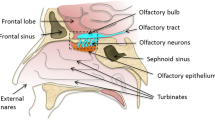
Purpose
The aim of this study was to quantify the olfactory transfer of morphine to the brain hemispheres by comparing brain tissue and plasma morphine levels after nasal administration with those after intravenous administration.
Methods
Morphine (1.0 mg/kg body weight) was administered via the right nostril or intravenously as a 15-min constant-rate infusion to male rats. The content of morphine and its metabolite morphine-3-glucuronide in samples of the olfactory bulbs, brain hemispheres, and plasma was assessed using high-performance liquid chromatography, and the areas under the concentration–time curves (AUC) were calculated.
Results
At both 5 and 15 min after administration, brain hemisphere morphine concentrations after nasal administration were similar to those after i.v. administration of the same dose, despite lower plasma concentrations after nasal administration. The brain hemispheres/plasma morphine AUC ratios for the 0–5 min period were thus approximately 3 and 0.1 after nasal and i.v. administration, respectively, demonstrating a statistically significant early distribution advantage of morphine to the brain hemispheres via the nasal route.
Conclusion
Morphine is transferred via olfactory pathways to the brain hemispheres, and drug transfer via this route significantly contributes to the early high brain concentrations after nasal administration to rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- LOB:
-
left olfactory bulb
- M3G:
-
morphine-3-glucuronide
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- ROB:
-
right olfactory bulb
References
O. Dale R. Hjortkjaer E. D. Kharasch (2002) ArticleTitleNasal administration of opioids for pain management in adults Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 46 759–770 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1399-6576.2002.460702.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38vktFSlug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12139528
J. M. Alexander-Williams D. J. Rowbotham (1998) ArticleTitleNovel routes of opioid administration Br. J. Anaesth. 81 3–7 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvksVajtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9771266
S. Mathison R. Nagilla U. B. Kompella (1998) ArticleTitleNasal route for direct delivery of solutes to the central nervous system: fact or fiction? J. Drug Target 5 415–441 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXntF2lsbg%3D Occurrence Handle9783675
L. Illum (2004) ArticleTitleIs nose-to-brain transport of drugs in man a reality? J. Pharm. Pharmacol 56 3–17 Occurrence Handle10.1211/0022357022539 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhvVCks7Y%3D Occurrence Handle14979996
G. W. Hanks F. Conno N. Cherny M. Hanna E. Kalso H. J. McQuay S. Mercadante J. Meynadier P. Poulain C. Ripamonti L. Radbruch J. R. Casas J. Säwe R. G. Twycross V. Ventafridda (2001) ArticleTitleMorphine and alternative opioids in cancer pain: the EAPC recommendations Br. J. Cancer 84 587–593 Occurrence Handle10.1054/bjoc.2001.1680 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXisVerur8%3D Occurrence Handle11237376
P. Bourget A. Lesne-Hulin V. Quinquis-Desmaris (1995) ArticleTitleStudy of the bioequivalence of two controlled-release formulations of morphine Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 33 588–594 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjvFOntQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8688982
D. Westerling C. Persson P. Höglund (1995) ArticleTitlePlasma concentrations of morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide, and morphine-6-glucuronide after intravenous and oral administration to healthy volunteers: relationship to nonanalgesic actions Ther. Drug Monit. 17 287–301 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXmslSmsLs%3D Occurrence Handle7624926
J. Säwe B. Dahlström A. Rane (1983) ArticleTitleSteady-state kinetics and analgesic effect of oral morphine in cancer patients Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 24 537–542 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00609900 Occurrence Handle6861871
S. L. Collins C. C. Faura R. A. Moore H. J. McQuay (1998) ArticleTitlePeak plasma concentrations after oral morphine: a systematic review J. Pain Symptom Manag. 16 388–402 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2FpsFagtQ%3D%3D
M. R. Bouw M. Gårdmark M. Hammarlund-Udenaes (2000) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modelling of morphine transport across the blood–brain barrier as a cause of the antinociceptive effect delay in rats—a microdialysis study Pharm. Res. 17 1220–1227 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1026414713509 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXit1Wk Occurrence Handle11145227
J. Lötsch C. Skarke H. Schmidt S. Grosch G. Geisslinger (2001) ArticleTitleThe transfer half-life of morphine-6-glucuronide from plasma to effect site assessed by pupil size measurement in healthy volunteers Anesthesiology 95 1329–1338 Occurrence Handle11748388
S. P. Letrent J. W. Polli J. E. Humphreys G. M. Pollack K. R. Brouwer K. L. Brouwer (1999) ArticleTitleP-glycoprotein-mediated transport of morphine in brain capillary endothelial cells Biochem. Pharmacol. 58 951–957 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-2952(99)00180-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXltlKlt7w%3D Occurrence Handle10509747
S. P. Letrent G. M. Pollack K. R. Brouwer K. L. Brouwer (1999) ArticleTitleEffects of a potent and specific P-glycoprotein inhibitor on the blood–brain barrier distribution and antinociceptive effect of morphine in the rat Drug Metab. Dispos. 27 827–834 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXkt1CjsLc%3D Occurrence Handle10383928
L. Illum P. Watts A. N. Fisher M. Hinchcliffe H. Norbury I. Jabbal-Gill R. Nankervis S. S. Davis (2002) ArticleTitleIntranasal delivery of morphine J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 301 391–400 Occurrence Handle10.1124/jpet.301.1.391 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xis1KqsLg%3D Occurrence Handle11907197
H. Pavis A. Wilcock J. Edgecombe D. Carr C. Manderson A. Church A. Fisher (2002) ArticleTitlePilot study of nasal morphine–chitosan for the relief of breakthrough pain in patients with cancer J. Pain Symptom Manag. 24 598–602 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmtFWhug%3D%3D
D. Fitzgibbon D. Morgan D. Dockter C. Barry E. D. Kharasch (2003) ArticleTitleInitial pharmacokinetic, safety and efficacy evaluation of nasal morphine gluconate for breakthrough pain in cancer patients Pain 106 309–315 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3959(03)00318-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXptlyjsrc%3D Occurrence Handle14659513
R. Kronstrand H. Druid P. Holmgren J. Rajs (1997) ArticleTitleA cluster of fentanyl-related deaths among drug addicts in Sweden Forensic Sci. Int. 88 185–193 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0379-0738(97)00068-6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiH3snpt1M%3D Occurrence Handle9291591
U. Westin E. Piras B. Jansson U. Bergström M. Dahlin E. Brittebo E. Björk (2005) ArticleTitleTransfer of morphine along the olfactory pathway to the central nervous system after nasal administration to rodents Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 24 565–573 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXisFGktrY%3D Occurrence Handle15784346
D. Betbeder S. Sperandio J. P. Latapie J. Nadai Particlede A. Etienne J. M. Zajac B. Frances (2000) ArticleTitleBiovector nanoparticles improve antinociceptive efficacy of nasal morphine Pharm. Res. 17 743–748 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1007594602449 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlvVCgt78%3D Occurrence Handle10955851
M. A. Hussain D. Rakestraw S. Rowe B. J. Aungst (1990) ArticleTitleNasal administration of a cognition enhancer provides improved bioavailability but not enhanced brain delivery J. Pharm. Sci. 79 771–772 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXmtVCgtb0%3D Occurrence Handle2273456
H. H. S. Chow Z. Chen G. T. Matsuura (1999) ArticleTitleDirect transport of cocaine from the nasal cavity to the brain following intranasal cocaine administration in rats J. Pharm. Sci. 88 754–758 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXktFektL0%3D Occurrence Handle10430537
H. H. S. Chow N. Anavy A. Villalobos (2001) ArticleTitleDirect nose–brain transport of benzoylecgonine following intranasal administration in rats J. Pharm. Sci. 90 1729–1735 Occurrence Handle10.1002/jps.1122 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXosVKltrs%3D Occurrence Handle11745730
S. P. Joel R. J. Osborne M. L. Slevin (1988) ArticleTitleAn improved method for the simultaneous determination of morphine and its principal glucuronide metabolites J. Chromatogr. 430 394–399 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXlvVaqsLc%3D Occurrence Handle3235512
Y. Wang R. Aun F. L. Tse (1998) ArticleTitleBrain uptake of dihydroergotamine after intravenous and nasal administration in the rat Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 19 571–575 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1099-081X(199812)19:9<571::AID-BDD142>3.0.CO;2-O Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXos1Wj Occurrence Handle9872338
G. Skopp L. Potsch B. Ganssmann R. Aderjan R. Mattern (1998) ArticleTitleA preliminary study on the distribution of morphine and its glucuronides in the subcompartments of blood J. Anal. Toxicol. 22 261–264 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXltVymtbw%3D Occurrence Handle9681326
J. Yuan (1993) ArticleTitleEstimation of variance for AUC in animal studies J. Pharm. Sci. 82 761–763 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXltlSru7s%3D Occurrence Handle8360854
P. R. Bevington D. K. Robinson (1992) Data Reduction and Error Analysis for the Physical Sciences McGraw-Hill New York 45–46
J. C. Miller J. N. Miller (1993) Statistics for Analytical Chemistry Ellis Horwood PTR, Prentice-Hall London 55–56
F. E. Satterthwaite (1946) ArticleTitleAn approximate distribution of estimates of variance components Biometrics 2 110–114
R. R. Wilcox (1987) ArticleTitleNew designs in analysis of variance Annu. Rev. Psychol. 38 29–60 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.ps.38.020187.000333
T. Sakane M. Akizuki S. Yamashita T. Nadai M. Hashida H. Sezaki (1991) ArticleTitleThe transport of a drug to the cerebrospinal fluid directly from the nasal cavity: the relation to the lipophilicity of the drug Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 39 2456–2458 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXms12qtr4%3D
U. Bickel O. P. Schumacher Y. S. Kang K. Voigt (1996) ArticleTitlePoor permeability of morphine 3-glucuronide and morphine 6-glucuronide through the blood–brain barrier in the rat J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 278 107–113 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XktlGhu7k%3D Occurrence Handle8764341
C. L. Graff G. M. Pollack (2003) ArticleTitleP-glycoprotein attenuates brain uptake of substrates after nasal instillation Pharm. Res. 20 1225–1230 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1025053115583 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmtVGrtb4%3D Occurrence Handle12948020
C. L. Graff G. M. Pollack (2005) ArticleTitleNasal drug administration: potential for targeted central nervous system delivery J. Pharm. Sci. 94 1187–1195 Occurrence Handle10.1002/jps.20318 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXkvF2qt7Y%3D Occurrence Handle15858850
C. K. Kuo N. Hanioka Y. Hoshikawa K. Oguri H. Yoshimura (1991) ArticleTitleSpecies difference of site-selective glucuronidation of morphine J. Pharmacobio-dyn. 14 187–193 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXksVWht7g%3D Occurrence Handle1941499
C. C. Faura S. L. Collins R. A. Moore H. J. McQuay (1998) ArticleTitleSystematic review of factors affecting the ratios of morphine and its major metabolites Pain 74 43–53 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3959(97)00142-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXivVSntQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9514559
A. Salem W. Hope (1997) ArticleTitleRole of morphine glucuronide metabolites in morphine dependence in the rat Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 57 801–807 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXlt1Wrt7w%3D Occurrence Handle9259009
D. Lazard K. Zupko Y. Poria P. Nef J. Lazarovits S. Horn M. Khen D. Lancet (1991) ArticleTitleOdorant signal termination by olfactory UDP glucuronosyl transferase Nature 349 790–793 Occurrence Handle10.1038/349790a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXlsFemtLY%3D Occurrence Handle1900353
R. Kumbale W. H. Frey S. Wilson Y. E. Rahman (1999) ArticleTitleGM1 delivery to the CSF via the olfactory pathway Drug Deliv. 6 23–30 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhs1ygsr8%3D
X. Q. Chen J. R. Fawcett Y. E. Rahman T. A. Ala I. W. Frey (1998) ArticleTitleDelivery of nerve growth factor to the brain via the olfactory pathway J. Alzheimer's Dis. 1 35–44 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkvFyitQ%3D%3D
M. Dahlin U. Bergman B. Jansson E. Björk E. Brittebo (2000) ArticleTitleTransfer of dopamine in the olfactory pathway following nasal administration in mice Pharm. Res. 17 737–742 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1007542618378 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlvVCgt74%3D Occurrence Handle10955850
E. L. Way T. K. Adler (1961) ArticleTitleThe biological disposition of morphine and its surrogates. I Bull W.H.O. 25 227–262 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CC2C1Mjis1M%3D Occurrence Handle14005367
S. Gizurarson (1990) ArticleTitleAnimal models for intranasal drug delivery studies. A review article Acta Pharm. Nord. 2 105–122 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXkslSmtrw%3D Occurrence Handle2191690
P. G. Djupesland A. Skretting M. Winderen T. Holand (2004) ArticleTitleBi-directional nasal delivery of aerosols can prevent lung deposition J. Aerosol Med. 17 249–259 Occurrence Handle10.1089/jam.2004.17.249 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXot1aiurY%3D Occurrence Handle15625817
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jessica Strömgren for excellent assistance with the animal experiments, and Britt Jansson for expert assistance with the HPLC system. The National Network of Drug Delivery (NNDD), part of the Swedish Foundation of Strategic Research, is acknowledged for financially supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westin, U.E., Boström, E., Gråsjö, J. et al. Direct Nose-to-Brain Transfer of Morphine After Nasal Administration to Rats. Pharm Res 23, 565–572 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9534-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9534-z