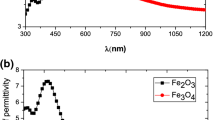
Abstract
Metal coated semiconductor nanoparticles are excellent absorbers or scatterers of electromagnetic radiation, depending on their shape, size, material composition, and the refractive index of the host medium. In this work, we investigated the optical and plasmonic properties of spheroidal spindle- and disc-shaped ZnO@Ag core–shell nanocomposites embedded in a dielectric passive host-matrix by varying the size, thickness of the metallic shell, and the dielectrics function of the host matrix. The theoretical and numerical analysis is carried out for the core–shell nanoparticles having volume less than 1.34 × 105 nm3 within the framework of quasistatic approximation. We found that the core–shell nanoparticles possess four resonances—two of which correspond to the silver/core and silver/host-matrix interfaces, while the other two correspond to the bonding/antibonding pairs due to separation of charges in the composite along the principal axes. The tunability of the plasmon resonances of the composite system enables it to exhibit very interesting material properties in a variety of applications extending from the UV to near-infrared spectral regions. The wavelength of disc-shaped core–shell nanostructure exhibits a red-shift relative to the spindle-shaped one for both longitudinal and transverse resonance modes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsawafta, M., Wahbeh, M., Truong, V.-V.: Plasmonic modes and optical properties of gold and silver ellipsoidal nanoparticles by the discrete dipole approximation. J. Nanomater. 2012, 1–10 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/457968
Beye, A.C., et al.: Control of the surface plasmon resonance of two configurations of nanoparticles: simple gold nanorod and gold/silica core/shell. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Res. 4, 1–6 (2017)
Beyene, G., Senbeta, T., Mesfin, B.: Size dependent optical properties of ZnO@Ag core/shell nanostructures. Chin. J. Phys. 58, 235–243 (2019)
Chen, M.S., Goodman, D.W.: Catalytically active Au: from nano-particles to ultra-thin films. Acc. Chem. Res. 39, 739–746 (2006)
Chen, F., Johnston, R.L.: Plasmonic properties of silver nanoparticles on two substrates plasmonic properties of silver nanoparticles on two substrates. Plasmonics 4, 147–152 (2009)
Gorokhova, E.I., et al.: Structural, optical, and luminescence properties of ZnO: Ga optical scintillation ceramic. J. Opt. Technol. 85, 90–100 (2018)
Grady, N.K., Halas, N.J., Nordlander, P.: Influence of dielectric function properties on the optical response of plasmon resonant metallic nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 399, 167–171 (2004)
Jain, P.K., El-sayed, M.A.: Surface plasmon resonance sensitivity of metal nanostructures: physical basis and universal scaling in metal nanoshells. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 17451–17454 (2007)
Jule, L., et al.: Fano-like resonance and scattering in dielectric(core)-metal(shell) composites embedded in active host matrices. Phys. Status Solidi Basic Res. 252, 2707–2713 (2015)
Kajikawa, Y.A.K.: Optical Properties of Advanced Materials. Springer Series in Materials Science, London (2013)
Kassahun, G.B.: High tunability of size dependent optical properties of ZnO@M@Au (M = SiO2, In2O3, TiO2) core/spacer/shell nanostructure. Adv. Nano Res. 2, 1–13 (2019)
Kim, M.R., et al.: Semiconductor and metallic core—shell nanostructures: synthesis and applications in solar cells and catalysis. Chem. A Eur. J. 20, 11256–11275 (2014)
Liu, M., Guyot-Sionnest, P.: Preparation and optical properties of silver chalcogenide coated gold nanorods. J. Mater. Chem. 16, 3942–3945 (2006)
Loo, C., et al.: Nanoshell-enabled photonics-based imaging and therapy of cancer. Technol. Cancer Reasearch Treat. 3, 33–40 (2015)
Noguez, C.: Surface plasmons on metal nanoparticles: The influence of shape and physical environment. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 3606–3619 (2007)
Oldenburg, S.J., et al.: Nanoengineering of optical resonances. Chem. Phys. Lett. 288, 243–247 (1998)
Oliver, A., et al.: Controlled anisotropic deformation of Ag nanoparticles by Si ion irradiation. Phys. Rev. 74, 245425 (2006)
Pal, U., Meléndrez, R., Chernov, V.: Thermoluminescence properties of ZnO and ZnO: Yb nanophosphors Thermoluminescence properties of ZnO and ZnO: Yb nanophosphors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 148–151 (2016)
Pan, T., Huang, J.P., Li, Z.Y.: Optical bistability in metal/dielectric composite with interfacial layer. Phys. B 301, 190–195 (2001)
Penninkhof, J.J., et al.: Optical properties of spherical and oblate spheroidal gold shell colloids optical properties of spherical and oblate spheroidal gold shell colloids. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 4146–4150 (2008)
Pillai, S., et al.: Enhanced emission from Si-based light-emitting diodes using surface plasmons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 16–18 (2006)
Piralaee, M., et al.: Modeling and optimizing the performance of plasmonic solar cells using effective medium theory. Phys. Lett. A 381, 489–493 (2016)
Piralaee, M., Asgari, A.: Modeling of optimum light absorption in random plasmonic solar cell using effective medium theory. Opt. Mater. 62, 399–402 (2016)
Sambou, A., et al.: Turnability of the plasmonic response of the gold nanoparticles in infrared region. Am. J. Nanomater. 4, 63–69 (2016)
Senthilkumar, N.: Two step synthesis of ZnO/Ag and ZnO/Au core/shell nanocomposites: Structural, optical and electrical property analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 750, 171–181 (2018)
Shah, N., et al.: Effective role of magnetic core–shell nanocomposites in removing organic and inorganic wastes from water. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 10, 202–212 (2016)
Shahamirifard, S.A., et al.: Application of nanostructure ZnLI2 complex in construction of optical pH sensor. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 33, 1–11 (2017)
Stuart, H.R., Hall, D.G.: Island size effects in nanoparticle-enhanced photodetectors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 3815–3817 (1998)
Tanabe, K.: A simple optical model well explains plasmonic-nanoparticle-enhanced spectral photocurrent in optically thin solar cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 236–245 (2016)
Wang, M., et al.: Subradiant plasmon modes in multilayer metal—Dielectric nanoshells. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 20920–20925 (2011)
Wilcoxon, J.P., Abrams, B.L.: Synthesis, structure and properties of metal nanoclusters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 35, 1162–1194 (2006)
Yang, N., Aoki, K., Nagasawa, H.: Thermal metallization of silver stearate-coated nanoparticles owing to the destruction of the shell structure. J. Phys. Chem. B. 108, 15027–15032 (2004)
Zeng, C., et al.: Fabrication of urchin-like Ag/ZnO hierarchical nano/microstructures based on galvanic replacement mechanism and their enhanced photocatalytic properties. Surf. Interface Anal. 49, 599–606 (2016)
Zhang, J., Zayats, A.: Multiple Fano resonances in single-layer nonconcentric core-shell nanostructures. Opt. Express 21, 707–715 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported financially by the NSFC (11474246, 11750110415, 11850410442), Addis Ababa University (AAU) and Adama Science and Technology University (ASTU).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beyene, G., Senbeta, T., Mesfin, B. et al. Plasmonic properties of spheroidal spindle and disc shaped core–shell nanostructures embedded in passive host-matrices. Opt Quant Electron 52, 157 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-2263-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-2263-4