Purpose
We hypothesized that sustained delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) using a polymer [85:15 poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLG)] would enhance angiogenesis and improve perfusion of ischemic tissue.
Methods
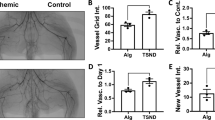
C57BL/6J mice (n = 20/group) underwent unilateral hind limb ischemia surgery and were randomized to groups of no scaffold implantation (∅-Implant), unloaded scaffold implantation (Empty-PLG), or implantation of scaffolds incorporating 3 μg of VEGF165 (PLG-VEGF). Endpoints included laser Doppler perfusion imaging (LDPI, ischemic/nonischemic limb, %), local vessel counts, immunohistochemistry for CD31, and α-smooth muscle actin. In vitro release kinetics of VEGF from PLG was also measured.
Results
PLG-VEGF resulted in improved lower extremity perfusion vs. controls as measured by LDPI% at 7, 14, 21, and 28 days (p < 0.05). PLG-VEGF was associated with significantly greater percentage of vessels staining for CD31 and α-smooth muscle actin compared to the Empty-PLG or ∅-Implant (p < 0.05 for both).
Conclusions
The PLG-VEGF scaffolds resulted in sustained VEGF delivery, improved tissue perfusion, greater capillary density, and more mature vasculature compared to the controls. The sustained-release PLG polymer vehicle is a promising delivery system for therapeutic neovascularization applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Empty-PLG:
-
PLG polymer not loaded with growth factor
- ∅-Implant:
-
hind limb surgery performed with no PLG polymer implanted
- PAD:
-
peripheral arterial disease
- PLG:
-
poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
- PLG-VEGF:
-
PLG polymer loaded with 3 μg of VEGF165
- SMA:
-
smooth muscle actin
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
References
J. M. Isnerand T. Asahara (1999) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis and vasculogenesis as therapeutic strategies for postnatal neovascularization J. Clin. Invest. 103 1231–1236
M. Simons R. O. Bonow N. A. Chronos D. J. Cohen F. J. Giordano H. K. Hammond R. J. Laham W. Li M. Pike F. W. Sellke T. J. Stegmann J. E. Udelson T. K. Rosengart (2000) ArticleTitleClinical trials in coronary angiogenesis: issues, problems, consensus: an expert panel summary Circulation 102 E73–E86
S. Rafii S. Meeus S. Dias K. Hattori B. Heissig S. Shmelkov D. Rafii D. Lyden (2002) ArticleTitleContribution of marrow-derived progenitors to vascular and cardiac regeneration Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 13 61–67
J. A. Nagy E. Vasile D. Feng C. Sundberg L. F. Brown M. J. Detmar J. A. Lawitts L. Benjamin X. Tan E. J. Manseau A. M. Dvorak H. F. Dvorak (2002) ArticleTitleVascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor induces lymphangiogenesis as well as angiogenesis J. Exp. Med. 196 1497–1506
H. K. Hammondand M. D. McKirnan (2001) ArticleTitleAngiogenic gene therapy for heart disease: a review of animal studies and clinical trials Cardiovasc. Res. 49 561–567
S. Rajagopalan E. R. Mohler SuffixIII R. J. Lederman F. O. Mendelsohn J. F. Saucedo C. K. Goldman J. Blebea J. Macko P. D. Kessler H. S. Rasmussen B. H. Annex (2003) ArticleTitleRegional angiogenesis with vascular endothelial growth factor in peripheral arterial disease: a phase II randomized, double-blind, controlled study of adenoviral delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor 121 in patients with disabling intermittent claudication Circulation 108 1933–1938
M. C. Peters P. J. Polverini D. J. Mooney (2002) ArticleTitleEngineering vascular networks in porous polymer matrices J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 60 668–678
M. Simonsand J. A. Ware (2003) ArticleTitleTherapeutic angiogenesis in cardiovascular disease Nat. Rev., Drug Discov. 2 863–871
M. C. Peters B. C. Isenberg J. A. Rowley D. J. Mooney (1998) ArticleTitleRelease from alginate enhances the biological activity of vascular endothelial growth factor J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed. 9 1267–1278
R. Langer (1998) ArticleTitleDrug delivery and targeting Nature 392 5–10
K. Park (Eds) (1997) Controlled Drug Delivery: Challenges and Strategies American Chemical Society Washington, Dc
W. L. Murphy M. C. Peters D. H. Kohn D. J. Mooney (2000) ArticleTitleSustained release of vascular endothelial growth factor from mineralized poly(lactide-co-glycolide) scaffolds for tissue engineering Biomaterials 21 2521–2527
D. Gilding (1981) Biodegradable Polymers CRC Press Boca Raton, FL
M. H. Sheridan L. D. Shea M. C. Peters D. J. Mooney (2000) ArticleTitleBioabsorbable polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering capable of sustained growth factor delivery J. Control. Rel. 64 91–102
T. P. Richardson M. C. Peters A. B. Ennett D. J. Mooney (2001) ArticleTitlePolymeric system for dual growth factor delivery Nat. Biotechnol. 19 1029–1034
J. L. Cleland E. T. Duenas A. Park A. Daugherty J. Kahn J. Kowalski A. Cuthbertson (2001) ArticleTitleDevelopment of poly-(d,l-lactide-coglycolide) microsphere formulations containing recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor to promote local angiogenesis J. Control Rel. 72 13–24
S. F. Schlossman (1995) Leucocyte Typing V: White Cell Differentiation Antigens: Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop and Conference held in Boston, USA, 3–7 November, 1993 Oxford University Press Oxford, NY
O. Skalli P. Ropraz A. Trzeciak G. Benzonana D. Gillessen G. Gabbiani (1986) ArticleTitleA monoclonal antibody against alpha-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation J. Cell Biol. 103 2787–2796
L. D. Harris B. S. Kim D. J. Mooney (1998) ArticleTitleOpen pore biodegradable matrices formed with gas foaming J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 42 396–402
A. Rivard J. E. Fabre M. Silver D. Chen T. Murohara M. Kearney M. Magner T. Asahara J. M. Isner (1999) ArticleTitleAge-dependent impairment of angiogenesis Circulation 99 111–120
S. Takeshita L. P. Zheng E. Brogi M. Kearney L. Q. Pu S. Bunting N. Ferrara J. F. Symes J. M. Isner (1994) ArticleTitleTherapeutic angiogenesis. A single intraarterial bolus of vascular endothelial growth factor augments revascularization in a rabbit ischemic hind limb model J. Clin. Invest. 93 662–670
S. Takeshita L. Q. Pu L. A. Stein A. D. Sniderman S. Bunting N. Ferrara J. M. Isner J. F. Symes (1994) ArticleTitleIntramuscular administration of vascular endothelial growth factor induces dose-dependent collateral artery augmentation in a rabbit model of chronic limb ischemia Circulation 90 II228–II234
B. Witzenbichler T. Asahara T. Murohara M. Silver I. Spyridopoulos M. Magner N. Principe M. Kearney J. S. Hu J. M. Isner (1998) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C/VEGF-2) promotes angiogenesis in the setting of tissue ischemia Am. J. Pathol. 153 381–394
S. Rajagopalan M. Shah A. Luciano R. Crystal E. G. Nabel (2001) ArticleTitleAdenovirus-mediated gene transfer of VEGF(121) improves lower-extremity endothelial function and flow reserve Circulation 104 753–755
J. E. Nor J. Christensen D. J. Mooney P. J. Polverini (1999) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated angiogenesis is associated with enhanced endothelial cell survival and induction of Bcl-2 expression Am. J. Pathol. 154 375–384
S. I. Stiver X. Tan L. F. Brown E. T. Hedley-Whyte H. F. Dvorak (2004) ArticleTitleVEGF-A angiogenesis induces a stable neovasculature in adult murine brain J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 63 841–855
M. Therin P. Christel S. Li H. Garreau M. Vert (1992) ArticleTitleIn vivo degradation of massive poly(alpha-hydroxy acids): validation of in vitro findings Biomaterials 13 594–600
A. G. Mikos Y. Bao L. G. Cima D. E. Ingber J. P. Vacanti R. Langer (1993) ArticleTitlePreparation of poly(glycolic acid) bonded fiber structures for cell attachment and transplantation J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 27 183–189
D. J. Mooney P. M. Kaufmann K. Sano K. M. McNamara J. P. Vacanti R. Langer (1994) ArticleTitleTransplantation of hepatocytes using porous, biodegradable sponges Transplant. Proc. 26 3425–3426
S. L. Ishaug-Riley G. M. Crane A. Gurlek M. J. Miller A. W. Yasko M. J. Yaszemski A. G. Mikos (1997) ArticleTitleEctopic bone formation by marrow stromal osteoblast transplantation using poly(dl-lactic-co-glycolic acid) foams implanted into the rat mesentery J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 36 1–8
B. S. Kimand D. J. Mooney (1998) ArticleTitleDevelopment of biocompatible synthetic extracellular matrices for tissue engineering Trends Biotechnol. 16 224–230
K. Y. Lee M. C. Peters K. W. Anderson D. J. Mooney (2000) ArticleTitleControlled growth factor release from synthetic extracellular matrices Nature 408 998–1000
C. A. Vacanti R. Langer B. Schloo J. P. Vacanti (1991) ArticleTitleSynthetic polymers seeded with chondrocytes provide a template for new cartilage formation Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 88 753–759
F. D. Fortuin P. Vale D. W. Losordo J. Symes G. A. DeLaria J. J. Tyner G. L. Schaer R. March R. J. Snell T. D. Henry J. Camp ParticleVan J. J. Lopez W. Richenbacher J. M. Isner R. A. Schatz (2003) ArticleTitleOne-year follow-up of direct myocardial gene transfer of vascular endothelial growth factor-2 using naked plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid by way of thoracotomy in no-option patients Am. J. Cardiol. 92 436–439
E. R. Mohler SuffixIII S. Rajagopalan J. W. Olin J. D. Trachtenberg H. Rasmussen R. Pak R. G. Crystal (2003) ArticleTitleAdenoviral-mediated gene transfer of vascular endothelial growth factor in critical limb ischemia: safety results from a phase I trial Vasc. Med. 8 9–13
J. A. Nagy A. M. Dvorak H. F. Dvorak (2003) ArticleTitleVEGF-A(164/165) and PlGF: roles in angiogenesis and arteriogenesis Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 13 169–175
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (R01 HL069957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Q., Chen, R.R., Shen, Y. et al. Sustained Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Delivery Enhances Angiogenesis and Perfusion in Ischemic Hind Limb. Pharm Res 22, 1110–1116 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-5644-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-5644-2