Abstract
Purpose
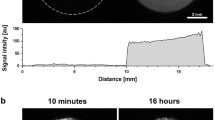
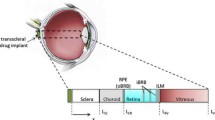
To determine the elimination rates of subconjunctivally injected model drugs using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI).
Methods
Gadolinium-diethylenetriaminopentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA) and gadolinium-albumin (Gd-albumin) were injected in rabbits. Experiments were performed in vivo and post mortem and injection volumes of 200 and 600 μl were administered. Signal intensity values from MR images were converted to concentration of contrast agent to determine the mass clearance rates from subconjunctival space.
Results
Injection volume did not have a significant effect on clearance rate for both Gd-DTPA and Gd-albumin. The clearance rate of Gd-DTPA in vivo was about nine times faster than that post mortem. The in vivo and post mortem clearance rates of Gd-albumin were not significantly different. The in vivo half-life of Gd-DTPA was about 22 min while that of Gd-albumin was about 5.3 h.
Conclusions
DCE-MRI was used to quantitatively compare the subconjunctival clearance rates of Gd-DTPA and Gd-albumin. Dynamic clearance mechanisms present in vivo significantly reduced the subconjunctival concentration of Gd-DTPA but not Gd-albumin. Lymphatic clearance does not seem to be as significant as clearance by blood, as evidenced by data from Gd-albumin injections. Larger injection volumes may allow for longer retention times and prolonged release of drug.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. A. Gaudio. A review of evidence guiding the use of corticosteroids in the treatment of intraocular inflammation. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 12:169–192 (2004).
R. J. Morris, D. McLeod, and Z. J. Gregor. Subconjunctival injections of antibiotics are used increasingly at the conclusion of intraocular and extraocular procedures. Eye 3(Pt 6):860–861 (1989).
H. J. McCartney, I. O. Drysdale, A. G. Gornall, and P. K. Basu. An autoradiographic study of the penetration of subconjunctivally injected hydrocortisone into the normal and inflamed rabbit eye. Invest. Ophthalmol. 4:297–302 (1965).
O. Weijtens, E. J. Feron, R. C. Schoemaker, A. F. Cohen, E. G. Lentjes, F. P. Romijn, and J. C. van Meurs. High concentration of dexamethasone in aqueous and vitreous after subconjunctival injection. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 128:192–197 (1999).
M. Barza, A. Kane, and J. L. Baum. Regional differences in ocular concentration of gentamicin after subconjunctival and retrobulbar injection in the rabbit. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 83:407–413 (1977).
A. Tsuji, I. Tamai, and K. Sasaki. Intraocular penetration kinetics of prednisolone after subconjunctival injection in rabbits. Ophthalmic Res. 20:31–43 (1988).
T. W. Kim, J. D. Lindsey, M. Aihara, T. L. Anthony, and R. N. Weinreb. Intraocular distribution of 70-kDa dextran after subconjunctival injection in mice. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 43:1809–1816 (2002).
P. H. Kalina, J. C. Erie, and L. Rosenbaum. Biochemical quantification of triamcinolone in subconjunctival depots. Arch. Ophthalmol. 113:867–869 (1995).
D. M. Maurice, and Y. Ota. The kinetics of subconjunctival injections. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 22:95–100 (1978).
S. K. Li, S. A. Molokhia, and E. K. Jeong. Assessment of subconjunctival delivery with model ionic permeants and magnetic resonance imaging. Pharm. Res. 21:2175–2184 (2004).
B. Reisfeld, S. Blackband, V. Calhoun, S. Grossman, S. Eller, and K. Leong. The use of magnetic resonance imaging to track controlled drug release and transport in the brain. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 11:247–252 (1993).
B. A. Berkowitz, Y. Sato, C. A. Wilson, and E. de Juan. Blood–retinal barrier breakdown investigated by real-time magnetic resonance imaging after gadolinium-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid injection. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 32:2854–2860 (1991).
E. L. Arrindell, J. C. Wu, M. D. Wolf, S. Nanda, D. P. Han, E. C. Wong, G. W. Abrams, W. F. Mieler, and J. S. Hyde. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of blood–retinal barrier integrity following transscleral diode laser treatment. Arch. Ophthalmol. 113:96–102 (1995).
B. A. Berkowitz, R. Roberts, H. Luan, J. Peysakhov, X. Mao, and K. A. Thomas. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI measurements of passive permeability through blood retinal barrier in diabetic rats. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 45:2391–2398 (2004).
W. E. Plehwe, D. W. McRobbie, R. A. Lerski, and E. M. Kohner. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of the blood–retinal barrier. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 29:663–670 (1988).
H. Kim, M. R. Robinson, M. J. Lizak, G. Tansey, R. J. Lutz, P. Yuan, N. S. Wang, and K. G. Csaky. Controlled drug release from an ocular implant: an evaluation using dynamic three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 45:2722–2731 (2004).
S. H. Kim, C. J. Galban, R. J. Lutz, R. L. Dedrick, K. G. Csaky, M. J. Lizak, N. S. Wang, G. Tansey, and M. R. Robinson. Assessment of subconjunctival and intrascleral drug delivery to the posterior segment using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 48:808–814 (2007).
H. Kim, M. J. Lizak, G. Tansey, K. G. Csaky, M. R. Robinson, P. Yuan, N. S. Wang, and R. J. Lutz. Study of ocular transport of drugs released from an intravitreal implant using magnetic resonance imaging. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33:150–164 (2005).
M. R. Robinson, S. S. Lee, H. Kim, S. Kim, R. J. Lutz, C. Galban, P. M. Bungay, P. Yuan, N. S. Wang, J. Kim, and K. G. Csaky. A rabbit model for assessing the ocular barriers to the transscleral delivery of triamcinolone acetonide. Exp. Eye Res. 82:479–487 (2006).
A. Supersaxo, W. R. Hein, and H. Steffen. Effect of molecular weight on the lymphatic absorption of water-soluble compounds following subcutaneous administration. Pharm. Res. 7:167–169 (1990).
A. C. Amrite, and U. B. Kompella. Size-dependent disposition of nanoparticles and microparticles following subconjunctival administration. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 57:1555–1563 (2005).
D. N. McLennan, C. J. H. Porter, and S. A. Charman. Subcutaneous drug delivery and the role of the lymphatics. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies. 2:89 (2005).
L. D. Samuels. Lymphoscintigraphy. Lymphology. 20:4–9 (1987).
M. K. Nawaz, M. M. Hamad, H. M. Abdel-Dayem, S. Sadek, and B. G. Eklof. Tc-99m human serum albumin lymphoscintigraphy in lymphedema of the lower extremities. Clin. Nucl. Med. 15:794–799 (1990).
S. J. Pain, R. S. Nicholas, R. W. Barber, J. R. Ballinger, A. D. Purushotham, P. S. Mortimer, and A. M. Peters. Quantification of lymphatic function for investigation of lymphedema: depot clearance and rate of appearance of soluble macromolecules in blood. J. Nucl. Med. 43:318–324 (2002).
G. F. Warner, E. L. Dobson, N. Pace, M. E. Johnston, and C. R. Finney. Studies of human peripheral blood flow; the effect of injection volume on the intramuscular radiosodium clearance rate. Circulation. 8:732–734 (1953).
R. B. Sund, and J. Schou. The determination of absorption rates from rat muscles: An experimental approach to kinetic descriptions. Acta Pharm. Toxicol. (Copenh). 21:313–325 (1964).
J. Blaser, H. L. Rieder, and R. Luthy. Interface-area-to-volume ratio of interstitial fluid in humans determined by pharmacokinetic analysis of netilmicin in small and large skin blisters. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 35:837–839 (1991).
K. Hirano, T. Ichihashi, and H. Yamada. Studies on the absorption of practically water-insoluble drugs following injection V: Subcutaneous absorption in rats from solutions in water immiscible oils. J. Pharm. Sci. 71:495–500 (1982).
A. J. Fischman, N. M. Alpert, J. W. Babich, and R. H. Rubin. The role of positron emission tomography in pharmacokinetic analysis. Drug Metab. Rev. 29:923–956 (1997).
S. R. Cherry. Fundamentals of positron emission tomography and applications in preclinical drug development. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 41:482–491 (2001).
O. Langer, and M. Muller. Methods to assess tissue-specific distribution and metabolism of drugs. Curr. Drug Metab. 5:463–481 (2004).
R. Hustinx, S. L. Eck, and A. Alavi. Potential applications of PET imaging in developing novel cancer therapies. J. Nucl. Med. 40:995–1002 (1999).
M. Dolovich, and R. Labiris. Imaging drug delivery and drug responses in the lung. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 1:329–337 (2004).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Robert L. Dedrick for insightful discussion and Dr. Craig J. Galban for assistance with image analysis. Veterinary technical expertise provided by Mark Lawson and Denise Parker is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.H., Csaky, K.G., Wang, N.S. et al. Drug Elimination Kinetics Following Subconjunctival Injection Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Pharm Res 25, 512–520 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9408-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9408-z