Abstract
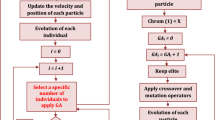
7 This paper elucidates the computation of optimal controls for steel annealing processes as hybrid systems which comprise of one or more furnaces integrated with plant-wide planning and scheduling operations. A class of hybrid system is considered to capture the trade-off between metallurgical quality requirement and timely product delivery. Various optimization algorithms including particle swarm optimization algorithm (PSO) with time varying inertia weight methods, PSO with globally and locally tuned parameters (GLBest PSO), parameter free PSO (pf-PSO) and PSO like algorithm via extrapolation (ePSO), real coded genetic algorithm (RCGA) and two-phase hybrid real coded genetic algorithm (HRCGA) are considered to solve the optimal control problems for the steel annealing processes (SAP). The optimal solutions including optimal line speed, optimal cost, and job completion time and convergence rate obtained through all these optimization algorithms are compared with each other and also those obtained via the existing method, forward algorithm (FA). Various statistical analyses and analysis of variance (ANOVA) test and hypothesis t-test are carried out in order to compare the performance of each method in solving the optimal control problems of SAP. The comparative study of the performance of the various algorithms indicates that the PSO like algorithms, pf-PSO and ePSO are equally good and are also better than all the other optimization methods considered in this chapter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angeline PJ (1998) Evolutionary optimization versus particle Swarm optimization: philosophy and performance differences. Evolutionary Programming VII (1998). Lecture notes in computer science, vol. 1447. Springer, Berlin, pp 601–610
Baskar S, Subbaraj P, Rao MVC (2001) Performance of hybrid real coded genetic algorithms. Int J Comput Eng Sci 2(4):583–601
Cassandras CG, Pepyne DL, Wardi Y (2001) Optimal control of a class of hybrid systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 46:398–415
Cho YC, Cassandras CG (2000) Optimal control of steel annealing processes as hybrid systems. In: Proc of 39th IEEE conf on decision and control, pp 540–545
Cho YC, Cassandras CG, Pepyne DL (2001) Forward decomposition algorithms for optimal of a class of hybrid systems. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 11(5):497–513
Cho YC, Cassandras CG, Kwon WK (2004) Optimal control for steel annealing processes as hybrid systems. Control Eng Pract 12(10):1319–1328
Davis L (1991) Handbook of genetic algorithms. Van Nostrand/Reinhold, New York
Eberhart RC, Shi Y (1998) Comparison between genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization. Evolutionary programming VII (1998). Lecture notes in computer science, vol 1447. Springer, Berlin, pp 611–616
Gen M, Cheng R (1997) Genetic algorithms and engineering design. Wiley, New York
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Addison–Wesley, Massachusetts
Goldberg DE (1991) Real coded genetic algorithms, virtual alphabets, and blocking. Complex Syst 5:139–167
Kennedy J (1997) The particle swarm: social adaptation of knowledge. In: Proc IEEE international conference on evolutionary computation, Indianapolis, Indiana. IEEE Service Center, Piscataway, pp 303–308
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proc IEEE international conference on neural networks, Perth, Australia, IEEE Service Center, Piscataway, pp 1942–1948
Luss R, Jaakola THI (1973) Optimization by direct search and system reduction of the size of search region. AIChE J 19(4):760–775
Michalewicz Z (1992) Genetic algorithms + data structures = evolution programs. Springer, Berlin
Pardalous PM, Resende MGC (2002) Handbook of applied optimization. Oxford University Press, London
Ratnaweera A, Halgamuge SK, Watson C (2004) Self-organizing hierarchical particle swarm optimizer with time-varying acceleration coefficient. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 8(3):240–255
Senthil Arumugam M, Rao MVC (2004) Novel hybrid approach for real coded genetic algorithm to compute the optimal control of a single stage hybrid manufacturing systems. Int J Comput Intell Res 1(3):231–249
Shi Y, Eberhart RC (1998a) A modified particle swarm optimizer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on evolutionary computation, Anchorage, Alaska
Shi Y, Eberhart RC (1998b) Parameter selection in particle swarm optimization. Evolutionary programming VII. Lecture notes in computer science, vol. 1447. Springer, Berlin, pp 591–600
Suganthan PN (1999) Particle swarm optimizer with neighborhood operator. In: Proceedings of the 1999 congress of evolutionary computation, vol 3. IEEE Press, New York, pp 1958–1962
Watanapongse CD, Gaskey KM (1998) Applications of modern control to a continuous anneal line. IEEE Control Syst Mag, 32–37
Yoshitani N (1998) Model-based control of strip temperature for the heating furnace in continuous annealing. IEEE Control Syst Technol, 146–156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arumugam, M.S., Chandramohan, A. & Murthy, G.R. On the optimal control of steel annealing processes via various versions of genetic and particle swarm optimization algorithms. Optim Eng 12, 371–392 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-011-9143-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-011-9143-5