Purpose
Orally administered rutin reportedly ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis of rats. We investigated the metabolic and pharmacological properties of rutin underlying the rutin-mediated amelioration of the rat colitis.
Methods
Apparent partition coefficients of rutin and its aglycone quercetin were compared. The biochemical/chemical stability of rutin was examined in the contents of various segments of gastrointestinal tracts of rats. Inflammatory indices were determined in the colitis rats after oral administration of rutin or rectal administration of quercetin. In human colon epithelial cells, the effect of quercetin on tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)-induced nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) activation was examined.
Results
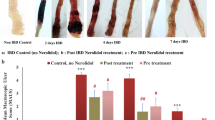
The sugar residue in rutin greatly lowered the apparent partition coefficient and was rapidly deglycosylated to liberate quercetin in the cecal contents, whereas it was stable in the contents of the upper intestine. Not only oral administration of rutin but also rectal administration of quercetin remarkably ameliorated TNBS-induced colitis rats, indicating that quercetin liberated from rutin is therapeutically active. Furthermore, quercetin dose-dependently inhibited an inflammatory signal TNF-α-dependent NFκB activation.
Conclusions
Our data suggest that rutin acted as a quercetin deliverer to the large intestine and its anti-inflammatory action in TNBS-induced colitis rats may be through quercetin-mediated inhibition of TNF-α-induced NFκB activation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl sulfoxide
- HIF-1α:
-
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha
- IBD:
-
inflammatory bowel disease
- NFDL:
-
NFκB-dependent luciferase
- NFκB:
-
nuclear factor kappa B
- TNBS:
-
2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid
- 5-ASA:
-
5-aminosalicylic acid
References
R. J. Nijveldt E. Nood Particlevan D. E. Hoorn Particlevan P. G. Boelens K. Norren Particlevan P. A. Leeuwen Particlevan (2001) ArticleTitleFlavonoids: a review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 74 IssueID4 418–425 Occurrence Handle11566638
P. C. Hollman M. B. Katan (1997) ArticleTitleAbsorption, metabolism and health effects of dietary flavonoids in man Biomed. Pharmacother. 51 IssueID8 305–310 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0753-3322(97)88045-6 Occurrence Handle9436520
J. M. Gee I. T. Johnson (2001) ArticleTitlePolyphenolic compounds: interactions with the gut and implications for human health Curr. Med. Chem. 8 IssueID11 1245–1255 Occurrence Handle11562264
C. Fiocchi (1997) ArticleTitleIntestinal inflammation: a complex interplay of immune and nonimmune cell interactions Am. J. Physiol. 273 IssueID4 Pt 1 G769–G775 Occurrence Handle9357817
M. F. Neurath C. Becker K. Barbulescu (1998) ArticleTitleRole of NF-kappaB in immune and inflammatory responses in the gut Gut 43 IssueID6 856–860 Occurrence Handle9824616
H. Ogata T. Hibi (2003) ArticleTitleCytokine and anti-cytokine therapies for inflammatory bowel disease Curr. Pharm. Des. 9 IssueID14 1107–1113 Occurrence Handle10.2174/1381612033455035 Occurrence Handle12769750
C. K. Weber S. Liptay T. Wirth G. Adler R. M. Schmid (2000) ArticleTitleSuppression of NF-kappaB activity by sulfasalazine is mediated by direct inhibition of IkappaB kinases alpha and beta Gastroenterology 119 IssueID5 1209–1218 Occurrence Handle10.1053/gast.2000.19458 Occurrence Handle11054378
F. Yan D. B. Polk (1999) ArticleTitleAminosalicylic acid inhibits IkappaB kinase alpha phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha in mouse intestinal epithelial cells J. Biol. Chem. 274 IssueID51 36631–36636 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.274.51.36631 Occurrence Handle10593965
N. Auphan J. A. DiDonato C. Rosette A. Helmberg M. Karin (1995) ArticleTitleImmunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-kappa B activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis Science 270 IssueID5234 286–290 Occurrence Handle7569976
P. C. Hollman M. N. Bijsman Y. Gameren Particlevan E. P. Cnossen J. H. Vries Particlede M. B. Katan (1999) ArticleTitleThe sugar moiety is a major determinant of the absorption of dietary flavonoid glycosides in man Free Radic. Res. 31 IssueID6 569–573 Occurrence Handle10630681
V. R. Sinha R. Kumria (2001) ArticleTitleColonic drug delivery: prodrug approach Pharm. Res. 18 IssueID5 557–564 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1011033121528 Occurrence Handle11465408
B. Crotty D. P. Jewell (1992) ArticleTitleDrug therapy of ulcerative colitis Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 34 IssueID3 189–198 Occurrence Handle1389944
Y. J. Jung J. S. Lee H. H. Kim Y. M. Kim S. K. Han (1998) ArticleTitleSynthesis and evaluation of 5-aminosalicyl-glycine as a potential colon-specific prodrug of 5-aminosalicylic acid Arch. Pharm. Res. 21 IssueID2 174–178 Occurrence Handle9875427
G. P. Morris P. L. Beck M. S. Herridge W. T. Depew M. R. Szewczuk J. L. Wallace (1989) ArticleTitleHapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat colon Gastroenterology 96 IssueID3 795–803 Occurrence Handle2914642
H. Yano F. Hirayama M. Kamada H. Arima K. Uekama (2002) ArticleTitleColon-specific delivery of prednisolone-appended alpha-cyclodextrin conjugate: alleviation of systemic side effect after oral administration J. Control. Release 79 IssueID1–3 103–112 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-3659(01)00532-6 Occurrence Handle11853922
M. W. Son J. I. Ko H. M. Doh W. B. Kim T. S. Park M. J. Shim B. K. Kim (1998) ArticleTitleProtective effect of taurine on TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease in rats Arch. Pharm. Res. 21 IssueID5 531–536 Occurrence Handle9875490
N. C. Andrews D. V. Faller (1991) ArticleTitleA rapid micropreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from limiting numbers of mammalian cells Nucleic Acids Res. 19 IssueID9 2499 Occurrence Handle2041787
R. R. Scheline (1973) ArticleTitleMetabolism of foreign compounds by gastrointestinal microorganisms Pharmacol. Rev. 25 IssueID4 451–523 Occurrence Handle4587548
P. Marteau P. Seksik F. Shanahan (2003) ArticleTitleManipulation of the bacterial flora in inflammatory bowel disease Best Pract. Res., Clin. Gastroenterol. 17 IssueID1 47–61
J. V. Formica W. Regelson (1995) ArticleTitleReview of the biology of quercetin and related bioflavonoids Food Chem. Toxicol. 33 IssueID12 1061–1080 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0278-6915(95)00077-1 Occurrence Handle8847003
A. M. Aura K. A. O’Leary G. Williamson M. Ojala M. Bailey R. Puupponen-Pimia A. M. Nuutila K. M. Oksman-Caldentey K. Poutanen (2002) ArticleTitleQuercetin derivatives are deconjugated and converted to hydroxyphenylacetic acids but not methylated by human fecal flora in vitro J. Agric. Food Chem. 50 IssueID6 1725–1730 Occurrence Handle10.1021/jf0108056 Occurrence Handle11879065
A. R. Rechner M. A. Smith G. Kuhnle G. R. Gibson E. S. Debnam S. K. Srai K. P. Moore C. A. Rice-Evans (2004) ArticleTitleColonic metabolism of dietary polyphenols: influence of structure on microbial fermentation products Free Radic. Biol. Med. 36 IssueID2 212–225 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2003.09.022 Occurrence Handle14744633
L. A. Christensen J. Fallingborg B. A. Jacobsen K. Abildgaard H. H. Rasmussen S. N. Rasmussen S. H. Hansen (1993) ArticleTitleBioavailability of 5-aminosalicyclic acid from slow release 5-aminosalicyclic acid drug and sulfasalazine in normal children Dig. Dis. Sci. 38 IssueID10 1831–1836 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01296106 Occurrence Handle8104772
T. Hibi N. Inoue H. Ogata M. Naganuma (2003) ArticleTitleIntroduction and overview: recent advances in the immunotherapy of inflammatory bowel disease J. Gastroenterol. 38 IssueIDSuppl. 15 36–42 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00535-003-1139-2 Occurrence Handle12698869
S. W. Kim S. C. Choi E. Y. Choi K. S. Kim J. M. Oh H. J. Lee H. M. Oh S. Kim B. S. Oh K. C. Kimm M. H. Lee G. S. Seo T. H. Kim H. C. Oh W. H. Woo Y. S. Kim H. O. Pae D. S. Park H. T. Chung C. D. Jun (2004) ArticleTitleCatalposide, a compound isolated from Catalpa ovata, attenuates induction of intestinal epithelial proinflammatory gene expression and reduces the severity of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 10 IssueID5 564–572 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00054725-200409000-00010 Occurrence Handle15472516
P. A. Baeuerle D. Baltimore (1988) ArticleTitleI kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor Science 242 IssueID4878 540–546 Occurrence Handle3140380
C. Kunsch S. M. Ruben C. A. Rosen (1992) ArticleTitleSelection of optimal kappa B/Rel DNA-binding motifs: interaction of both subunits of NF-kappa B with DNA is required for transcriptional activation Mol. Cell. Biol. 12 IssueID10 4412–4421 Occurrence Handle1406630
S. Baba T. Furuta M. Fujioka T. Goromaru (1983) ArticleTitleStudies on drug metabolism by use of isotopes: XXVII. Urinary metabolites of rutin in rats and the role of intestinal microflora in the metabolism of rutin J. Pharm. Sci. 72 IssueID10 1155–1158 Occurrence Handle6644562
P. C. Hollman M. Gaag Particlevd M. J. Mengelers J. M. Trijp Particlevan J. H. Vries Particlede M. B. Katan (1996) ArticleTitleAbsorption and disposition kinetics of the dietary antioxidant quercetin in man Free Radic. Biol. Med. 21 IssueID5 703–707 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0891-5849(96)00129-3 Occurrence Handle8891673
T. Walle T. S. Vincent U. K. Walle (2003) ArticleTitleEvidence of covalent binding of the dietary flavonoid quercetin to DNA and protein in human intestinal and hepatic cells Biochem. Pharmacol. 65 IssueID10 1603–1610 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-2952(03)00151-5 Occurrence Handle12754096
T. Cruz J. Galvez M. A. Ocete M. E. Crespo L. H. F. Sanchez de Medina A. Zarzuelo (1998) ArticleTitleOral administration of rutoside can ameliorate inflammatory bowel disease in rats Life Sci. 62 IssueID7 687–695 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0024-3205(97)01164-8 Occurrence Handle9472728
S. Y. Zhou D. Fleisher L. H. Pao C. Li B. Winward E. M. Zimmermann (1999) ArticleTitleIntestinal metabolism and transport of 5-aminosalicylate Drug Metab. Dispos. 27 IssueID4 479–485 Occurrence Handle10101143
K. Muraoka K. Shimizu X. Sun T. Tani R. Izumi K. Miwa K. Yamamoto (2002) ArticleTitleFlavonoids exert diverse inhibitory effects on the activation of NF-kappaB Transplant. Proc. 34 IssueID4 1335–1340 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0041-1345(02)02795-1 Occurrence Handle12072354
S. Y. Cho S. J. Park M. J. Kwon T. S. Jeong S. H. Bok W. Y. Choi W. I. Jeong S. Y. Ryu S. H. Do C. S. Lee J. C. Song K. S. Jeong (2003) ArticleTitleQuercetin suppresses proinflammatory cytokines production through MAP kinases and NF-kappaB pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage Mol. Cell. Biochem. 243 IssueID1–2 153–160 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1021624520740 Occurrence Handle12619901
M. M. Mu D. Chakravortty T. Sugiyama N. Koide K. Takahashi I. Mori T. Yoshida T. Yokochi (2001) ArticleTitleThe inhibitory action of quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells J. Endotoxin Res. 7 IssueID6 431–438 Occurrence Handle10.1179/096805101101533034 Occurrence Handle11753212
A. J. Garcia-Pineres V. Castro G. Mora T. J. Schmidt E. Strunck H. L. Pahl I. Merfort (2001) ArticleTitleCysteine 38 in p65/NF-kappaB plays a crucial role in DNA binding inhibition by sesquiterpene lactones J. Biol. Chem. 276 IssueID43 39713–39720 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M101985200 Occurrence Handle11500489
F. Sanchez de Medina J. Galvez J. A. Romero A. Zarzuelo (1996) ArticleTitleEffect of quercetin on acute and chronic experimental colitis in the rat J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 278 IssueID2 771–779 Occurrence Handle8768730
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a Pusan National University research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Kong, H., Choi, B. et al. Metabolic and Pharmacological Properties of Rutin, a Dietary Quercetin Glycoside, for Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Pharm Res 22, 1499–1509 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-6250-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-6250-z