Abstract
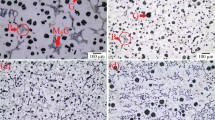
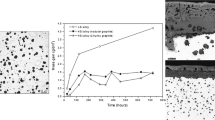
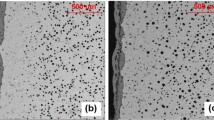
The oxidation behavior of two ductile cast irons was investigated in synthetic diesel and gasoline exhaust gases. The alloys were a SiMo (Fe3.86Si0.6Mo3C) and a Ni-Resist (Fe32Ni5.3Si2.1C). Polished sections were exposed at temperatures between 650 and 1,050 °C, mostly for 50 h. The oxidation product was characterized by means of SEM/EDX, AES, XPS and XRD. Iron oxides nodules formed above a continuous layer of Fe–Si-oxide for SiMo. The alloy failed in forming a continuous silica layer at low temperatures. At 850 °C and above silica was formed, but austenite formation enhanced the decarburization. Escaping CO/CO2 increased the oxide porosity, and consequently the oxidation rate. The oxidation resistance of Ni-Resist was dependent on Cr assisting the formation of SiO2. However, this effect was restrained to cell boundaries in particular when water enhanced the Cr evaporation or the diffusion was slow at low temperatures. Then, the rapid oxidation left metallic Ni particles in the inner oxide.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Tholence and M. Norell, Materials Science Forum 369–372, 197 (2001).
W. Fairhurst and K. Röhrig, Foundry Trade Journal 146, 657 (1979).
K. Röhrig, in Proceedings of the conf. on Castings for the Chemical Process Industry, Saint-Etienne, France, (Bulletin du Cercle d’Etudes des Metaux (France), 1993) p. 9.1
Nickel as an Alloy in Cast Iron. Current information report, ed. American Foundrymen’s Society, Golf & Wolf Rd. Des Plaines, III. 60016 (1978), p. 29
D. L. Torkington, Metal Progress 119, 38 (1981).
P. Bastid, E. Andrieu, C. Grente, M. Ortiz, and E. Marconnet, Ingénieurs de l’automobile 686, 43 (1994).
High Temperature Materials for Exhaust Manifolds. SAE (1999), SAE Standards Report no. J2515.
D. Li, R. Perrin, G. Burger, D. McFarlan, B. Black, R. Logan, and R. Williams, SAE Technical Paper Series, 2004–01–0792 (2004).
S. H. Park, J. M. Kim, H. J. Kim, S. J. Ko, H. S. Park, and J. D. Lim, SAE Technical Paper Series, SAE 2005–01–1688 (2005).
C. Pelhan, Giessereiforschung 25, 73 (1973).
A. Rahmel, Nickel-Berichte 25, 1 (1967).
C. Pehlan, in Proceedings of 2nd Internat. Symposium on the Metallurgy of Cast Iron (1976), p. 841.
C. Pelhan and J. Lamut, Fonderia Ital. 9–10, 73 (1983).
H. D. Merchant, in Proceedings of a seminar on Recent Research on Cast Iron, Detroit, USA (Gordon & Breach, New York, 16–18 June 1964), p. 793.
H. D. Merchant, Oxidation of Metals 2, 145 (1970).
F. Tholence and M. Norell, Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 66, 530 (2005).
J. A. Nelson, in Metals Handbook, Cast Irons, 9th edn. (ASM, Materials Park, Ohio, 1985), p. 242.
R. Boeri and F. Weinberg, Transactions of the American Foundrymen’s Society 97, 179 (1989).
N. K. Datta and N. N. Engel, Transactions of American Foundrymen’s Society 84, 431 (1976).
P. C. Liu and C. R. Loper Jr., Transactions of the American Foundrymen’s Society 89, 131 (1981).
B. Sundman, B. Jansson, and J. O. Andersson, Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry 9, 153 (1985).
F. Tholence and M. Norell, Surface and Interface Analysis 34, 535 (2002).
A. Järdnäs, J.-E. Svensson, and L.-G. Johansson, Materials Science Forum 369–372, 173 (2001).
V. Lanteri, D. Huin, P. Drillet, D. Bouleau, P. Henry, and H. Gaye, in Microscopy of Oxidation 3, Cambridge (The Institute of Metals, London, 1996), p. 535.
I. Barin, Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances (VCH Verschlagsgesellschaft mbH. Weinheim, 1993).
A. Atkinson, Corrosion Science 22, 87 (1982).
I. Svedung and N.-G. Vannerberg, Corrosion Science 14, 391 (1974).
F. Gesmundo and F. Viani, Oxidation of Metals 25, 269 (1986).
I. C. H. Hughes, B.C.I.R.A. Journal 8, 7 (1960).
R. J. Maitland and I. C. H. Hughes, B.C.I.R.A. Journal 7, 203 (1958).
R. Durham, J. Lacaze, D. Monceau, and B. Pieraggi, Materials Science Forum 369–372, 181 (2001).
C. W. Tuck, Corrosion Science 5, 631 (1965).
K. Hauffe, in DECHEMA Corrosion Handbook, Hot Oxidizing Gases (VCH Publishers, New York, 1989), p. 77.
T. Ban, K. Bohnenkamp, and H. J. Engell, Corrosion Science 19, 283 (1979).
M. J. Brabers and C. E. Birchenall, Corrosion 14, 179t (1958).
J. Robertson and M. I. Manning, Materials Science and Technology 5, 741 (1989).
C. Wagner, Corrosion Science 5, 751 (1965).
H. Asteman, J.-E. Svensson, L.-G. Johansson, and M. Norell, Oxidation of Metals 52, 95 (1999).
H. Asteman, J.-E. Svensson, M. Norell, and L.-G. Johansson, Oxidation of Metals 54, 11 (2000).
T. J. Carter, G. L. Wulf, and G. R. Wallwork, Corrosion Science 9, 471 (1969).
G. E. Wasielewski and R. A. Rapp, in The superalloys, High-Temperature Oxidation (Wiley, New York, 1972), p. 287.
C. Gindorf, L. Singheiser, and K. Hilpert, Steel Research 72, 528 (2001).
Acknowledgments
This work was done within the Swedish competence centre for High Temperature Corrosion. The authors acknowledge Volvo Truck Corporation for financial support and in particular U. Boman for valuable co-operation. Synthetic exhaust gas exposures were done at Volvo Technology Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tholence, F., Norell, M. High Temperature Corrosion of Cast Alloys in Exhaust Environments I-Ductile Cast Irons. Oxid Met 69, 13–36 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-007-9081-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-007-9081-y