ABSTRACT
Purpose
To develop Fe3O4-PEI-RITC magnetic nanoparticles with multimodal MRI-fluorescence imaging and transfection capability, for use in neural cell replacement therapies.
Methods
The Fe3O4-PEI-RITC MNPs were synthesised through a multi-step chemical grafting procedure: (i) Silanisation of MNPs with 3-iodopropyltrimethoxysilane; (ii) PEI coupling with iodopropyl groups on the MNP surface; and (iii) RITC binding onto the PEI coating. The cell labelling and transfection capabilities of these particles were evaluated in astrocytes derived from primary cultures.
Results
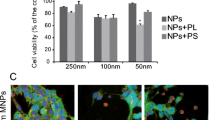
Fe3O4-PEI-RITC MNPs did not exert acute toxic effects in astrocytes (at ≤6 days). Cells showed rapid and extensive particle uptake with up to 100% cellular labelling observed by 24 h. MRI and microscopy studies demonstrate that the particles have potential for use in bimodal MR-fluorescence imaging. Additionally, the particles were capable of delivering plasmids encoding reporter protein (approximately 4 kb) to astrocytes, albeit with low efficiencies.
Conclusions
Multifunctional Fe3O4-PEI-RITC MNPs were successfully prepared using a multi-step synthetic pathway, with the PEI and RITC chemically bound onto the MNP surface. Their combined MR-fluorescence imaging capabilities with additional potential for transfection applications can provide a powerful tool, after further development, for non-invasive cell tracking and gene transfer to neural transplant populations.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CHN:
-
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DLS:
-
dynamic Light Scattering
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- FTIR spectroscopy:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- GFAP:
-
glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- MCT:
-
multiple comparison test
- MNP:
-
magnetic nanoparticle
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PEI:
-
polyethyleneimine
- PVA:
-
polyvinyl alcohol
- RITC:
-
rhodamine B isothiocyanate
- RT:
-
room temperature
- TEM:
-
transmission electron microscopy
- TGA:
-
thermogravimetric analysis
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
REFERENCES
Gögel S, Gubernator M, Minger SL. Progress and prospects: stem cells and neurological diseases. Gene Ther. 2011;18(1):1–6.
Chari DM. Remyelination in multiple sclerosis. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2007;79:589–620.
Herranz F, Almarza E, Rodríguez I, Salinas B, Rosell Y, Desco M, Bulte JW, Ruiz-Cabello J. The application of nanoparticles in gene therapy and magnetic resonance imaging. Microsc Res Tech. 2011;74(7):577–91.
Gleave JA, Valliant JF, Doering LC. 99mTc-based imaging of transplanted neural stem cells and progenitor cells. J Nucl Med Tech. 2011;39(2):114–20.
Chari DM, Blakemore WF. New insights into remyelination failure in multiple sclerosis: implications for glial cell transplantation. Mult Scler. 2002;8(4):271–7.
Ruff CA, Wilcox JT, Fehlings MG. Cell-based transplantation strategies to promote plasticity following spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2011. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.02.010.
Pickard MR, Barraud P, Chari DM. The transfection of multipotent neural precursor/stem cell transplant populations with magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2010;32(9):2274–84.
Jenkins SI, Pickard MR, Granger N, Chari DM. Magnetic nanoparticle-mediated gene transfer to oligodendrocyte precursor cell transplant populations is enhanced by magnetofection strategies. ACS Nano. 2011;5(8):6527–38.
McBain SC, Yiu HHP, Dobson J. Magnetic nanoparticles for gene and drug delivery. Int J Nanomed. 2008;3(2):169–80.
Hyeon T. Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem Commun. 2003;8:927–34.
Berry CC, Curtis ASG. Functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2003;36(13):R198–206.
Yiu HHP, McBain SC, Lethbridge ZAD, Lees MR, Dobson J. Preparation and characterization of polyethylenimine-coated Fe3O4-MCM-48 nanocomposite particles as a novel agent for magnet-assisted transfection. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;92A(1):386–92.
Veiseh O, Sun C, Fang C, Bhattarai N, Gunn J, Kievit F, Du K, Pullar B, Lee D, Ellenbogen RG, Olson J, Zhang MQ. Specific targeting of brain tumors with an optical/magnetic resonance imaging nanoprobe across the blood-brain barrier. Cancer Res. 2009;69(15):6200–7.
Olariu CI, Yiu HHP, Bouffier L, Nedjadi T, Costello E, Williams SR, Halloran CM, Rosseinsky MJ. Multifunctional Fe3O4 nanoparticles for targeted bi-modal imaging of pancreatic cancer. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(34):12650–9.
Lu AH, Salabas EL, Schuth F. Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Intl Ed. 2007;46(8):1222–44.
Berman SMC, Walczak P, Bulte JWM. Tracking stem cells using magnetic nanoparticles. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2011;3(4):343–55.
Pickard MR, Jenkins SI, Koller CJ, Furness DN, Chari DM. Magnetic nanoparticle labeling of astrocytes derived for neural transplantation. Tissue Eng C Meth. 2011;17(1):89–99.
Pickard M, Chari D. Enhancement of magnetic nanoparticle-mediated gene transfer to astrocytes by ‘magnetofection’: effects of static and oscillating fields. Nanomedicine. 2010;5(2):217–32.
Nishida K, Tanaka N, Nakanishi K, Kamei N, Hamasaki T, Yanada S, Mochizuki Y, Ochi M. Magnetic targeting of bone marrow stromal cells into spinal cord: through cerebrospinal fluid. Neuroreport. 2006;17(12):1269–72.
Veiseh O, Kievit FM, Fang C, Mu N, Jana S, Leung MC, Mok H, Ellenbogen RG, Park JO, Zhang MQ. Chlorotoxin bound magnetic nanovector tailored for cancer cell targeting, imaging, and siRNA delivery. Biomaterials. 2010;31(31):8032–42.
McBain SC, Yiu HHP, El Haj A, Dobson J. Polyethyleneimine functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles as agents for DNA delivery and transfection. J Mater Chem. 2007;17(24):2561–5.
Hennig J, Nauerth A, Friedburg H. RARE imaging: a fast imaging method for clinical MR. Magn Reson Med. 1986;3(6):823–33.
Hall JB, Dobrovolskaia MA, Patri AK, McNeil SE. Characterization of nanoparticles for therapeutics. Nanomedicine. 2007;2(6):789–803.
Steitz B, Hofmann H, Kamau SW, Hassa PO, Hottiger MO, von Rechenberg B, Hofmann-Amtenbrink M, Petri-Fink A. Characterization of PEI-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for transfection: size distribution, colloidal properties and DNA interaction. J Magn Magn Mater. 2007;311(1):300–5.
Chorny M, Polyak B, Alferiev IS, Walsh K, Friedman G, Levy RJ. Magnetically driven plasmid DNA delivery with biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. FASEB J. 2007;21(10):2510–9.
Petri-Finka A, Steitza B, Finka A, Salaklanga J, Hofmann H. Effect of cell media on polymer coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): colloidal stability, cytotoxicity, and cellular uptake studies. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;68(1):129–37.
Arsianti M, Lim M, Marquis CP, Amal R. Assembly of polyethylenimine-based magnetic iron oxide vectors: insights into gene delivery. Langmuir. 2010;26(10):7314–26.
Ang D, Nguyen QV, Kayal S, Preiser PR, Rawat RS, Ramanujan RV. Insights into the mechanism of magnetic particle assisted gene delivery. Acta Biomaterialia. 2011;7(3):1319–26.
Godbey WT, Wu KK, Mikos AG. Size matters: molecular weight affects the efficiency of poly(ethylenimine) as a gene delivery vehicle. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;45(3):268–75.
Kobbert C, Apps R, Bechmann I, Lanciego JL, Mey J, Thanos S. Current concepts in neuroanatomical tracing. Prog Neurobiol. 2000;62(4):327–51.
Ma O, Lavertu M, Sun J, Nguyen S, Buschmann MD, Winnik FM, Hoemann CD. Precise derivatization of structurally distinct chitosans with rhodamine B isothiocyanate. Carbohydr Polym. 2008;72(4):616–24.
Can K, Ozmen M, Ersoz M. Immobilization of albumin on aminosilane modified superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles and its characterization. Colloid Surf B Biointerfaces. 2009;71(1):154–9.
Murray P, Palona I, Yiu HHP, Olariu CI, Rosseinsky MJ. Unpublished results.
Lerones C, Mariscal A, Carnero M, Garcia-Rodriguez A, Fernandez-Crehuet J. Assessing the residual antibacterial activity of clinical materials disinfected with glutaraldehyde, o-phthalaldehyde, hydrogen peroxide or 2-bromo-2-nitro-1,3-propanediol by means of a bacterial toxicity assay. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004;10(11):984–9.
Pattnaik G, Rama Raju KS, Heeralal B, Ali S. Nanovehicles: an efficient carrier for active molecules for entry into the cell. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2010;4(3):3.
Yiu HHP, Bouffier L, Boldrin P, Long J, Claridge JB, Rosseinsky MJ. Direct grafting of amine groups onto iron(II,III) oxide nanoparticles to generate a positively charged three-dimensional coating–I: DNA binding through electrostatic interaction. submitted.
Scherer F, Anton M, Schillinger U, Henkel J, Bergemann C, Kruger A, Gansbacher B, Plank C. Magnetofection: enhancing and targeting gene delivery by magnetic force in vitro and in vivo. Gene Ther. 2002;9(2):102–9.
Sapet C, Laurent N, Le Gourrierec L, Augier S, Zelphati O. In vitro and in vivo magnetofection (TM): a move towards gene therapy. Ann Biol Clin. 2010;68(2):133–42.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS & DISCLOSURES
DMC is supported by a New Investigator Award from the British Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. The authors acknowledge EPSRC (EP/C511794) for financial support. We thank Dr. James Long (IOTA Nanosolutions) for the zeta potential measurements and Dr. Laurent Bouffier (now at Université Bordeaux) for his assistance with FTIR spectroscopy and Ms Karen Davies who performed the MRI measurements at the University of Manchester.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yiu, H.H.P., Pickard, M.R., Olariu, C.I. et al. Fe3O4-PEI-RITC Magnetic Nanoparticles with Imaging and Gene Transfer Capability: Development of a Tool for Neural Cell Transplantation Therapies. Pharm Res 29, 1328–1343 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-011-0632-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-011-0632-1