Abstract
Purpose
Mechanism for double-peak occurrence in plasma concentration profile after oral administration of drugs is controversial, although irregular gastric emptying would be an important factor. The objective of this study was to assess the effect of gastric emptying and a weight function, i.e. pharmacokinetics after reaching the systemic circulation, on the double-peak appearance in plasma concentration profiles.
Materials and Methods
Alprazolam, which generates irregular gastric emptying, was orally co-administered with theophylline to rats, and the plasma concentration profiles or absorption rates were compared between the two drugs. Both drugs are highly absorbable, but alprazolam is rapidly eliminated from plasma, while the elimination of theophylline is very slow.
Results
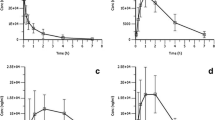
Oral administration of alprazolam generated the irregular gastric emptying profiles, resulting in multiple peaks in the absorption rate profiles of both drugs. The double peaks in the absorption rate profiles led to the double peaks in plasma concentration profiles for alprazolam, but not necessarily for theophylline. Simulation study clearly indicated that the slower elimination from plasma made the first peak less recognizable.
Conclusions
The irregular gastric emptying could be a main reason for the double peaks in plasma concentration profiles. However, the frequency of double-peak occurrence depends on the weight function, particularly the elimination rate, of each drug.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Higaki, S. Yamashita, and G. L. Amidon. Time-dependent oral absorption models. J. Pharmacokin. Phrmacodyn. 28:109–128 (2001).
T. Kimura, and K. Higaki. Gastrointestinal transit and drug absorption. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25:149–164 (2002).
J. A. Clements, R. C. Heading, W. S. Nimmo, and L. F. Prescott. Kinetics of acetaminophen absorption and gastric emptying in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 24:420–431 (1978).
W. D. Mason, N. Winer, G. Kochak, I. Cohen, and R. Bell. Kinetics and absolute bioavailability of atenolol. Clin. Pharmacol. 25:408–415 (1979).
W. N. Charman, M. C. Rogge, A. W. Boddy, W. H. Barr, and B. M. Berger. Absorption of danazol after administration to different sites of the gastrointestinal tract and the relationship to single- and double-peak phenomena in the plasma profiles. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 33:1207–1213 (1993).
J. B. Dressman, R. R. Berardi, G. H. Elta, T. M. Gray, P. A. Montgomery, H. S. Lau, K. L. Pelekoudas, G. J. Szpunar, and J. G. Wabner. Absorption of flurbiprofen in the fed and fasted states. Pharm. Res. 9:901–907 (1992).
J-P. Reymond, J-L. Steimer, and W. Niederberger. On the dose dependency of cyclosporin A absorption and disposition in healthy volunteers. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 16:331–353 (1988).
E. Lipka, I-D. Lee, P. Langguth, H. Spahn-Langguth, E. Mutschler, and G. L. Amidon. Celiprolol double-peak occurrence and gastric motility: nonlinear mixed effects modeling of bioavailability data obtained in dogs. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 23:267–286 (1995).
G. A. Digenis, E. P. Sandefer, R. C. Page, and W. J. Doll. Gamma scintigraphy: an evolving technology in pharmaceutical formulation development—Part 2. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 1:160–165 (1998).
H. Lennernäs, and C-G. Regårdh. Evidence for an interaction between the β-blocker pafenolol and bile salts in the intestinal lumen of the rat leading to dose-dependent oral absorption and double peaks in the plasma concentration–time profile. Pharm. Res. 10:879–88 (1993).
T. Yamaguchi, T. Oida, C. Ikeda, and Y. Sekine. Intestinal absorption of a β-adrenergic blocking agent nadolol. . Chem. Pharm. Bull. 34:4259–4264 (1986).
J-E. Peris-Ribera, F. Torres-Molina, M. C. Garcia-Carbonell, J. C. Aristorena, and J. M. Pla-Delfina. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of diclofenac in the rat. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:615–633 (1986).
R. F. Bergstrom, D. R. Kay, T. M. Harkcom, and J. G. Wagner. Penicillamine kinetics in normal subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 30:404–413 (1981).
Y. Plusquellec, G. Campistron, S. Staveris, J. Barre, L. Jung, J. P. Tillement, and G. Houin. A double-peak phenomenon in the pharmacokinetics of veralipride after oral administration: a double-site model for drug absorption. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 15:225–239 (1987).
D. Brockmeier, H. G. Grigoleit, and H. Leonhardt. The absorption of piretanide from the gastrointestinal tract is site-dependent. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 30:79–82 (1986).
H. Lennern+//0Aw//9AKQ-s, and C. G. Reg+//0Aw//9AKU-rdh. Regional gastrointestinal absorption of the beta-blocker pafenolol in the rat and intestinal transit rate determined by movement of 14C-PEG 4000. Pharm. Res. 10:130–135 (1993).
R. Miller. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of ranitidine in humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 73:1376–1379 (1984).
R. L. Oberle, and G. L. Amidon. The influence of variable gastric emptying and intestinal transit rates on the plasma level curve of cimetidine; an explanation for the double peak phenomenon. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 15:529–544 (1987).
P. Veng-Pedersen, and R. Miller. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of cimetidine in humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 69:394–398 (1980).
N. Piyapolrungroj, Y. S. Zhou, C. Li, G. Liu, E. Zimmermann, and D. Fleisher. Cimetidine absorption and elimination in rat small intestine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 28:65–72 (2000).
G. Mullersman, V. P. Gotz, W. L. Russell, and H. Derendorf. Lack of clinically significant in vitro and in vivo interactions between ranitidine and sucralfate. J. Pharm. Sci. 75:995–998 (1986).
A. B. Suttle, and K. L. R. Brouwer. Gastrointestinal transit and distribution of ranitidine in the rat. Pharm. Res. 12:1316–1322 (1995).
K. S. Reynolds, M. H. Song, W. D. Heizer, C. B. Burns, D. A. Sica, and K. L. R. Brouwer. Effect of pancreatico-biliary secretions and GI tract time on the absorption and pharmacokinetic profile of ranitidine in humans. Pharm. Res. 15:1281–1285 (1998).
V. Mummaneni, G. L. Amidon, and J. B. Dressman. Gastric pH influences the appearance of double peaks in the plasma concentration–time profiles of cimetidine after oral administration in dogs. Pharm. Res. 12:780–786 (1995).
G. L. Amidon, H. Lennernäs, V. P. Shar, and J. R. Crison. A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 12:413–420 (1995).
R. L. Oberle, T-S. Chen, C. Lloyd, J. L. Barnett, C. Owyang, J. Meyer, and G. L. Amidon. The influence of the interdigestive migrating myoelectric complex on the gastric emptying of liquids. Gastroenterol. 99:1275–1282 (1990).
N. Takamatsu, L. S. Welage, Y. Hayashi, R. Yamamoto, J. L. Barnett, V. P. Shah, L. J. Lesko, C. Ramachandran, and G. L. Amidon. Variability in cimetidine absorption and plasma double peaks following oral administration in the fasted state in humans: correlation with antral gastric motility. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 53:37–47 (2002).
S. K. Sarna. Cyclic motor activity; Migrating motor complex. Gastroenterol. 89:894–913 (1985).
H. C. Kutchai. The gastrointestinal system. In R. M. Berne, and M. N. Levy (eds.), Physiology, 4th ed, Mosby, St. Louis, 1998, pp. 589–674.
G. S. Hebbard, W. M. Sun, F. Bochner, and M. Horowitz. Pharmacokinetic considerations in gastrointestinal motor disorders. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 28:41–66 (1995).
L. A. Houghton, Y. F. Mangnall, and N. W. Read. Effect of incorporating fat into a liquid test meal on the relation between intragastric distribution and gastric emptying in human volunteers. Gut 31:1226–1229 (1990).
C. Feinle, D. Grundy, B. Otto, and M. Fried. Relationship between increasing duodenal lipid doses, gastric perception, and plasma hormone levels in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 278:R1217–1223 (2000).
J. T. McLaughlin, L. E. A. Troncon, J. Barlow, L. J. Heggie, and D. G. Thompson. Evidence for a lipid specific effect in nutrient induced human proximal gastric relaxation. Gut 43:248–251 (1998).
S. Haruta, N. Iwasaki, K. Ogawara, K. Higaki, and T. Kimura. Absorption behavior of orally administered drugs in rats treated with propantheline. J. Pharm. Sci. 87:1081–1085 (1998).
M. J. Fargeas, J. Fioramonti, and L. Bueno. Time-related effects of benzodiazepines on intestinal motility in conscious dogs Journal. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 36:130–132 (1984).
Y. Wang, A. Roy, L. Sun, and C. E. Lau. A double-peak phenomenon in the pharmacokinetics of alprazolam after oral administration. Drug Metab. Dispos. 27:855–859 (1999).
S. Y. Yu, H. C. Chung, E. J. Kim, S. H. Kim, I. Lee, S. G. Kim, and M. G. Lee. Effects of acute renal failure induced by uranyl nitrate on the pharmacokinetics of intravenous theophylline in rats: the role of CYP2E1 induction in 1,3-demethyluric acid formation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 54:1687–19692 (2002).
L. S. Schanker, P. A. Shore, B. B. Brodie, and C. A. M. Hogben. Absorption of drugs from the stomach. I. The rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 120:528–539 (1957).
K. Yamaoka, Y. Tanigawara, Y. Nakagawa, and T. Uno. A pharmacokinetic analysis program (MULTI) for microcomputer. J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 4:879–855 (1981).
J.C.K. Loo, and S. Riegelman. New method for calculating the intrinsic absorption rate of drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 57:918–928 (1968).
K. Yamaoka and Y. Tanigawara. Deconvolution. In: Introduction to Pharmacokinetic Analysis by Microcomputer, Nankodo, Tokyo, 1984, pp. 91–112.
L. L. von Moltke, D. J. Greenblatt, J. S. Harmatz, and R. I. Shader. Alprazolam metabolism in vitro: studies of human, monkey, mouse, and rat liver microsomes. Pharmacol. 47:268–276 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metsugi, Y., Miyaji, Y., Ogawara, Ki. et al. Appearance of Double Peaks in Plasma Concentration–time Profile after Oral Administration Depends on Gastric Emptying Profile and Weight Function. Pharm Res 25, 886–895 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9469-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9469-z