJ. Biological activity and structural stability of N-deglycosylated recombinant human erythropoietin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;176(2):698–704.
Spentzos D, Sytkowski AJ. Clinical applications of recombinant human erythropoietin. In: Dembowsky K, Stadler P, editors. Novel Therapeutic Proteins [Internet]. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH; 2007 [cited 2013 Jul 5]. p. 29–57. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9783527613021.ch02/summary.
Reichel C, Thevis M. Gel electrophoretic methods for the analysis of biosimilar pharmaceuticals using the example of recombinant erythropoietin. Bioanalysis. 2013;5(5):587–602.
Schellekens H. Bioequivalence and the immunogenicity of biopharmaceuticals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1(6):457–62.
Carpenter JF, Randolph TW, Jiskoot W, Crommelin DJA, Middaugh CR, Winter G. Potential inaccurate quantitation and sizing of protein aggregates by size exclusion chromatography: essential need to use orthogonal methods to assure the quality of therapeutic protein products. J Pharm Sci. 2010;99(5):2200–8.
Hawe A, Friess W, Sutter M, Jiskoot W. Online fluorescent dye detection method for the characterization of immunoglobulin G aggregation by size exclusion chromatography and asymmetrical flow field flow fractionation. Anal Biochem. 2008;378(2):115–22.
Hawe A, Romeijn S, Filipe V, Jiskoot W. Asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation method for the analysis of submicron protein aggregates. J Pharm Sci. 2012;101(11):4129–39.
Chirino AJ, Mire-Sluis A. Characterizing biological products and assessing comparability following manufacturing changes. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22(11):1383–91.
Schmidt Cleber A RAS. Avaliação da atividade e caracterização de eritropoietina humana recombinante em produtos farmacêuticos. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab. 2003.
Boven K, Knight J, Bader F, Rossert J, Eckardt K-U, Casadevall N. Epoetin-associated pure red cell aplasia in patients with chronic kidney disease: Solving the mystery. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20(suppl_3):iii33–40.
Hermeling S, Schellekens H, Maas C, Gebbink MFBG, Crommelin DJA, Jiskoot W. Antibody response to aggregated human interferon alpha2b in wild-type and transgenic immune tolerant mice depends on type and level of aggregation. J Pharm Sci. 2006;95(5):1084–96.
Schellekens H. Relationship between biopharmaceutical immunogenicity of epoetin alfa and pure red cell aplasia. Curr Med Res Opin. 2003;19(5):433–4.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS AND DISCLOSURES
This work was supported by an educational grant from HEXAL AG, Holzkirchen, Germany. The authors also thank Linda McPhee for critically reviewing the manuscript. L.A.H., V.B., W.J., S.R., K.P., A.A. and H.S. declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halim, L.A., Brinks, V., Jiskoot, W. et al. How Bio-questionable are the Different Recombinant Human Erythropoietin Copy Products in Thailand?. Pharm Res 31, 1210–1218 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-1243-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-1243-9