Abstract
Purpose
Pluronic F-127 (PF127) has previously shown to prolong the sustained release of various proteinous drugs and their serum half-lives. Subsequently, we have extended this approach to look at in vitro release, in vivo efficacy and pharmacokinetics of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra).
Methods
Various concentrations of PF127 gels were prepared using cold method. In vitro drug release kinetic studies were performed using membraneless dissolution method. Stability of IL-1Ra was assessed by SDS-PAGE. In vivo studies and in vivo bioactivity of IL-1Ra were also performed on wistar rats.
Results
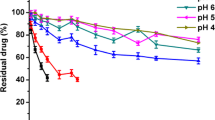
IL-1Ra loaded PF127 gels showed in vitro sustained release of IL-1Ra, depending on the concentration of gel used. SDS-PAGE confirmed the stability of protein during its in vitro release. PF127 gel also exhibited prolonged release of IL-1Ra in rats as compared to that of IL-1Ra aq. solution. In vivo bioactivity of IL-1Ra loaded in gel was confirmed by its ability to inhibit IL-1β-stimulated induction of IL-6.
Conclusions
When compared directly, IL-1Ra loaded PF127 gel exhibited prolonged in vitro and in vivo release, greater efficacy to induce hypoglycemia and inhibited IL-1β-stimulated production of IL-6 as compared to IL-1Ra aq. solution. We believe that this methodology for sustained delivery of IL-1Ra probably be suitable for the convenience of patients to achieve desired therapeutic potentials without exceeding dose limits and frequent administration.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steinkasserer A, Spurr NK, Cox S, Jeggo P, Sim RB. The human IL-1 receptor antagonist gene (IL1RN) maps to chromosome 2q14-q21, in the region of the IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta loci. Genomics. 1992;13:654–7.
Arend WP, Malyak M, Guthridge CJ, Gabay C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: role in biology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:27–55.
Donath MY, Shoelson SE. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nature Rev Immunol. 2011;11:98–107.
Kolb H, Mandrup-Poulsen T. An immune origin of type 2 diabetes? Diabetologia. 2005;48:1038–50.
Dinarello CA. Blocking interleukin -1β in acute and chronic autoinflammatory diseases. J Intern Med. 2011;269:16–28.
Dayer JM, Feige U, Edwards CK, Burger D. Anti-interleukin-1 therapy in rheumatic diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001;13:170–6.
Bresnihan B. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999;58:196–8.
Campion GV, Lebsack ME, Lookabaugh J, Gordon G, Catalano M. Dose-range and dose-frequency study of recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The IL-1Ra Arthritis Study Group. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39:1092–101.
Larsen CM, Faulenbach M, Vaag A, Volund A, Ehses JE, Seifert B, et al. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1417–526.
Mandrup-Poulsen T, Pickersgill L, Donath MY. Blockade of interleukin 1 in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010;6:158–66.
Cawthorne C, Prenant C, Smigova A, Julyan P, Maroy R, Herholz K, et al. Biodistribution, pharmacokinetics and metabolism of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) using [18F]-IL1RA and PET imaging in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;162:659–72.
Holt LJ, Basran A, Jones K, Chorlton J, Jespers SL, Brewis ND, et al. Anti-serum albumin domain antibodies for extending the half-lives of short lived drugs. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2008;21:283–8.
Lavi G, Dinarello CA, Apte RN, Cohen S. Sustained release of IL-1Ra from biodegradable microspheres prolongs its IL-1-neutralizing effects. Israel J Chem. 2005;45:457–64.
Pichika R, Betre H, Setton LA, An HS, Masuda K. Bioactivity of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) and a related fusion protein in inhibiting IL-1–mediated effects in human intervertebral disc cells. Trans Orthop Res Soc. 2006;52.
Lavi G, Voronov E, Dinarello CA, Apte RN, Cohen S. Sustained delivery of IL-1Ra from biodegradable microspheres reduces the number of murine B16 melanoma lung metastases. J Control Release. 2007;123:123–30.
Shamji MF, Betre H, Kraus VB, Chen J, Chilkoti A, Pichika R, et al. Development and characterization of a fusion protein between thermally responsive elastin-like polypeptide and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: sustained release of a local anti-inflammatory therapeutic. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:3650–61.
Kim DH, Smith JT, Chilkoti A, Reichert WM. The effect of covalently immobilized rhIL-1ra-ELP fusion protein on the inflammatory profile of LPS-stimulated human monocytes. Biomaterials. 2007;28:3369–77.
Dai SF, Shen Q, Chen S. Inhomogeneous expression of fusion protein HSA/IL-1Ra pichia pastoris. J Zhejiang Univ (Medical Sci). 2008;37:134–8.
Jun JB, Kim JK, Kim TH, Na Y, Choi CH, Kim YH. Inhibition of the IL-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases by controlled release of IL-1 receptor antagonist using injectable and thermo-reversible gels in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. J Rheum Dis. 2011;18:85–93.
Akash MSH, Shen Q, Rehman K, Chen S. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: a new therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pharm Sci. 2012;10:1647–58.
Barichello JM, Morishita M, Takayama K, Nagai T. Absorption of insulin from pluronic F-127 gels following subcutaneous administration in rats. Int J Pharm. 1999;184:189–98.
Katakam M, Bell LN, Banga AK. Effect of surfactants on the physical stability of rhGH. J Pharm Sci. 1995;84:13–716.
Stratton LP, Dong A, Manning MC, Carpenter JF. Drug delivery matrix containing native protein precipitates suspended in a polomaxamer gel. J Pharm Sci. 1997;86:1006–10.
Liu Y, Lu WL, Wang JC, Zhang X, Zhang H, Wang XQ, et al. Controlled delivery of recombinant hirudin based on thermo-sensitive pluronic® F127 hydrogel for subcutaneous administration: In vitro and in vivo characterization. J Control Release. 2007;117:387–95.
Johnston TP, Punjabi MA, Froelich CJ. Sustained delivery of interleukin-2 from a poloxamer 407 gel matrix following intraperitoneal injection in mice. Pharm Res. 1992;9:425–34.
Soga O, Van Nostrum CF, Fens M, Fijcken CJF, Schiffelers RM, Storm G, et al. Thermosensitive and biodegradable polymeric micelles for paclitaxel delivery. J Control Release. 2005;103:341–53.
Varshosaz J, Tabbakhian M, Salmani Z. Designing of a thermosensitive Chitosan/poloxamer in situ gel for ocular delivery of ciprofloxacin. Open Drug Delivery J. 2008;2:61–70.
Hyun H, Kim YH, Song IB, Lee JW, Kim MS, Khang G, et al. In vitro and in vivo release of albumin using a biodegradable MPEG-PCL diblock copolymer as an in situ gel-forming carrier. Biomarcomolecules. 2007;78:1093–100.
Zhang L, Parsons DL, Navarre C, Kompella UB. Development and in-vitro evaluation of sustained release poloxamer 407 (P407) gel formulations of ceftiofur. J Control Release. 2002;85:73–81.
Zhang Y, Huo M, Zhou J, Zou A, Li W, Yao C, et al. DDSolver: an add-in program for modeling and comparison of drug dissolution profiles. AAPS J. 2010;12:263–71.
Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Automat Control. 1974;19:716–23.
Khan SA, Ahmad M, Murtaza G, Shehnaz G, Aamir MN, Rasool F. Design of nimesulide-chitosan microparticles by pH change coacervation. Lat Am J Pharmacy. 2011;30:1260–6.
Peppas NA. Analysis of Fickian and non-Fickian drug release from polymers. Pharm Acta Helv. 1985;60:110–1.
Wagner JG, Nelson E. Percent absorbed time plots derived from blood level and/or urinary excretion data. J Pharm Sci. 1963;52:610–1.
Wannachaiyasit S, Phaechamud T. Development of chlorhexidine thermosensitive gels as a mouth antiseptic. J Metals Mater Miner. 2010;20:165–8.
Nie S, Hsiao WW, Pan W, Yang Z. Thermosensitive pluronic® F127-based hydrogel containing liposomes for the controlled delivery of paclitaxel: in vitro drug release, cell cytotoxicity, and uptake studies. Int J Nanomed. 2011;6:151–61.
Bonacucina G, Spina M, Misici-Falzi M, Cespi M, Pucciarelli S, Angeletti M, et al. Effect of hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin on the self-assembling and thermogelation properties of poloxamer 407. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2007;32:115–22.
Costa FO, Sousa JJ, Pais AA, Formosinho SJ. Comparison of dissolution profiles of Ibuprofen pellets. J Control Release. 2003;89:199–212.
Veyries ML, Couarraze G, Geiger S. Controlled release of vancomycin from poloxamer 407 gels. Int J Pharm. 1999;192:183–93.
Pandit NK, Wang D. Salt effects on the diffusion and release rate of propranolol from poloxamer 407 gels. Int J Pharm. 1998;167:183–9.
Reza MS, Quadir MA, Haider SS. Development of theophylline sustained release dosage form based on kollidon SR. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2002;15:63–70.
Kuksal A, Tiwary AK, Jain NK, Jain S. Formulation and in vitro, in vivo evaluation of extended-release matrix tablet of zidovudine: influence of combination of hydrophilic and hydrophobic matrix formers. AAPS PrarmSciTech. 2006;7:E1–9.
Akash MSH, Rehman K, Rasool F, Sethi A, Abrar MA, Irshad A, et al. Alternate therapy of Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with Nigella (Ranunculaceae). J Med Plants Res. 2011;5:6885–9.
Homo-Delarche F, Calderari S, Irminger JC, Gangnerau MN, Coulaud J, Rickenbach K, et al. Islet inflammation and fibrosis in a spontaneous model of type 2 diabetes, the GK rat. Diabetes. 2006;55:1625–33.
Dinarello CA. The role of the interleukin-1-receptor antagonist in blocking inflammation mediated by interleukin-1. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:732–4.
Banerjee PS, Hosny EA, Robinson JR. Parenteral delivery of peptides and protein drugs. In: Lee VHL, editor. Peptide and protein drug delivery. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1991. p. 487–543.
Lu G, Jun HW. Diffusion studies of methotrexate in Carbopol and Poloxamer gels. Int J Pharm. 1998;160:1–9.
Granowitz EV, Porat R, Mier JW, Pribble JP, Stiles DM, Bloedow DC, et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety and immunomodulatory effects of human recombinant interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in healthy humans. Cytokine. 1992;4:353–60.
McIntyre KW, Stepan GJ, Kolinsky KD, Benjamin WR, Plocinski JM, Kaffka KL, et al. Inhibition of interleukin 1 (IL-1) binding and bioactivity in vitro and modulation of acute inflammation in vivo by IL-1 receptor antagonist and anti-IL-1 receptor monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1991;173:931–9.
Ehses JA, Ellingsgaard H, Boni-Schnetzler M, Donath MY. Pancreatic islet inflammation in type 2 diabetes: from α and β cell compensation to dysfunction. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2009;115:240–7.
Acknowledgments and Disclosures
In vivo results presented here are not efficacy data. They can only be considered as animal-based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic results.
This work was financially supported by the grant (No. 2010C13006) from the Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province, China.
We acknowledge the China Scholarship Council to award scholarship for PhD to Muhammad Sajid Hamid Akash and Kanwal Rehman. IL-1Ra was generously provided by Hisun Pharmaceuticals but the company was not involved in the design, conduct and/or analysis of experiments. One of the authors would like to admire his wife Kanwal Rehman for her motivation and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akash, M.S.H., Rehman, K., Li, N. et al. Sustained Delivery of IL-1Ra from Pluronic F127-Based Thermosensitive Gel Prolongs its Therapeutic Potentials. Pharm Res 29, 3475–3485 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0843-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-012-0843-0